Proteomics technologies for cancer liquid biopsies
- PMID: 35168611
- PMCID: PMC8845389
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-022-01526-8
Proteomics technologies for cancer liquid biopsies
Abstract
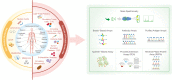
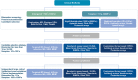
Alterations in DNAs could not reveal what happened in proteins. The accumulated alterations of DNAs would change the manifestation of proteins. Therefore, as is the case in cancer liquid biopsies, deep proteome profiling will likely provide invaluable and clinically relevant information in real-time throughout all stages of cancer progression. However, due to the great complexity of proteomes in liquid biopsy samples and the limitations of proteomic technologies compared to high-plex sequencing technologies, proteomic discoveries have yet lagged behind their counterpart, genomic technologies. Therefore, novel protein technologies are in urgent demand to fulfill the goals set out for biomarker discovery in cancer liquid biopsies.Notably, conventional and innovative technologies are being rapidly developed for proteomic analysis in cancer liquid biopsies. These advances have greatly facilitated early detection, diagnosis, prognosis, and monitoring of cancer evolution, adapted or adopted in response to therapeutic interventions. In this paper, we review the high-plex proteomics technologies that are capable of measuring at least hundreds of proteins simultaneously from liquid biopsy samples, ranging from traditional technologies based on mass spectrometry (MS) and antibody/antigen arrays to innovative technologies based on aptamer, proximity extension assay (PEA), and reverse phase protein arrays (RPPA).
Keywords: Antibody arrays; Aptamer; Cancer liquid biopsy; Mass spectrometry (MS); Proteomics; Proximity extension assay (PEA); Reverse phase protein arrays (RPPA).
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
ZD and NW were employees of Fynn Biotechnologies Ltd. The remaining authors declare no conflicts of interests and no competing interests of this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of Proteomic Technologies for Blood-Based Detection of Colorectal Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 26;22(3):1189. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031189. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33530402 Free PMC article.
-
Optomechanical devices for deep plasma cancer proteomics.Semin Cancer Biol. 2018 Oct;52(Pt 1):26-38. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2017.08.011. Epub 2017 Sep 1. Semin Cancer Biol. 2018. PMID: 28867489 Review.
-
[Applications of high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry in proteomics].Se Pu. 2024 Jul;42(7):601-612. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2023.11006. Se Pu. 2024. PMID: 38966969 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Proteomics of liquid biopsies: Depicting RCC infiltration into the renal vein by MS analysis of urine and plasma.J Proteomics. 2019 Jan 16;191:29-37. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2018.04.029. Epub 2018 Apr 22. J Proteomics. 2019. PMID: 29689304
-
Parallel Analyses by Mass Spectrometry (MS) and Reverse Phase Protein Array (RPPA) Reveal Complementary Proteomic Profiles in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) Patient Tissues and Cell Cultures.Proteomics. 2024 Nov 16:e202400107. doi: 10.1002/pmic.202400107. Online ahead of print. Proteomics. 2024. PMID: 39548956
Cited by
-
Associations between genetically predicted concentrations of plasma proteins and the risk of prostate cancer.BMC Cancer. 2024 Jul 27;24(1):905. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12659-y. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39068416 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic and transcriptomic analyses identify apo-transcobalamin-II as a biomarker of overall survival in osteosarcoma.Front Oncol. 2024 Oct 18;14:1417459. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1417459. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39493449 Free PMC article.
-
The Swedish initiative for the study of Primary sclerosing cholangitis (SUPRIM).EClinicalMedicine. 2024 Mar 11;70:102526. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102526. eCollection 2024 Apr. EClinicalMedicine. 2024. PMID: 38500838 Free PMC article.
-
Revisiting the standards of cancer detection and therapy alongside their comparison to modern methods.World J Methodol. 2024 Jun 20;14(2):92982. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v14.i2.92982. eCollection 2024 Jun 20. World J Methodol. 2024. PMID: 38983668 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiomic Approaches for Cancer Biomarker Discovery in Liquid Biopsies: Advances and Challenges.Biomark Insights. 2023 Oct 14;18:11772719231204508. doi: 10.1177/11772719231204508. eCollection 2023. Biomark Insights. 2023. PMID: 37846373 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alix-Panabières C, Pantel K. Liquid biopsy: from discovery to clinical application. Cancer Discov. 2021;11(4):858–873. - PubMed
-
- Rossi G, Ignatiadis M. Promises and pitfalls of using liquid biopsy for precision medicine. Cancer Res. 2019;79(11):2798–2804. - PubMed
-
- Li H, Vanarsa K, Zhang T, Soomro S, Cicalese PA, Duran V, et al. Comprehensive aptamer-based screen of 1317 proteins uncovers improved stool protein markers of colorectal cancer. J Gastroenterol. 2021;56(7):659–672. - PubMed
-
- Suhre K, McCarthy MI, Schwenk JM. Genetics meets proteomics: perspectives for large population-based studies. Nat Rev Genet. 2021;22(1):19–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

