Intravenous immunoglobulins in patients with COVID-19-associated moderate-to-severe acute respiratory distress syndrome (ICAR): multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial
- PMID: 34774185
- PMCID: PMC8585489
- DOI: 10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00440-9
Intravenous immunoglobulins in patients with COVID-19-associated moderate-to-severe acute respiratory distress syndrome (ICAR): multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial
Abstract
Background: Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a major complication of COVID-19 and is associated with high mortality and morbidity. We aimed to assess whether intravenous immunoglobulins (IVIG) could improve outcomes by reducing inflammation-mediated lung injury.
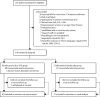
Methods: In this multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, done at 43 centres in France, we randomly assigned patients (1:1) receiving invasive mechanical ventilation for up to 72 h with PCR confirmed COVID-19 and associated moderate-to-severe ARDS to receive either IVIG (2 g/kg over 4 days) or placebo. Random assignment was done with a web-based system and was stratified according to the participating centre and the duration of invasive mechanical ventilation before inclusion in the trial (<12 h, 12-24 h, and >24-72 h), and treatment was administered within the first 96 h of invasive mechanical ventilation. To minimise the risk of adverse events, the IVIG administration was divided into four perfusions of 0·5 g/kg each administered over at least 8 hours. Patients in the placebo group received an equivalent volume of sodium chloride 0·9% (10 mL/kg) over the same period. The primary outcome was the number of ventilation-free days by day 28, assessed according to the intention-to-treat principle. This trial was registered on ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT04350580.
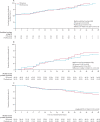
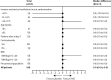
Findings: Between April 3, and October 20, 2020, 146 patients (43 [29%] women) were eligible for inclusion and randomly assigned: 69 (47%) patients to the IVIG group and 77 (53%) to the placebo group. The intention-to-treat analysis showed no statistical difference in the median number of ventilation-free days at day 28 between the IVIG group (0·0 [IQR 0·0-8·0]) and the placebo group (0·0 [0·0-6·0]; difference estimate 0·0 [0·0-0·0]; p=0·21). Serious adverse events were more frequent in the IVIG group (78 events in 22 [32%] patients) than in the placebo group (47 events in 15 [20%] patients; p=0·089).
Interpretation: In patients with COVID-19 who received invasive mechanical ventilation for moderate-to-severe ARDS, IVIG did not improve clinical outcomes at day 28 and tended to be associated with an increased frequency of serious adverse events, although not significant. The effect of IVIGs on earlier disease stages of COVID-19 should be assessed in future trials.
Funding: Programme Hospitalier de Recherche Clinique.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests We declare no competing interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
Why the application of IVIG might be beneficial in patients with COVID-19.Lancet Respir Med. 2022 Feb;10(2):e15. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00549-X. Lancet Respir Med. 2022. PMID: 35120611 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Why the application of IVIG might be beneficial in patients with COVID-19 - Authors' reply.Lancet Respir Med. 2022 Feb;10(2):e16. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00550-6. Lancet Respir Med. 2022. PMID: 35120612 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Effect of early treatment with polyvalent immunoglobulin on acute respiratory distress syndrome associated with SARS-CoV-2 infections (ICAR trial): study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2021 Feb 28;22(1):170. doi: 10.1186/s13063-021-05118-7. Trials. 2021. PMID: 33648563 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and Efficacy of Imatinib for Hospitalized Adults with COVID-19: A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2020 Oct 28;21(1):897. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04819-9. Trials. 2020. PMID: 33115543 Free PMC article.
-
Double-blind, randomized, controlled, trial to assess the efficacy of allogenic mesenchymal stromal cells in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome due to COVID-19 (COVID-AT): A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2021 Jan 6;22(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04964-1. Trials. 2021. PMID: 33407777 Free PMC article.
-
Ivermectin for preventing and treating COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jun 21;6(6):CD015017. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015017.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35726131 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interventions for necrotizing soft tissue infections in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 May 31;5(5):CD011680. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011680.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29851032 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Why the application of IVIG might be beneficial in patients with COVID-19.Lancet Respir Med. 2022 Feb;10(2):e15. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00549-X. Lancet Respir Med. 2022. PMID: 35120611 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Effect of intravenous immunoglobulin on mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Health Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 8;7(7):e2239. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.2239. eCollection 2024 Jul. Health Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38983684 Free PMC article.
-
Beneficial Immune Regulation by Biological Response Modifier Glucans in COVID-19 and Their Envisaged Potentials in the Management of Sepsis.Front Immunol. 2022 Jun 27;13:870632. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.870632. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35833122 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IgG response to spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 in healthy individuals and potential of intravenous IgG as treatment for COVID-19.Virol J. 2022 Nov 13;19(1):186. doi: 10.1186/s12985-022-01921-z. Virol J. 2022. PMID: 36372879 Free PMC article.
-
A single-center experience of COVID-19 infection in patients with primary immunodeficiency.J Allergy Clin Immunol Glob. 2024 Mar 7;3(2):100241. doi: 10.1016/j.jacig.2024.100241. eCollection 2024 May. J Allergy Clin Immunol Glob. 2024. PMID: 38585448 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO WHO coronavirus disease (COVID-19) dashboard. 2021. https://covid19.who.int
-
- Herridge MS, Tansey CM, Matté A, et al. Functional disability 5 years after acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:1293–1304. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

