DNA Functional Nanomaterials for Controlled Delivery of Nucleic Acid-Based Drugs
- PMID: 34490226
- PMCID: PMC8418061
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.720291
DNA Functional Nanomaterials for Controlled Delivery of Nucleic Acid-Based Drugs
Abstract
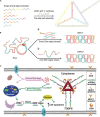
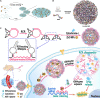
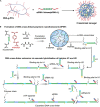
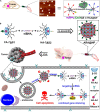
Nucleic acid-based drugs exhibited great potential in cancer therapeutics. However, the biological instability of nucleic acid-based drugs seriously hampered their clinical applications. Efficient in vivo delivery is the key to the clinical application of nucleic acid-based drugs. As a natural biological macromolecule, DNA has unique properties, such as excellent biocompatibility, molecular programmability, and precise assembly controllability. With the development of DNA nanotechnology, DNA nanomaterials have demonstrated significant advantages as delivery vectors of nucleic acid-based drugs by virtue of the inherent nucleic acid properties. In this study, the recent progress in the design of DNA-based nanomaterials for nucleic acid delivery is summarized. The DNA nanomaterials are categorized according to the components including pure DNA nanomaterials, DNA-inorganic hybrid nanomaterials, and DNA-organic hybrid nanomaterials. Representative applications of DNA nanomaterials in the controlled delivery of nucleic acid-based drugs are exemplified to show how DNA nanomaterials are rationally and exquisitely designed to address application issues in cancer therapy. At the end of this study, the challenges and future development of DNA nanomaterials are discussed.
Keywords: DNA assembly; DNA nanomaterials; DNA nanotechnology; drug delivery; nucleic acid-based drugs.
Copyright © 2021 Lv, Zhu and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nucleic Acid-Based Functional Nanomaterials as Advanced Cancer Therapeutics.Small. 2019 Jun;15(26):e1900172. doi: 10.1002/smll.201900172. Epub 2019 Apr 11. Small. 2019. PMID: 30972963 Review.
-
Advances in DNA nanotechnology for chronic wound management: Innovative functional nucleic acid nanostructures for overcoming key challenges.J Control Release. 2024 Nov;375:155-177. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2024.09.004. Epub 2024 Sep 8. J Control Release. 2024. PMID: 39242033 Review.
-
Gene Therapy Based on Nucleic Acid Nanostructure.Adv Healthc Mater. 2020 Oct;9(19):e2001046. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202001046. Epub 2020 Aug 31. Adv Healthc Mater. 2020. PMID: 32864890 Review.
-
Multimodules integrated functional DNA nanomaterials for intelligent drug delivery.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2022 Jan;14(1):e1753. doi: 10.1002/wnan.1753. Epub 2021 Aug 30. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2022. PMID: 34463046 Review.
-
Nucleic Acids and Their Analogues for Biomedical Applications.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Feb 4;12(2):93. doi: 10.3390/bios12020093. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35200353 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Progressive cancer _targeting by programmable aptamer-tethered nanostructures.MedComm (2020). 2024 Oct 20;5(11):e775. doi: 10.1002/mco2.775. eCollection 2024 Nov. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 39434968 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances and Prospects of Nucleic Acid Therapeutics for Anti-Cancer Therapy.Molecules. 2024 Oct 7;29(19):4737. doi: 10.3390/molecules29194737. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39407665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Template-Assisted Assembly of Hybrid DNA/RNA Nanostructures Using Branched Oligodeoxy- and Oligoribonucleotides.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 5;24(21):15978. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115978. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958961 Free PMC article.
-
Facile preparation of toluidine blue-loaded DNA nanogels for anticancer photodynamic therapy.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Apr 18;11:1180448. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1180448. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37143599 Free PMC article.
-
Bio-Tailored Sensing at the Nanoscale: Biochemical Aspects and Applications.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Jan 13;23(2):949. doi: 10.3390/s23020949. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36679744 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amo-Ochoa P., Zamora F. (2014). Coordination polymers with nucleobases: from structural aspects to potential applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 276 34–58. 10.1016/j.ccr.2014.05.017 - DOI
-
- Ashton P. R., Königer R., Stoddart F., Alker D., Harding V. D. (1996). Amino acid derivatives of β-cyclodextrin. J. Org. Chem. 61 903–908. 10.1021/jo951396d - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

