Unenhanced computed tomography for non-invasive diagnosis of hepatic steatosis with low tube potential protocol
- PMID: 35111629
- PMCID: PMC8739110
- DOI: 10.21037/qims-21-474
Unenhanced computed tomography for non-invasive diagnosis of hepatic steatosis with low tube potential protocol
Abstract
Background: Lowering kVp affects the image contrast and computed tomography (CT) attenuation values of low kVp CT is different from those of conventional 120-kVp scans. The purpose of this study is to determine the diagnostic performance and to establish the reference range of low-kVp unenhanced CT for the assessment of hepatic steatosis in liver transplantation donors using magnetic resonance (MR) spectroscopy as a reference standard.
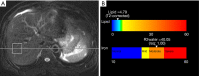
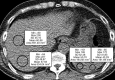
Methods: This retrospective study included 165 potential donors (male:female =114:51, 36.5±12.0 years old) who underwent 100-kVp single-slice unenhanced CT scan and MR spectroscopy. The difference between hepatic and splenic attenuation (CTL-S) and liver-to-spleen attenuation ratio (CTL/S) were calculated. Reference standard was the fat signal fraction measured by MR spectroscopy. Limits of agreement between CT measurements and the reference standard were calculated. Areas under receiver operating characteristic curves (AUROCs) of CTL-S and CTL/S were compared for the diagnosis of moderate to severe steatosis. Cut-off values of CTL-S and CTL/S that provided a balance between sensitivity and specificity and the highest specificity using the lower limit of the reference range were calculated.
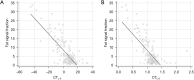
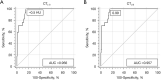
Results: Eighty-seven subjects had a non-steatotic liver. Sixty-one subjects had mild steatosis and 17 subjects had moderate to severe steatosis based on MR spectroscopy. CTL-S and CTL/S values were negatively correlated with the fat signal fraction (P<0.001) and limits of agreement were -8.4% to 8.4% for CTL-S and -9.6% to 9.6% for CTL/S. AUROCs of CTL-S and CTL/S for diagnosing moderate to severe steatosis were 0.956 and 0.957, respectively. Cut-off values of CTL-S and CTL/S for diagnosis of moderate to severe steatosis by the Youden index were -0.5 HU for CTL-S and 0.99 for CTL/S. Reference ranges of non-steatotic liver were -6.90 to 31.40 HU for CTL-S and 0.89 to 1.77 for CTL/S. Using -6.9 HU for CTL-S and 0.89 for CTL/S as cut-off values, the sensitivity and specificity for diagnosing moderate to severe steatosis were 70.59% and 90.54% (CTL-S) and 76.47% and 90.54% (CTL/S), respectively.
Conclusions: Measurements from a low-kVp unenhanced CT scan were negatively correlated with the degree of hepatic steatosis. Low-kVp unenhanced CT is a robust technique with reduced radiation exposure for diagnosing moderate to severe hepatic steatosis.
Keywords: Liver; computed tomography (CT); magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS); steatosis.
2022 Quantitative Imaging in Medicine and Surgery. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://dx.doi.org/10.21037/qims-21-474). JIC reports that he received grants from Guerbet Koreaand Samsung Medison. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CT indices for the diagnosis of hepatic steatosis using non-enhanced CT images: development and validation of diagnostic cut-off values in a large cohort with pathological reference standard.Eur Radiol. 2019 Aug;29(8):4427-4435. doi: 10.1007/s00330-018-5905-1. Epub 2018 Dec 19. Eur Radiol. 2019. PMID: 30569183
-
Liver Steatosis Categorization on Contrast-Enhanced CT Using a Fully Automated Deep Learning Volumetric Segmentation Tool: Evaluation in 1204 Healthy Adults Using Unenhanced CT as a Reference Standard.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2021 Aug;217(2):359-367. doi: 10.2214/AJR.20.24415. Epub 2020 Sep 16. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2021. PMID: 32936018
-
Macrovesicular hepatic steatosis in living liver donors: use of CT for quantitative and qualitative assessment.Radiology. 2006 Apr;239(1):105-12. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2391050361. Epub 2006 Feb 16. Radiology. 2006. PMID: 16484355
-
Post-contrast CT liver attenuation alone is superior to the liver-spleen difference for identifying moderate hepatic steatosis.Eur Radiol. 2024 Nov;34(11):7041-7052. doi: 10.1007/s00330-024-10816-2. Epub 2024 Jun 4. Eur Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38834787
-
Liver fat imaging-a clinical overview of ultrasound, CT, and MR imaging.Br J Radiol. 2018 Sep;91(1089):20170959. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20170959. Epub 2018 Jun 6. Br J Radiol. 2018. PMID: 29722568 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Association of liver multi-parameter quantitative metrics determined by dual-layer spectral detector computed tomography (SDCT) with coronary plaque scores.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024 Oct 1;14(10):7392-7405. doi: 10.21037/qims-24-53. Epub 2024 Sep 21. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024. PMID: 39429605 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of automatic tube current modulation related settings of a modern GE CT scanner on image quality and patient dose; details do matter.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024 Jun;25(6):e14356. doi: 10.1002/acm2.14356. Epub 2024 Apr 24. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024. PMID: 38659159 Free PMC article.
-
The diagnostic value of novel ultrasound attenuation analysis in detecting liver steatosis identified by the controlled attenuation parameter: a diagnostic accuracy study.Ann Transl Med. 2023 Jan 31;11(2):38. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-5821. Epub 2023 Jan 9. Ann Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 36819532 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
