Specific electromagnetic radiation in the wireless signal range increases wakefulness in mice
- PMID: 34330835
- PMCID: PMC8346830
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2105838118
Specific electromagnetic radiation in the wireless signal range increases wakefulness in mice
Abstract
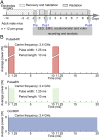
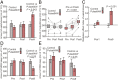
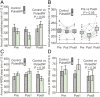
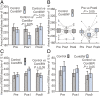
Electromagnetic radiation (EMR) in the environment has increased sharply in recent decades. The effect of environmental EMR on living organisms remains poorly characterized. Here, we report the impact of wireless-range EMR on the sleep architecture of mouse. Prolonged exposure to 2.4-GHz EMR modulated by 100-Hz square pulses at a nonthermal output level results in markedly increased time of wakefulness in mice. These mice display corresponding decreased time of nonrapid eye movement (NREM) and rapid eye movement (REM). In contrast, prolonged exposure to unmodulated 2.4-GHz EMR at the same time-averaged output level has little impact on mouse sleep. These observations identify alteration of sleep architecture in mice as a specific physiological response to prolonged wireless-range EMR exposure.
Keywords: electromagnetic radiation; mouse model; public health; sleep; wireless signal.
Copyright © 2021 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of specific electromagnetic radiation on wakefulness in mice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Apr 9;121(15):e2313903121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2313903121. Epub 2024 Apr 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38557178 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of light on the sleep-wakefulness cycle of mice mediated by intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022 Feb 12;592:93-98. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2022.01.023. Epub 2022 Jan 11. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022. PMID: 35033872
-
Exposure to pulsed high-frequency electromagnetic field during waking affects human sleep EEG.Neuroreport. 2000 Oct 20;11(15):3321-5. doi: 10.1097/00001756-200010200-00012. Neuroreport. 2000. PMID: 11059895
-
Genotoxic effects of electromagnetic field radiations from mobile phones.Environ Res. 2022 Sep;212(Pt D):113321. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2022.113321. Epub 2022 May 1. Environ Res. 2022. PMID: 35508219 Review.
-
EUROPAEM EMF Guideline 2016 for the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of EMF-related health problems and illnesses.Rev Environ Health. 2016 Sep 1;31(3):363-97. doi: 10.1515/reveh-2016-0011. Rev Environ Health. 2016. PMID: 27454111 Review.
Cited by
-
Designing Symmetric Gradient Honeycomb Structures with Carbon-Coated Iron-Based Composites for High-Efficiency Microwave Absorption.Nanomicro Lett. 2024 Jul 2;16(1):234. doi: 10.1007/s40820-024-01435-z. Nanomicro Lett. 2024. PMID: 38954048 Free PMC article.
-
Architecture inspired structure engineering toward carbon nanotube hybrid for microwave absorption promotion.iScience. 2022 Sep 23;25(10):105203. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.105203. eCollection 2022 Oct 21. iScience. 2022. PMID: 36248731 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship of Problematic Smartphone Use, Sleep Quality, and Daytime Fatigue Among Quarantined Medical Students During the COVID-19 Pandemic.Front Psychiatry. 2021 Nov 10;12:755059. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.755059. eCollection 2021. Front Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34858229 Free PMC article.
-
Carbon nanolayer-mounted single metal sites enable dipole polarization loss under electromagnetic field.Nat Commun. 2024 Oct 21;15(1):9077. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53465-1. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39433804 Free PMC article.
-
Flexible and excellent electromagnetic interference shielding film with porous alternating PVA-derived carbon and graphene layers.iScience. 2023 Sep 21;26(10):107975. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107975. eCollection 2023 Oct 20. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37841593 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pereda D. G., Fernandez Andres M., Pena Valverde I., Gil Abaunza U., Arrinda Sanzberro A., “Time variability of electromagnetic exposure due to Wi Fi networks” in 2019 International Conference on Electromagnetics in Advanced Applications (ICEAA) (IEEE, 2019), pp. 1199–1202.
-
- Alsop T., WLAN connected devices worldwide 2016–2021. https://www.statista.com/statistics/802706/world-wlan-connected-device/. Accessed 29 December 2020.
-
- Kocevska D., et al. ., Sleep characteristics across the lifespan in 1.1 million people from the Netherlands, United Kingdom and United States: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nat. Hum. Behav. 5, 113–122 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Vander Borght M., Wyns C., Fertility and infertility: Definition and epidemiology. Clin. Biochem. 62, 2–10 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Baxter A. J., Scott K. M., Vos T., Whiteford H. A., Global prevalence of anxiety disorders: A systematic review and meta-regression. Psychol. Med. 43, 897–910 (2013). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

