Dehydrocrenatidine extracted from Picrasma quassioides induces the apoptosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells through the JNK and ERK signaling pathways
- PMID: 34165177
- PMCID: PMC8218301
- DOI: 10.3892/or.2021.8117
Dehydrocrenatidine extracted from Picrasma quassioides induces the apoptosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells through the JNK and ERK signaling pathways
Abstract
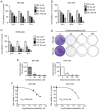
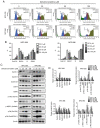
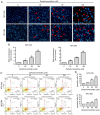
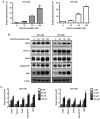
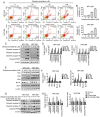
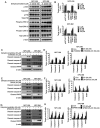
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is an indicator disease in Asia due to its unique geographical and ethnic distribution. Dehydrocrenatidine (DC) is a β‑carboline alkaloid abundantly present in Picrasma quassioides (D. Don) Benn, a deciduous shrub or small tree native to temperate regions of southern Asia, and β‑carboline alkaloids play anti‑inflammatory and antiproliferative roles in various cancers. However, the mechanism and function of DC in human NPC cells remain only partially explored. The present study aimed to examine the cytotoxicity and biochemical role of DC in human NPC cells. The MTT method, cell cycle analysis, DAPI determination, Annexin V/PI double staining, and mitochondrial membrane potential examination were performed to evaluate the effects of DC treatment on human NPC cell lines. In addition, western blotting analysis was used to explore the effect of DC on apoptosis and signaling pathways in related proteins. The analysis results confirmed that DC significantly reduced the viability of NPC cell lines in a dose‑ and time‑dependent manner and induced apoptosis through internal and external apoptotic pathways (including cell cycle arrest, altered mitochondrial membrane potential, and activated death receptors). Western blot analysis illustrated that DC's effect on related proteins in the mitogen‑activated protein kinase pathway can induce apoptosis by enhancing ERK phosphorylation and inhibiting Janus kinase (JNK) phosphorylation. Notably, DC induced apoptosis by affecting the phosphorylation of JNK and ERK, and DC and inhibitors (SP600125 and U0126) in combination restored the overexpression of p‑JNK and p‑ERK. To date, this is the first study to confirm the apoptosis pathway induced by DC phosphorylation of p‑JNK and p‑REK in human NPC. On the basis of evidence obtained from this study, DC _targeting the inhibition of NPC cell lines may be a promising future strategy for NPC treatment.
Keywords: MAPK pathway; apoptosis; dehydrocrenatidine; nasopharyngeal cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Apoptotic effects of dehydrocrenatidine via JNK and ERK pathway regulation in oral squamous cell carcinoma.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 May;137:111362. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111362. Epub 2021 Feb 9. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 33578238
-
Tetrandrine Induces Apoptosis of Human Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma NPC-TW 076 Cells through Reactive Oxygen Species Accompanied by an Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Signaling Pathway.Molecules. 2016 Oct 12;21(10):1353. doi: 10.3390/molecules21101353. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 27754332 Free PMC article.
-
Asiatic Acid, Extracted from Centella asiatica and Induces Apoptosis Pathway through the Phosphorylation p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase in Cisplatin-Resistant Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cells.Biomolecules. 2020 Jan 25;10(2):184. doi: 10.3390/biom10020184. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 31991751 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Roles of JNK and p38 MAPK Signaling in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 20;23(3):1108. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031108. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163030 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The efficacy of natural products for the treatment of nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2024 Jan;103(1):e14411. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.14411. Epub 2023 Dec 11. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2024. PMID: 38073436 Review.
Cited by
-
Naturally derived indole alkaloids _targeting regulated cell death (RCD) for cancer therapy: from molecular mechanisms to potential therapeutic _targets.J Hematol Oncol. 2022 Sep 14;15(1):133. doi: 10.1186/s13045-022-01350-z. J Hematol Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36104717 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Semilicoisoflavone B Induces Apoptosis of Oral Cancer Cells by Inducing ROS Production and Downregulating MAPK and Ras/Raf/MEK Signaling.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 24;24(5):4505. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054505. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36901935 Free PMC article.
-
Dehydrocrenatidine Induces Liver Cancer Cell Apoptosis by Suppressing JNK-Mediated Signaling.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Mar 25;15(4):402. doi: 10.3390/ph15040402. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35455398 Free PMC article.
-
Glutamine ameliorates hyperoxia-induced hippocampal damage by attenuating inflammation and apoptosis via the MKP-1/MAPK signaling pathway in neonatal rats.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Feb 2;14:1096309. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1096309. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36817145 Free PMC article.
-
Progress in the study of chemical composition, biological activity, and its metabolism of the Picrasma quassioides.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 3;10(15):e35761. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35761. eCollection 2024 Aug 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39170506 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

