Survival improvement and prognosis for hepatocellular carcinoma: analysis of the SEER database
- PMID: 34715816
- PMCID: PMC8555190
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-021-08904-3
Survival improvement and prognosis for hepatocellular carcinoma: analysis of the SEER database
Abstract
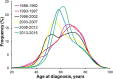
Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) incidences have been increasing in the United States. This study aimed to examine temporal trend of HCC survival and determine prognostic factors influencing HCC survival within the U.S.
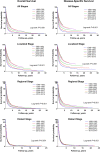
Methods: The Surveillance Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database was used to identify patients diagnosed with primary HCC from 1988 to 2015. Overall survival (OS) and disease-specific survival (DSS) were calculated by the Kaplan-Meier method. Univariate and multivariate Cox regression models were used to estimate hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for prognostic factors and comparing survival between patients diagnosed at different periods (per 5-year interval). Results A total of 80,347 patients were included. The proportions of both young patients (< 45 years) and old patients (≥75 years) decreased over time (P < 0.001) and the male-to-female ratio increased over time (P < 0.001). Significant decreasing temporal trends were observed for HCC severity at diagnosis, including SEER stage, tumor size, tumor extent, and lymph node involvement (P < 0.001 for all). OS and DSS of patients with HCC improved over time (P < 0.001). After adjusting for patient and tumor characteristics and treatment difference, period of diagnosis retained an independent factor for improved DSS and its prognostic significance was evident for localized and regional HCC (P < 0.001), but not for distant HCC. On multivariate analyses, young age, female gender, Hispanic ethnicity, and married status were predictors favoring DSS, whereas a worse DSS was observed for patients with tumor > 5 cm, with vascular invasion, and with lymph node involvement. Patients treated with liver-directed therapy (HR = 0.54, 95% CI: 0.35-0.56), hepatic resection (HR = 0.35, 95% CI: 0.33-0.37), and transplantation (HR = 0.14, 95% CI: 0.13-0.15) had significantly longer DSS compared with those who received no surgery. In stratified analyses, the beneficial effects of surgical approach, regardless therapy type, were significant across all stages.
Conclusions: Our results indicate a significant improvement in survival for HCC patients from 1988 to 2015, which may be attributable to advances in early diagnosis and therapeutic approaches.
Keywords: Disease specific survival; Liver cancer; Overall survival; Prognosis; Survival trend.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Does fibrosis have an impact on survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: evidence from the SEER database?BMC Cancer. 2018 Nov 16;18(1):1125. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4996-z. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30445928 Free PMC article.
-
Racial/ethnic disparities in access to care and survival for patients with early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma.Arch Surg. 2010 Dec;145(12):1158-63. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.2010.272. Arch Surg. 2010. PMID: 21173289
-
Predictors of survival after resection of early hepatocellular carcinoma.Ann Surg. 2009 May;249(5):799-805. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e3181a38eb5. Ann Surg. 2009. PMID: 19387322
-
Precision diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma.Chin Med J (Engl). 2023 May 20;136(10):1155-1165. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000002641. Epub 2023 Mar 17. Chin Med J (Engl). 2023. PMID: 36939276 Free PMC article. Review.
-
De novo Versus Secondary Dedifferentiated Chordomas: A Population-Based Analysis and Integrated Individual Participant Data Meta-Analysis.World Neurosurg. 2023 May;173:208-217.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2023.02.062. Epub 2023 Feb 16. World Neurosurg. 2023. PMID: 36804481 Review.
Cited by
-
Disrupting Poly(ADP-ribosyl)ating Pathway Creates Premalignant Conditions in Mammalian Liver.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 6;24(24):17205. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417205. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139034 Free PMC article.
-
Predictors of early and late hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence.World J Gastroenterol. 2023 Feb 28;29(8):1243-1260. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i8.1243. World J Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 36925456 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Additive Value of Radiomics Features Extracted from Baseline MR Images to the Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) Staging System in Predicting Transplant-Free Survival in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Single-Center Retrospective Analysis.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Feb 2;13(3):552. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13030552. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36766656 Free PMC article.
-
Tenofovir vs Entecavir Among Patients With HBV-Related HCC After Resection.JAMA Netw Open. 2023 Oct 2;6(10):e2340353. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.40353. JAMA Netw Open. 2023. PMID: 37906195 Free PMC article.
-
Risk of cardiovascular death in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma based on the Fine-Gray model.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024 Mar 15;16(3):844-856. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i3.844. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38577452 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tang X, Allain JP, Wang H, Rong X, Chen J, Huang K, Xu R, Wang M, Huang J, Liao Q, Shan Z, Luo S, Li T, Li C, Fu Y. Incidence of hepatitis B virus infection in young Chinese blood donors born after mandatory implementation of neonatal hepatitis B vaccination nationwide. J Viral Hepat. 2018;25(9):1008–1016. doi: 10.1111/jvh.12901. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical