Dual inhibition of αvβ6 and αvβ1 reduces fibrogenesis in lung tissue explants from patients with IPF
- PMID: 34666752
- PMCID: PMC8524858
- DOI: 10.1186/s12931-021-01863-0
Dual inhibition of αvβ6 and αvβ1 reduces fibrogenesis in lung tissue explants from patients with IPF
Abstract
Rationale: αv integrins, key regulators of transforming growth factor-β activation and fibrogenesis in in vivo models of pulmonary fibrosis, are expressed on abnormal epithelial cells (αvβ6) and fibroblasts (αvβ1) in fibrotic lungs.
Objectives: We evaluated multiple αv integrin inhibition strategies to assess which most effectively reduced fibrogenesis in explanted lung tissue from patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
Methods: Selective αvβ6 and αvβ1, dual αvβ6/αvβ1, and multi-αv integrin inhibitors were characterized for potency, selectivity, and functional activity by ligand binding, cell adhesion, and transforming growth factor-β cell activation assays. Precision-cut lung slices generated from lung explants from patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis or bleomycin-challenged mouse lungs were treated with integrin inhibitors or standard-of-care drugs (nintedanib or pirfenidone) and analyzed for changes in fibrotic gene expression or TGF-β signaling. Bleomycin-challenged mice treated with dual αvβ6/αvβ1 integrin inhibitor, PLN-74809, were assessed for changes in pulmonary collagen deposition and Smad3 phosphorylation.
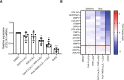
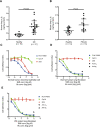
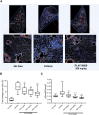
Measurements and main results: Inhibition of integrins αvβ6 and αvβ1 was additive in reducing type I collagen gene expression in explanted lung tissue slices from patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. These data were replicated in fibrotic mouse lung tissue, with no added benefit observed from inhibition of additional αv integrins. Antifibrotic efficacy of dual αvβ6/αvβ1 integrin inhibitor PLN-74809 was confirmed in vivo, where dose-dependent inhibition of pulmonary Smad3 phosphorylation and collagen deposition was observed. PLN-74809 also, more potently, reduced collagen gene expression in fibrotic human and mouse lung slices than clinically relevant concentrations of nintedanib or pirfenidone.
Conclusions: In the fibrotic lung, dual inhibition of integrins αvβ6 and αvβ1 offers the optimal approach for blocking fibrogenesis resulting from integrin-mediated activation of transforming growth factor-β.
Keywords: Antifibrotic; PLN-74809; Precision-cut lung slice; Transforming growth factor-β; αv integrin.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
MLD, JRS, CC, JC, GGL, MR, SSH, VR, MMM, PK, EHB, LH, JW, MF, SPM, SH, MC, MM, TFH, FR, KL, E-IL, EAL, SMT: Employee of Pliant Therapeutics and holds shares in the company. PJW, TJD: Received funding from Pliant Therapeutics for tissue collection/research. DJM, PA: Former employee of Pliant Therapeutics and holds shares in the company.
Figures
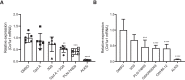
Similar articles
-
Potential of αvβ6 and αvβ1 integrin inhibition for treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Expert Opin Ther _targets. 2024 Jul;28(7):575-585. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2024.2375375. Epub 2024 Jul 2. Expert Opin Ther _targets. 2024. PMID: 38949181 Review.
-
A dual αvβ1/αvβ6 integrin inhibitor Bexotegrast (PLN-74809) ameliorates organ injury and fibrogenesis in fibrotic kidney disease.Eur J Pharmacol. 2024 Nov 15;983:176983. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2024.176983. Epub 2024 Sep 6. Eur J Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39243926
-
Defining the mechanism of galectin-3-mediated TGF-β1 activation and its role in lung fibrosis.J Biol Chem. 2024 Jun;300(6):107300. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107300. Epub 2024 Apr 18. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 38641066 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological characterisation of GSK3335103, an oral αvβ6 integrin small molecule RGD-mimetic inhibitor for the treatment of fibrotic disease.Eur J Pharmacol. 2021 Dec 15;913:174618. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174618. Epub 2021 Nov 8. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34762934
-
Epithelial-mesenchymal interactions in fibrosis and repair. Transforming growth factor-β activation by epithelial cells and fibroblasts.Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2015 Mar;12 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S21-3. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201406-245MG. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2015. PMID: 25830829 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Distinct fibroblast functions associated with fibrotic and immune-mediated inflammatory diseases and their implications for therapeutic development.F1000Res. 2024 Jan 10;13:54. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.143472.1. eCollection 2024. F1000Res. 2024. PMID: 38681509 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathological mechanisms and novel drug _targets in fibrotic interstitial lung disease.Inflamm Regen. 2024 Jul 19;44(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s41232-024-00345-2. Inflamm Regen. 2024. PMID: 39026335 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Therapeutic _targets for Hepatic Fibrosis in the Integrin Family, α8β1 and α11β1, Induced Specifically on Activated Stellate Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 26;22(23):12794. doi: 10.3390/ijms222312794. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34884600 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reviewing the Regulators of COL1A1.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 11;24(12):10004. doi: 10.3390/ijms241210004. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37373151 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current and Future Treatment Landscape for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis.Drugs. 2023 Nov;83(17):1581-1593. doi: 10.1007/s40265-023-01950-0. Epub 2023 Oct 26. Drugs. 2023. PMID: 37882943 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lederer DJ, Martinez FJ. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 2018;379(8):797–798. - PubMed
-
- Lancaster L, Crestani B, Hernandez P, Inoue Y, Wachtlin D, Loaiza L, Quaresma M, Stowasser S, Richeldi L. Safety and survival data in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis treated with nintedanib: pooled data from six clinical trials. BMJ Open Respir Res. 2019;6(1):e000397. doi: 10.1136/bmjresp-2018-000397. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

