The Advancing of Selenium Nanoparticles Against Infectious Diseases
- PMID: 34393776
- PMCID: PMC8361478
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.682284
The Advancing of Selenium Nanoparticles Against Infectious Diseases
Abstract
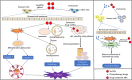
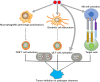
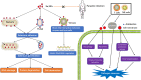
Infectious diseases, caused by the direct exposure of cellular or acellular pathogens, are found to be closely associated with multiple inflammation and immune responses, keeping one of the top threats to human health. As an indispensable trace element, Selenium (Se) plays important roles in antioxidant defence and redox state regulation along with a variety of specific metabolic pathways. In recent decades, with the development of novel nanotechnology, Selenium nanoparticles (Se NPs) emerged as a promising agent for biomedical uses due to their low toxicity, degradability and high bioavailability. Taking the advantages of the strong ability to trigger apoptosis or autophagy by regulating reactive oxygen species (ROS), Se NPs have been widely used for direct anticancer treatments and pathogen killing/clearance in host cells. With excellent stability and drug encapsulation capacity, Se NPs are now serving as a kind of powerful nano-carriers for anti-cancer, anti-inflammation and anti-infection treatments. Notably, Se NPs are also found to play critical roles in immunity regulations, such as macrophage and T effector cell activation, which thus provides new possibilities to achieve novel nano-immune synergetic strategy for anti-cancer and anti-infection therapies. In this review, we summarized the progress of preparation methods for Se NPs, followed by the advances of their biological functions and mechanisms for biomedical uses, especially in the field of anti-infection treatments. Moreover, we further provide some prospects of Se NPs in anti-infectious diseases, which would be helpful for facilitating their future research progress for anti-infection therapy.
Keywords: anti-infection therapy; infectious diseases; nano-immune synergetic strategy; pathogens; selenium nanoparticles.
Copyright © 2021 Lin, Zhang, Xu and Pi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Immunomodulatory roles of selenium nanoparticles: Novel arts for potential immunotherapy strategy development.Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 26;13:956181. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.956181. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35958612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Trends and recent progresses of selenium nanoparticles as novel autophagy regulators for therapeutic development.Front Nutr. 2023 Feb 2;10:1116051. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1116051. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 36819694 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prospects and future perspectives of selenium nanoparticles: An insight of growth promoter, antioxidant and anti-bacterial potentials in productivity of poultry.J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2021 Dec;68:126862. doi: 10.1016/j.jtemb.2021.126862. Epub 2021 Sep 20. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 34555772 Review.
-
Nano-selenium on reproduction and immunocompetence: an emerging progress and prospect in the productivity of poultry research.Trop Anim Health Prod. 2021 May 15;53(2):324. doi: 10.1007/s11250-021-02698-z. Trop Anim Health Prod. 2021. PMID: 33991248 Review.
-
Engineering highly effective antimicrobial selenium nanoparticles through control of particle size.Nanoscale. 2019 Aug 8;11(31):14937-14951. doi: 10.1039/c9nr04424h. Nanoscale. 2019. PMID: 31363721
Cited by
-
Selenium nanoparticles enhance the efficacy of homologous vaccine against the highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N1 virus in chickens.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2022 Apr;29(4):2095-2111. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.11.051. Epub 2021 Nov 25. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35531142 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial Activity of Selenium Nanoparticles (SeNPs) against Potentially Pathogenic Oral Microorganisms: A Scoping Review.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Aug 31;15(9):2253. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15092253. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37765222 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Snapshot of Selenium-enclosed Nanoparticles for the Management of Cancer.Curr Pharm Des. 2024;30(11):841-858. doi: 10.2174/0113816128297329240305071103. Curr Pharm Des. 2024. PMID: 38462835 Review.
-
In vitro antifungal activity of biosynthesized selenium nanoparticles using plant extracts and six comparators against clinical Fusarium strains.Curr Med Mycol. 2023 Dec;9(4):17-23. doi: 10.22034/CMM.2024.345189.1504. Curr Med Mycol. 2023. PMID: 38983615 Free PMC article.
-
Thiolated chitosan nanoparticles encapsulated nisin and selenium: antimicrobial/antibiofilm/anti-attachment/immunomodulatory multi-functional agent.BMC Microbiol. 2024 Jul 12;24(1):257. doi: 10.1186/s12866-024-03400-7. BMC Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38997643 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altuwirqi R. M., Albakri A. S., Al-Jawhari H., Ganash E. A. (2020). Green Synthesis of Copper Oxide Nanoparticles by Pulsed Laser Ablation in Spinach Leaves Extract - ScienceDirect. Optik 219, 165280. 10.1016/j.ijleo.2020.165280 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials