PET-Based Staging Is Cost-Effective in Early-Stage Follicular Lymphoma
- PMID: 34413148
- PMCID: PMC8973292
- DOI: 10.2967/jnumed.121.262324
PET-Based Staging Is Cost-Effective in Early-Stage Follicular Lymphoma
Abstract
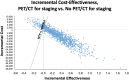
The objective was to assess the cost-effectiveness of staging PET/CT in early-stage follicular lymphoma (FL) from the Canadian health-care system perspective. Methods: The study population was FL patients staged as early-stage using conventional CT imaging and planned for curative-intent radiation therapy (RT). A decision analytic model simulated the management after adding staging PET/CT versus using staging CT alone. In the no-PET/CT strategy, all patients proceeded to curative-intent RT as planned. In the PET/CT strategy, PET/CT information could result in an increased RT volume, switching to a noncurative approach, or no change in RT treatment as planned. The subsequent disease course was described using a state-transition cohort model over a 30-y time horizon. Diagnostic characteristics, probabilities, utilities, and costs were derived from the literature. Baseline analysis was performed using quality-adjusted life years (QALYs), costs (2019 Canadian dollars), and the incremental cost-effectiveness ratio. Deterministic sensitivity analyses were conducted, evaluating net monetary benefit at a willingness-to-pay threshold of $100,000/QALY. Probabilistic sensitivity analysis using 10,000 simulations was performed. Costs and QALYs were discounted at a rate of 1.5%. Results: In the reference case scenario, staging PET/CT was the dominant strategy, resulting in an average lifetime cost saving of $3,165 and a gain of 0.32 QALYs. In deterministic sensitivity analyses, the PET/CT strategy remained the preferred strategy for all scenarios supported by available data. In probabilistic sensitivity analysis, the PET/CT strategy was strongly dominant in 77% of simulations (i.e., reduced cost and increased QALYs) and was cost-effective in 89% of simulations (i.e., either saved costs or had an incremental cost-effectiveness ratio below $100,000/QALY). Conclusion: Our analysis showed that the use of PET/CT to stage early-stage FL patients reduces cost and improves QALYs. Patients with early-stage FL should undergo PET/CT before curative-intent RT.
Keywords: PET/CT; cost-effectiveness analysis; follicular lymphoma; radiation therapy; staging.
© 2022 by the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A cost-utility analysis comparing CT surveillance, PET-CT surveillance, and planned postradiation neck dissection for advanced nodal HPV-positive oropharyngeal cancer.Cancer. 2021 Sep 15;127(18):3372-3380. doi: 10.1002/cncr.33653. Epub 2021 Jun 1. Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34062618
-
Evaluating the use of fluorine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography in the workup of Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia: a cost-utility analysis.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2023 Nov;29(11):1417-1423. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2023.06.022. Epub 2023 Jun 21. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2023. PMID: 37353076
-
Frontline rituximab monotherapy induction versus a watch and wait approach for asymptomatic advanced-stage follicular lymphoma: A cost-effectiveness analysis.Cancer. 2015 Aug 1;121(15):2637-45. doi: 10.1002/cncr.29372. Epub 2015 Apr 15. Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25877511
-
The value of FDG positron emission tomography/computerised tomography (PET/CT) in pre-operative staging of colorectal cancer: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2011 Sep;15(35):1-192, iii-iv. doi: 10.3310/hta15350. Health Technol Assess. 2011. PMID: 21958472 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An economic evaluation of positron emission tomography (PET) and positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) for the diagnosis of breast cancer recurrence.Health Technol Assess. 2011 Apr;15(18):iii-iv, 1-54. doi: 10.3310/hta15180. Health Technol Assess. 2011. PMID: 21524363 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prognostic value of interim 18F-FDG PET/CT in adult follicular lymphoma treated with R-CHOP.Ann Hematol. 2023 Apr;102(4):795-800. doi: 10.1007/s00277-023-05138-0. Epub 2023 Feb 20. Ann Hematol. 2023. PMID: 36806973
-
Duodenal-type follicular lymphoma in 18F-FDG PET/CT imaging: a case report.Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2023 Aug 15;13(4):164-170. eCollection 2023. Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2023. PMID: 37736494 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mac Manus MP, Hoppe RT. Is radiotherapy curative for stage I and II low-grade follicular lymphoma? Results of a long-term follow-up study of patients treated at Stanford University. J Clin Oncol. 1996;14:1282–1290. - PubMed
-
- Wilder RB, Jones D, Tucker SL, et al. . Long-term results with radiotherapy for stage I-II follicular lymphomas. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2001;51:1219–1227. - PubMed
-
- Lo AC, Campbell BA, Pickles T, et al. . Long-term outcomes for patients with limited-stage follicular lymphoma: update of a population-based study. Blood. 2020;136:1006–1010. - PubMed
-
- Dreyling M, Ghielmini M, Rule S, et al. . Newly diagnosed and relapsed follicular lymphoma: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2016;27(suppl 5):v83–v90. - PubMed
-
- König L, Herfarth K, Hörner-Rieber J, Dietrich S, Wiegel T, Jürgen D, et al. . Oncological outcome and recurrence pattern analysis after involved-field irradiation in combination with rituximab for early-stage nodal and extranodal follicular lymphoma. Strahlenther Onkol. 2020;196:705–714. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
