Real-Time Flash Glucose Monitoring Had Better Effects on Daily Glycemic Control Compared With Retrospective Flash Glucose Monitoring in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes on Premix Insulin Therapy
- PMID: 35222287
- PMCID: PMC8867069
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.832102
Real-Time Flash Glucose Monitoring Had Better Effects on Daily Glycemic Control Compared With Retrospective Flash Glucose Monitoring in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes on Premix Insulin Therapy
Abstract
Background and aims: To compare the effects of real-time and retrospective flash glucose monitoring (FGM) on daily glycemic control and lifestyle in patients with type 2 diabetes on premix insulin therapy.
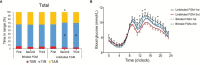
Methods and results: A total of 172 patients using premix insulin, with HbA1c ≥ 7.0% (56 mmol/mol), or the time below the _target (TBR) ≥ 4%, or the coefficient of variation (CV) ≥36% during the screening period, were randomly assigned to retrospective FGM (n = 89) or real-time FGM group (n = 83). Another two retrospective or real-time 14-day FGMs were performed respectively, 1 month apart. Both groups received educations and medication adjustment after each FGM. Time in range (3.9~10.0 mmol/l, TIR) increased significantly after 3 months in the real-time FGM group (6.5%) compared with the retrospective FGM group (-1.1%) (p = 0.014). HbA1c decreased in both groups (both p < 0.01). Real-time FGMs increased daily exercise time compared with the retrospective group (p = 0.002).
Conclusions: Real-time FGM with visible blood glucose improves daily glycemic control and diabetes self-care behaviors better than retrospective FGM in patients with type 2 diabetes on premix insulin therapy.
Clinical trial registration: https://clinicaltrials.gov/NCT04847219.
Keywords: flash glucose monitoring; premix insulin; real-time glucose monitoring; time in _target range; type 2 diabetes.
Copyright © 2022 Yan, Cai, Jiang, Jing, Cai, Xie, Su, Xu, He, Cheng, Cheng, Liu, Hu and Ma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Flash glucose monitoring helps achieve better glycemic control than conventional self-monitoring of blood glucose in non-insulin-treated type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial.BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2020 Jun;8(1):e001115. doi: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2019-001115. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2020. PMID: 32518063 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of flash glucose monitoring in pregnant women with poorly controlled pregestational diabetes (FlashMom): A randomized pilot study.Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2021 Jun 7;31(6):1851-1859. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2021.03.013. Epub 2021 Mar 24. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2021. PMID: 33975741 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of Flash Glucose Monitoring Technology on Glycemic Control and Treatment Satisfaction in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes.Diabetes Care. 2019 Jul;42(7):1178-1184. doi: 10.2337/dc18-0166. Epub 2019 Apr 29. Diabetes Care. 2019. PMID: 31036546 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of flash glucose monitoring on glycemic control in participants with diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.J Diabetes Complications. 2022 Nov;36(11):108314. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2022.108314. Epub 2022 Sep 28. J Diabetes Complications. 2022. PMID: 36208566 Review.
-
Flash Glucose Monitoring: A Review of the Literature with a Special Focus on Type 1 Diabetes.Nutrients. 2018 Jul 29;10(8):992. doi: 10.3390/nu10080992. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 30060632 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Leveraging continuous glucose monitoring as a catalyst for behaviour change: a scoping review.Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2024 Jul 10;21(1):74. doi: 10.1186/s12966-024-01622-6. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2024. PMID: 38987796 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Individualized intensive insulin therapy of diabetes: Not only the goal, but also the time.World J Diabetes. 2024 Jan 15;15(1):11-14. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i1.11. World J Diabetes. 2024. PMID: 38313848 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ajjan RA, Jackson N, Thomson SA. Reduction in HbA1c Using Professional Flash Glucose Monitoring in Insulin-Treated Type 2 Diabetes Patients Managed in Primary and Secondary Care Settings: A Pilot, Multicentre, Randomised Controlled Trial. Diabetes Vasc Dis Res (2019) 16(4):385–95. doi: 10.1177/1479164119827456 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

