Taxifolin Protects Dental Pulp Stem Cells under Hypoxia and Inflammation Conditions
- PMID: 34292054
- PMCID: PMC8312191
- DOI: 10.1177/09636897211034452
Taxifolin Protects Dental Pulp Stem Cells under Hypoxia and Inflammation Conditions
Abstract
Background: Dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) are a unique source for future clinical application in dentistry such as periodontology or endodontics. However, DPSCs are prone to apoptosis under abnormal conditions. Taxifolin is a natural flavonoid and possesses many pharmacological activities including anti-hypoxic and anti-inflammatory. We aimed to elucidate the mechanisms of taxifolin protects DPSC under hypoxia and inflammatory conditions.
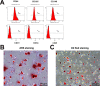
Methods: DPSCs from human dental pulp tissue was purchased from Lonza (cat. no. PT-5025. Basel, Switzerland)) and identified by DPSC's biomarkers. DPSC differentiation in vitro following the manufacturers' instructions. ARS staining and Oil red staining verify the efficiency of differentiation in vitro after 2 weeks. The changes of various genes and proteins were identified by Q-PCR and western-blot, respectively. Cell viability was determined by the CCK-8 method, while apoptosis was determined by Annexin V/PI staining.
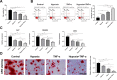
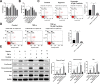
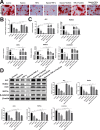
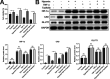
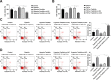
Results: DPSC differentiation in vitro shows that hypoxia and TNF-α synergistically inhibit the survival and osteogenesis of DPSCs. A final concentration of 10 μM Taxifolin can significantly reduce the apoptosis of DPSCs under inflammation and hypoxia conditions. Taxifolin substantially increases carbonic anhydrase IX (CA9) expression but not HIF1a, and inhibitions of CA9 expression nullify the protective role of taxifolin under hypoxia and inflammatory condition.
Conclusion: Taxifolin significantly increased the expression of CA9 when it inhibits DPSC apoptosis and taxifolin synergistically to protect DPSCs against apoptosis with CA9 under hypoxia and inflammatory conditions. Taxifolin can be used as a potential drug for clinical treatment of DPSC-related diseases.
Keywords: CA9; DPSCs; apoptosis; hypoxia and inflammation; taxifolin.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Artemisinin protects DPSC from hypoxia and TNF-α mediated osteogenesis impairments through CA9 and Wnt signaling pathway.Life Sci. 2021 Jul 15;277:119471. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119471. Epub 2021 Mar 31. Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33811898
-
Analysis of the characteristics and expression profiles of coding and noncoding RNAs of human dental pulp stem cells in hypoxic conditions.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019 Mar 12;10(1):89. doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1192-2. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 30867055 Free PMC article.
-
Bcl-2 Overexpression and Hypoxia Synergistically Enhance Angiogenic Properties of Dental Pulp Stem Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 26;21(17):6159. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176159. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32859045 Free PMC article.
-
Determinants of Dental Pulp Stem Cell Heterogeneity.J Endod. 2022 Oct;48(10):1232-1240. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2022.06.013. Epub 2022 Jul 7. J Endod. 2022. PMID: 35809811 Review.
-
Specific microRNAs Regulate Dental Pulp Stem Cell Behavior.J Endod. 2022 Jun;48(6):688-698. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2022.02.012. Epub 2022 Mar 7. J Endod. 2022. PMID: 35271859 Review.
Cited by
-
A novel hypoxic lncRNA, HRL-SC, promotes the proliferation and migration of human dental pulp stem cells through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022 Jun 28;13(1):286. doi: 10.1186/s13287-022-02970-5. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 35765088 Free PMC article.
-
Botanicals and Oral Stem Cell Mediated Regeneration: A Paradigm Shift from Artificial to Biological Replacement.Cells. 2022 Sep 7;11(18):2792. doi: 10.3390/cells11182792. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36139367 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Hypoxia in Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Dental Pulp: Influence, Mechanism and Application.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024 Jun;82(2):535-547. doi: 10.1007/s12013-024-01274-0. Epub 2024 May 7. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024. PMID: 38713403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecules Inducing Dental Stem Cells Differentiation and Bone Regeneration: State of the Art.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 8;24(12):9897. doi: 10.3390/ijms24129897. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37373044 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Cellular Metabolism in Maintaining the Function of the Dentine-Pulp Complex: A Narrative Review.Metabolites. 2023 Apr 5;13(4):520. doi: 10.3390/metabo13040520. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 37110177 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

