H2B.V demarcates divergent strand-switch regions, some tDNA loci, and genome compartments in Trypanosoma cruzi and affects parasite differentiation and host cell invasion
- PMID: 35180281
- PMCID: PMC8893665
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009694
H2B.V demarcates divergent strand-switch regions, some tDNA loci, and genome compartments in Trypanosoma cruzi and affects parasite differentiation and host cell invasion
Abstract
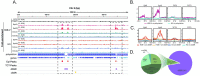
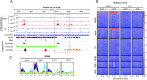
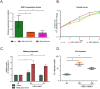
Histone variants play a crucial role in chromatin structure organization and gene expression. Trypanosomatids have an unusual H2B variant (H2B.V) that is known to dimerize with the variant H2A.Z generating unstable nucleosomes. Previously, we found that H2B.V protein is enriched in tissue-derived trypomastigote (TCT) life forms, a nonreplicative stage of Trypanosoma cruzi, suggesting that this variant may contribute to the differences in chromatin structure and global transcription rates observed among parasite life forms. Here, we performed the first genome-wide profiling of histone localization in T. cruzi using epimastigotes and TCT life forms, and we found that H2B.V was preferentially located at the edges of divergent transcriptional strand switch regions, which encompass putative transcriptional start regions; at some tDNA loci; and between the conserved and disrupted genome compartments, mainly at trans-sialidase, mucin and MASP genes. Remarkably, the chromatin of TCT forms was depleted of H2B.V-enriched peaks in comparison to epimastigote forms. Interactome assays indicated that H2B.V associated specifically with H2A.Z, bromodomain factor 2, nucleolar proteins and a histone chaperone, among others. Parasites expressing reduced H2B.V levels were associated with higher rates of parasite differentiation and mammalian cell infectivity. Taken together, H2B.V demarcates critical genomic regions and associates with regulatory chromatin proteins, suggesting a scenario wherein local chromatin structures associated with parasite differentiation and invasion are regulated during the parasite life cycle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genome-wide localization of histone variants in Toxoplasma gondii implicates variant exchange in stage-specific gene expression.BMC Genomics. 2022 Feb 14;23(1):128. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08338-6. BMC Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35164683 Free PMC article.
-
Open chromatin analysis in Trypanosoma cruzi life forms highlights critical differences in genomic compartments and developmental regulation at tDNA loci.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2022 Jun 1;15(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s13072-022-00450-x. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2022. PMID: 35650626 Free PMC article.
-
H2A.Z and H2B.Z double-variant nucleosomes define intergenic regions and dynamically occupy var gene promoters in the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum.Mol Microbiol. 2013 Mar;87(6):1167-82. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12154. Epub 2013 Feb 4. Mol Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23373537
-
Mechanistic and structural insights into histone H2A-H2B chaperone in chromatin regulation.Biochem J. 2020 Sep 18;477(17):3367-3386. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20190852. Biochem J. 2020. PMID: 32941645 Review.
-
The role of histone H2A and H2B post-translational modifications in transcription: a genomic perspective.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009 Jan;1789(1):37-44. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2008.07.001. Epub 2008 Jul 14. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009. PMID: 18675384 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-wide chromatin interaction map for Trypanosoma cruzi.Nat Microbiol. 2023 Nov;8(11):2103-2114. doi: 10.1038/s41564-023-01483-y. Epub 2023 Oct 12. Nat Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37828247 Free PMC article.
-
Histone variant H2B.Z acetylation is necessary for maintenance of Toxoplasma gondii biological fitness.Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2023 Sep;1866(3):194943. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2023.194943. Epub 2023 May 20. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2023. PMID: 37217032 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoprecipitation of RNA-DNA hybrid interacting proteins in Trypanosoma brucei reveals conserved and novel activities, including in the control of surface antigen expression needed for immune evasion by antigenic variation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Nov 10;51(20):11123-11141. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad836. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 37843098 Free PMC article.
-
Histone variant H2B.Z acetylation is necessary for maintenance of Toxoplasma gondii biological fitness.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Feb 24:2023.02.14.528480. doi: 10.1101/2023.02.14.528480. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2023 Sep;1866(3):194943. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2023.194943 PMID: 36824796 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Gene editing of putative cAMP and Ca2+ -regulated proteins using an efficient cloning-free CRISPR/Cas9 system in Trypanosoma cruzi.J Eukaryot Microbiol. 2023 Nov-Dec;70(6):e12999. doi: 10.1111/jeu.12999. Epub 2023 Sep 19. J Eukaryot Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37724511 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

