Accuracy and Acceptability of Wrist-Wearable Activity-Tracking Devices: Systematic Review of the Literature
- PMID: 35060915
- PMCID: PMC8817215
- DOI: 10.2196/30791
Accuracy and Acceptability of Wrist-Wearable Activity-Tracking Devices: Systematic Review of the Literature
Abstract
Background: Numerous wrist-wearable devices to measure physical activity are currently available, but there is a need to unify the evidence on how they compare in terms of acceptability and accuracy.
Objective: The aim of this study is to perform a systematic review of the literature to assess the accuracy and acceptability (willingness to use the device for the task it is designed to support) of wrist-wearable activity trackers.
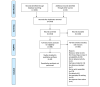
Methods: We searched MEDLINE, Embase, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, and SPORTDiscus for studies measuring physical activity in the general population using wrist-wearable activity trackers. We screened articles for inclusion and, for the included studies, reported data on the studies' setting and population, outcome measured, and risk of bias.
Results: A total of 65 articles were included in our review. Accuracy was assessed for 14 different outcomes, which can be classified in the following categories: count of specific activities (including step counts), time spent being active, intensity of physical activity (including energy expenditure), heart rate, distance, and speed. Substantial clinical heterogeneity did not allow us to perform a meta-analysis of the results. The outcomes assessed most frequently were step counts, heart rate, and energy expenditure. For step counts, the Fitbit Charge (or the Fitbit Charge HR) had a mean absolute percentage error (MAPE) <25% across 20 studies. For heart rate, the Apple Watch had a MAPE <10% in 2 studies. For energy expenditure, the MAPE was >30% for all the brands, showing poor accuracy across devices. Acceptability was most frequently measured through data availability and wearing time. Data availability was ≥75% for the Fitbit Charge HR, Fitbit Flex 2, and Garmin Vivofit. The wearing time was 89% for both the GENEActiv and Nike FuelBand.
Conclusions: The Fitbit Charge and Fitbit Charge HR were consistently shown to have a good accuracy for step counts and the Apple Watch for measuring heart rate. None of the tested devices proved to be accurate in measuring energy expenditure. Efforts should be made to reduce the heterogeneity among studies.
Keywords: diagnosis; measurement; mobile phone; wrist-wearable devices.
©Federico Germini, Noella Noronha, Victoria Borg Debono, Binu Abraham Philip, Drashti Pete, Tamara Navarro, Arun Keepanasseril, Sameer Parpia, Kerstin de Wit, Alfonso Iorio. Originally published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research (https://www.jmir.org), 21.01.2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Accuracy of Consumer Wearable Heart Rate Measurement During an Ecologically Valid 24-Hour Period: Intraindividual Validation Study.JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2019 Mar 11;7(3):e10828. doi: 10.2196/10828. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2019. PMID: 30855232 Free PMC article.
-
Wrist-worn devices for the measurement of heart rate and energy expenditure: A validation study for the Apple Watch 6, Polar Vantage V and Fitbit Sense.Eur J Sport Sci. 2023 Feb;23(2):165-177. doi: 10.1080/17461391.2021.2023656. Epub 2022 Jan 31. Eur J Sport Sci. 2023. PMID: 34957939
-
A catalog of validity indices for step counting wearable technologies during treadmill walking: the CADENCE-adults study.Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2022 Sep 8;19(1):117. doi: 10.1186/s12966-022-01350-9. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2022. PMID: 36076265 Free PMC article.
-
Accuracy of Fitbit Devices: Systematic Review and Narrative Syntheses of Quantitative Data.JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2018 Aug 9;6(8):e10527. doi: 10.2196/10527. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2018. PMID: 30093371 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reporting adherence, validity and physical activity measures of wearable activity trackers in medical research: A systematic review.Int J Med Inform. 2022 Apr;160:104696. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2022.104696. Epub 2022 Jan 31. Int J Med Inform. 2022. PMID: 35121356 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring Pain Reduction through Physical Activity: A Case Study of Seven Fibromyalgia Patients.Bioengineering (Basel). 2024 Jul 29;11(8):765. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering11080765. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39199723 Free PMC article.
-
Study protocol: A comparison of mobile and clinic-based spirometry for capturing the treatment effect in moderate asthma.Clin Transl Sci. 2023 Nov;16(11):2112-2122. doi: 10.1111/cts.13615. Epub 2023 Sep 8. Clin Transl Sci. 2023. PMID: 37602889 Free PMC article.
-
Using wearable activity trackers for research in the global south: Lessons learned from adolescent psychotherapy research in Kenya.Glob Ment Health (Camb). 2023 Dec 4;10:e86. doi: 10.1017/gmh.2023.85. eCollection 2023. Glob Ment Health (Camb). 2023. PMID: 38161741 Free PMC article.
-
Accuracy and Systematic Biases of Heart Rate Measurements by Consumer-Grade Fitness Trackers in Postoperative Patients: Prospective Clinical Trial.J Med Internet Res. 2022 Dec 30;24(12):e42359. doi: 10.2196/42359. J Med Internet Res. 2022. PMID: 36583938 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effectiveness of support from community health workers on the sustained use of a wearable monitoring device among community-dwelling older adults: A randomized trial protocol.PLoS One. 2023 Dec 22;18(12):e0294517. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0294517. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 38134126 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Seifert A, Schlomann A, Rietz C, Schelling HR. The use of mobile devices for physical activity tracking in older adults' everyday life. Digit Health. 2017 Nov 09;3:2055207617740088. doi: 10.1177/2055207617740088. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/2055207617740088?url_ver=Z39.88... 10.1177_2055207617740088 - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rütten A, Ziemainz H, Schena F, Stahl T, Stiggelbout M, Auweele YV, Vuillemin A, Welshman J. Using different physical activity measurements in eight European countries. Results of the European Physical Activity Surveillance System (EUPASS) time series survey. Public Health Nutr. 2003 Jun;6(4):371–6. doi: 10.1079/PHN2002450. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ranganathan P, Pramesh CS, Aggarwal R. Common pitfalls in statistical analysis: measures of agreement. Perspect Clin Res. 2017;8(4):187–91. doi: 10.4103/picr.PICR_123_17. http://www.picronline.org/article.asp?issn=2229-3485;year=2017;volume=8;... PCR-8-187 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources