Overexpression of NtCBL5A Leads to Necrotic Lesions by Enhancing Na+ Sensitivity of Tobacco Leaves Under Salt Stress
- PMID: 34603362
- PMCID: PMC8484801
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2021.740976
Overexpression of NtCBL5A Leads to Necrotic Lesions by Enhancing Na+ Sensitivity of Tobacco Leaves Under Salt Stress
Abstract
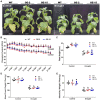
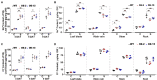
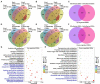
Many tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) cultivars are salt-tolerant and thus are potential model plants to study the mechanisms of salt stress tolerance. The CALCINEURIN B-LIKE PROTEIN (CBL) is a vital family of plant calcium sensor proteins that can transmit Ca2+ signals triggered by environmental stimuli including salt stress. Therefore, assessing the potential of NtCBL for genetic improvement of salt stress is valuable. In our studies on NtCBL members, constitutive overexpression of NtCBL5A was found to cause salt supersensitivity with necrotic lesions on leaves. NtCBL5A-overexpressing (OE) leaves tended to curl and accumulated high levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) under salt stress. The supersensitivity of NtCBL5A-OE leaves was specifically induced by Na+, but not by Cl-, osmotic stress, or drought stress. Ion content measurements indicated that NtCBL5A-OE leaves showed sensitivity to the Na+ accumulation levels that wild-type leaves could tolerate. Furthermore, transcriptome profiling showed that many immune response-related genes are significantly upregulated and photosynthetic machinery-related genes are significantly downregulated in salt-stressed NtCBL5A-OE leaves. In addition, the expression of several cation homeostasis-related genes was also affected in salt-stressed NtCBL5A-OE leaves. In conclusion, the constitutive overexpression of NtCBL5A interferes with the normal salt stress response of tobacco plants and leads to Na+-dependent leaf necrosis by enhancing the sensitivity of transgenic leaves to Na+. This Na+ sensitivity of NtCBL5A-OE leaves might result from the abnormal Na+ compartmentalization, plant photosynthesis, and plant immune response triggered by the constitutive overexpression of NtCBL5A. Identifying genes and pathways involved in this unusual salt stress response can provide new insights into the salt stress response of tobacco plants.
Keywords: CBL PROTEIN; Na+; immune response; necrotic lesions; photosystem; reactive oxygen species; salt stress; tobacco.
Copyright © 2021 Mao, Yuan, Mo, An, Shi, Visser, Bai, Sun, Liu, Liu, Wang and van der Linden.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
TaPUB1, a Putative E3 Ligase Gene from Wheat, Enhances Salt Stress Tolerance in Transgenic Nicotiana benthamiana.Plant Cell Physiol. 2017 Oct 1;58(10):1673-1688. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcx101. Plant Cell Physiol. 2017. PMID: 29016965
-
The Transcription Factor MYB37 Positively Regulates Photosynthetic Inhibition and Oxidative Damage in Arabidopsis Leaves Under Salt Stress.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Jul 12;13:943153. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.943153. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35903240 Free PMC article.
-
OsACA6, a P-type IIB Ca²⁺ ATPase promotes salinity and drought stress tolerance in tobacco by ROS scavenging and enhancing the expression of stress-responsive genes.Plant J. 2013 Dec;76(6):997-1015. doi: 10.1111/tpj.12352. Epub 2013 Nov 29. Plant J. 2013. PMID: 24128296
-
The improvement of salt tolerance in transgenic tobacco by overexpression of wheat F-box gene TaFBA1.Plant Sci. 2017 Jun;259:71-85. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2017.03.010. Epub 2017 Mar 23. Plant Sci. 2017. PMID: 28483055
-
Regulation of Na(+) fluxes in plants.Front Plant Sci. 2014 Sep 16;5:467. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00467. eCollection 2014. Front Plant Sci. 2014. PMID: 25278946 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-wide identification of Shaker K+ channel family in Nicotiana tabacum and functional analysis of NtSKOR1B in response to salt stress.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Apr 10;15:1378738. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1378738. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38660442 Free PMC article.
-
The role of CBL-CIPK signaling in plant responses to biotic and abiotic stresses.Plant Mol Biol. 2024 May 7;114(3):53. doi: 10.1007/s11103-024-01417-0. Plant Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38714550 Review.
-
The Roles of Calcineurin B-like Proteins in Plants under Salt Stress.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 30;24(23):16958. doi: 10.3390/ijms242316958. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38069281 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- An L. L., Mao J. J., Che H. Y., Shi S. J., Dong L. H., Xu D. Z., et al. . (2020). Screening and identification of NsylCBL family members interacting with protein kinase NsylCIPK24a in Nicotiana Sylvestris. Mol. Plant Breed. 11, 1–10. doi: 10.5376/pgt.2020.10.0005 - DOI
-
- Attia H., Karray N., Lachaâl M. (2009). Light interacts with salt stress in regulating superoxide dismutase gene expression in Arabidopsis. Plant Sci. 177, 161–167. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2009.05.002 - DOI
-
- Bartels D., Sunkar R. (2005). Drought and salt tolerance in plants. CRC Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 24, 23–58. doi: 10.1080/07352680590910410 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

