The Effect of Ascophyllum nodosum Extract on the Nutraceutical Antioxidant Potential of Vigna radiata Sprout under Salt Stress
- PMID: 34203887
- PMCID: PMC8232706
- DOI: 10.3390/plants10061216
The Effect of Ascophyllum nodosum Extract on the Nutraceutical Antioxidant Potential of Vigna radiata Sprout under Salt Stress
Abstract
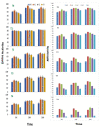
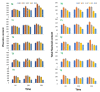
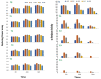
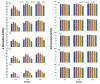
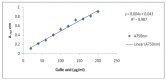
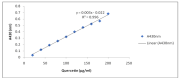
Mung bean (Vigna radiata L.) sprout is a popular fresh vegetable, tasty and high in antioxidants. To increase yield and quality after the occurrence of both abiotic and biotic stresses, the application of seaweed extracts is of great importance. Hence, this study was conducted to determine the effect of Ascophyllum nodosum extract (ANE) in the presence of salt on the antioxidant potential of V. radiata sprouts. Different concentrations of ANE viz. 0.00, 0.01, 0.05, 0.10, and 0.50% and NaCl 0, 25, 50, 75, and 100 mM alone and in combinations were tested for researching the antioxidant potential of V. radiata sprouts at 0, 24, and 36 h of sprouting. The DPPH free-radical-scavenging activity of sprouts of V. radiata was found to increase with time and peaked at 24 h of treatment. The A. nodosum extract (0.01%) could reverse the ill effect of the low level of salinity posed by up to 25 mM NaCl. The increasing salinity deteriorated the antioxidant activity using ABTS method of sprouts down to 20.45% of the control at 100 mM NaCl. The total phenolic content (TPC), total flavonoid content (TFC), and reducing power of V. radiata sprouts was found to increase till 36 h of sprouting. A slight increase in TPC, TFC and reducing power was observed when seeds were treated with low concentrations of ANE. The elevation in TPC, TFC and reducing power upon treatment with low concentrations of ANE was also noticed in sprouts in saline combinations. Alpha amylase inhibition activity was found to reach a (67.16% ± 0.9) maximum at 24 h of sprouting at a 0.01% concentration of ANE. Tyrosinase inhibition and alpha glucosidase inhibition was 88.0% ± 2.11 and 84.92% ± 1.2 at 36 h of sprouting, respectively, at 0.01% concentration of ANE. A. nodosum extract is natural, environmentally friendly, and safe, and could be used as one of the strategies to decline stress at a low level and enhance the antioxidant activities in V. radiata sprouts, thus increasing its potential to be developed as an antioxidant-based functional food.
Keywords: Ascophyllum nodosum; antioxidants; germination; salinity; sprouts.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of Germination and Illumination on Melatonin and Its Metabolites, Phenolic Content, and Antioxidant Activity in Mung Bean Sprouts.Plants (Basel). 2022 Nov 6;11(21):2990. doi: 10.3390/plants11212990. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36365443 Free PMC article.
-
Proximate composition, phenolic content and in vitro antioxidant activity of aqueous extracts of the seaweeds Ascophyllum nodosum, Bifurcaria bifurcata and Fucus vesiculosus. Effect of addition of the extracts on the oxidative stability of canola oil under accelerated storage conditions.Food Res Int. 2017 Sep;99(Pt 3):986-994. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2016.11.009. Epub 2016 Nov 12. Food Res Int. 2017. PMID: 28865625
-
Effect of germination on phytochemical profiles and antioxidant activity of mung bean sprouts (Vigna radiata).J Agric Food Chem. 2012 Nov 7;60(44):11050-5. doi: 10.1021/jf304443u. Epub 2012 Oct 30. J Agric Food Chem. 2012. PMID: 23088738
-
Total polyphenols and bioactivity of seeds and sprouts in several legumes.Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19(34):6112-24. doi: 10.2174/1381612811319340005. Curr Pharm Des. 2013. PMID: 23448441 Review.
-
Neuroprotective Potential of Mung Bean (Vigna radiata L.) Polyphenols in Alzheimer's Disease: A Review.J Agric Food Chem. 2021 Oct 6;69(39):11554-11571. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.1c04049. Epub 2021 Sep 22. J Agric Food Chem. 2021. PMID: 34551518 Review.
Cited by
-
Salinity Stress Influences the Main Biochemical Parameters of Nepeta racemosa Lam.Plants (Basel). 2023 Jan 29;12(3):583. doi: 10.3390/plants12030583. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36771667 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Use of Ascophyllum nodosum as a Biostimulant for Improving the Growth Performance of Vigna aconitifolia (Jacq.) Marechal.Plants (Basel). 2021 Nov 2;10(11):2361. doi: 10.3390/plants10112361. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34834727 Free PMC article.
-
The interaction effect of water deficit stress and seaweed extract on phytochemical characteristics and antioxidant activity of licorice (Glycyrrhiza glabra L.).Front Plant Sci. 2024 Oct 7;15:1474399. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1474399. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 39435025 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Randhir R., Shetty K. Mung beans processed by solid-state bioconversion improve phenolic content and functionality relevant for diabetes and ulcer management. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2007;8:197–204. doi: 10.1016/j.ifset.2006.10.003. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

