Application of Terrestrial Laser Scanning (TLS) in the Architecture, Engineering and Construction (AEC) Industry
- PMID: 35009806
- PMCID: PMC8749828
- DOI: 10.3390/s22010265
Application of Terrestrial Laser Scanning (TLS) in the Architecture, Engineering and Construction (AEC) Industry
Abstract
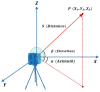
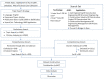
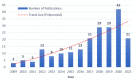
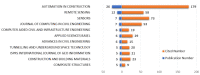
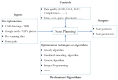
As a revolutionary technology, terrestrial laser scanning (TLS) is attracting increasing interest in the fields of architecture, engineering and construction (AEC), with outstanding advantages, such as highly automated, non-contact operation and efficient large-scale sampling capability. TLS has extended a new approach to capturing extremely comprehensive data of the construction environment, providing detailed information for further analysis. This paper presents a systematic review based on scientometric and qualitative analysis to summarize the progress and the current status of the topic and to point out promising research efforts. To begin with, a brief understanding of TLS is provided. Following the selection of relevant papers through a literature search, a scientometric analysis of papers is carried out. Then, major applications are categorized and presented, including (1) 3D model reconstruction, (2) object recognition, (3) deformation measurement, (4) quality assessment, and (5) progress tracking. For widespread adoption and effective use of TLS, essential problems impacting working effects in application are summarized as follows: workflow, data quality, scan planning, and data processing. Finally, future research directions are suggested, including: (1) cost control of hardware and software, (2) improvement of data processing capability, (3) automatic scan planning, (4) integration of digital technologies, (5) adoption of artificial intelligence.
Keywords: architecture; citespace; engineering and construction (AEC); point cloud; terrestrial laser scanning (TLS).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

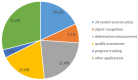

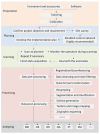
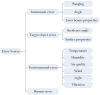
Similar articles
-
Terrestrial laser scanning: a new standard of forest measuring and modelling?Ann Bot. 2021 Oct 27;128(6):653-662. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcab111. Ann Bot. 2021. PMID: 34487143 Free PMC article.
-
Digital Technologies in the Architecture, Engineering and Construction (AEC) Industry-A Bibliometric-Qualitative Literature Review of Research Activities.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Jun 6;18(11):6135. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18116135. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34204147 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Review on the Research and Applications of TLS in Ground Surface and Constructions Deformation Monitoring.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Nov 25;22(23):9179. doi: 10.3390/s22239179. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36501880 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Special Issue on "Terrestrial Laser Scanning": Editors' Notes.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Oct 21;19(20):4569. doi: 10.3390/s19204569. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31640146 Free PMC article.
-
Terrestrial LiDAR: a three-dimensional revolution in how we look at trees.New Phytol. 2019 Jun;222(4):1736-1741. doi: 10.1111/nph.15517. Epub 2018 Nov 5. New Phytol. 2019. PMID: 30295928 Review.
Cited by
-
Digital Twins and Enabling Technologies in Museums and Cultural Heritage: An Overview.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Feb 1;23(3):1583. doi: 10.3390/s23031583. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36772623 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative Analysis on the Effect of Surface Reflectance for Laser 3D Scanner Calibrator.Micromachines (Basel). 2022 Sep 27;13(10):1607. doi: 10.3390/mi13101607. Micromachines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36295962 Free PMC article.
-
Multisensor and Multiscale Data Integration Method of TLS and GPR for Three-Dimensional Detailed Virtual Reconstruction.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Dec 14;23(24):9826. doi: 10.3390/s23249826. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38139672 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic Process of an Ancient Colonnade Using 3D High-Resolution Models with Non-Invasive Multi Techniques.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Mar 14;23(6):3098. doi: 10.3390/s23063098. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36991808 Free PMC article.
-
Terrestrial Laser Scanning of Lunar Soil Simulants.Materials (Basel). 2022 Dec 8;15(24):8773. doi: 10.3390/ma15248773. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36556577 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang M., Wang C.C., Sepasgozar S., Zlatanova S. A systematic review of digital technology adoption in off-site construction: Current status and future direction towards industry 4.0. Buildings. 2020;10:204. doi: 10.3390/buildings10110204. - DOI
-
- Pan Y., Zhang L. Roles of artificial intelligence in construction engineering and management: A critical review and future trends. Autom. Constr. 2021;122:103517. doi: 10.1016/j.autcon.2020.103517. - DOI
-
- Štefanič M., Stankovski V. Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers-Civil Engineering. Thomas Telford Ltd.; London, UK: 2018. A review of technologies and applications for smart construction; pp. 83–87.
-
- Opoku D.-G.J., Perera S., Osei-Kyei R., Rashidi M. Digital twin application in the construction industry: A literature review. J. Build. Eng. 2021;40:102726. doi: 10.1016/j.jobe.2021.102726. - DOI
-
- Jiang F., Ma L., Broyd T., Chen K. Digital twin and its implementations in the civil engineering sector. Autom. Constr. 2021;130:103838. doi: 10.1016/j.autcon.2021.103838. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

