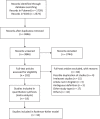
A risk scoring system to predict the individual incidence of early-onset colorectal cancer
- PMID: 35093005
- PMCID: PMC8801093
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-022-09238-4
A risk scoring system to predict the individual incidence of early-onset colorectal cancer
Abstract
Background: The incidence of early-onset colorectal cancer (EOCRC) is increasing at an alarming rate and further studies are needed to identify risk factors and to develop prevention strategies.
Methods: Risk factors significantly associated with EOCRC were identified using meta-analysis. An individual risk appraisal model was constructed using the Rothman-Keller model. Next, a group of random data sets was generated using the binomial distribution function method, to determine nodes of risk assessment levels and to identify low, medium, and high risk populations.
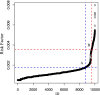
Results: A total of 32,843 EOCRC patients were identified in this study, and nine significant risk factors were identified using meta-analysis, including male sex, Caucasian ethnicity, sedentary lifestyle, inflammatory bowel disease, and high intake of red meat and processed meat. After simulating the risk assessment data of 10,000 subjects, scores of 0 to 0.0018, 0.0018 to 0.0036, and 0.0036 or more were respectively considered as low-, moderate-, and high-risk populations for the EOCRC population based on risk trends from the Rothman-Keller model.
Conclusion: This model can be used for screening of young adults to predict high risk of EOCRC and will contribute to the primary prevention strategies and the reduction of risk of developing EOCRC.
Keywords: Early-onset colorectal cancer; Meta-analysis; Risk assessment; Risk factors; Rothman–Keller model.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Red Flag Signs and Symptoms for Patients With Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.JAMA Netw Open. 2024 May 1;7(5):e2413157. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.13157. JAMA Netw Open. 2024. PMID: 38787555 Free PMC article.
-
Risk factors for early-onset colorectal cancer: A Canadian prospective cohort study.Cancer Epidemiol. 2024 Aug;91:102578. doi: 10.1016/j.canep.2024.102578. Epub 2024 May 14. Cancer Epidemiol. 2024. PMID: 38749340
-
Burden of early-onset colorectal cancer along with attributable risk factors from 1990 to 2019: a comparative study between China and other G20 countries.BMC Public Health. 2023 Jul 31;23(1):1463. doi: 10.1186/s12889-023-16407-y. BMC Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37525147 Free PMC article.
-
Early-onset colorectal cancer: why it should be high on our list of differentials.ANZ J Surg. 2022 Jul;92(7-8):1638-1643. doi: 10.1111/ans.17698. Epub 2022 Apr 21. ANZ J Surg. 2022. PMID: 35451218 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Risk Factors for Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Jun;20(6):1229-1240.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.01.037. Epub 2021 Jan 29. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 33524598 Review.
Cited by
-
Distinct clinical characteristics in stage III rectal cancer among different age groups and treatment outcomes after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy.Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2024 Feb 11;16:17588359241229434. doi: 10.1177/17588359241229434. eCollection 2024. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38347922 Free PMC article.
-
Survival Analysis of Metastatic Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer Compared to Metastatic Average-Onset Colorectal Cancer: A SEER Database Analysis.Cancers (Basel). 2024 May 25;16(11):2004. doi: 10.3390/cancers16112004. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38893124 Free PMC article.
-
Orbital Apex Metastases From Primary Colorectal Adenocarcinoma: A Rare Cause for Unilateral Vision Loss.Cureus. 2024 May 1;16(5):e59485. doi: 10.7759/cureus.59485. eCollection 2024 May. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38826902 Free PMC article.
-
Risk Prediction Modeling for Colorectal Adenomas: An Avenue Toward Prevention of Early Onset Colorectal Cancer.Gastro Hep Adv. 2024 Apr 25;3(6):728-730. doi: 10.1016/j.gastha.2024.04.009. eCollection 2024. Gastro Hep Adv. 2024. PMID: 39280910 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Bibliometric analysis of global research on physical activity and sedentary behavior in the context of cancer.Front Oncol. 2023 Jan 26;13:1095852. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1095852. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36776335 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global Cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–249. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical