Association Between Serum Albumin Levels and Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy Among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Effect Modification of Body Mass Index
- PMID: 35228809
- PMCID: PMC8881928
- DOI: 10.2147/DMSO.S347349
Association Between Serum Albumin Levels and Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy Among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Effect Modification of Body Mass Index
Abstract
Background: The role of serum albumin in the risk of diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) remains unclear. This study aimed to explore the relationship between serum albumin level and DPN, and to examine any possible effect modifiers among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Methods: This cross-sectional study was conducted in Jiangxi, China, from May 2012 to December 2014. Serum albumin levels were determined in 523 subjects, and the association between serum albumin level and DPN was evaluated using linear regression models (odds ratio [OR] and corresponding 95% confidence interval [CI]).
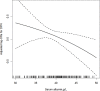
Results: There was a significant inverse association between serum albumin level (per 1 g/L increment, OR 0.95 [95% CI 0.92-0.98]) and the risk of DPN. Accordingly, when serum albumin was assessed as quartiles, a significantly lower risk of DPN was found in participants in quartile 4 (OR 0.49 [95% CI 0.25-0.95]), compared with those in quartile 1. Consistently, higher albumin levels (≥35 g/L) were associated with decreased odds for DPN (OR 0.36 [95% CI 0.17-0.74]) compared with lower levels. Furthermore, the albumin-DPN association was significantly stronger in patients with a relatively high body mass index (BMI; ≥24 kg/m2; OR 0.91 [95% CI 0.85-0.98]) than in those with a low BMI (<24 kg/m2; OR 0.99 [95% CI 0.94-1.04]; P for interaction = 0.042).
Conclusion: These data suggest that serum albumin level could be a novel risk factor for DPN among patients with type 2 diabetes and relatively high BMI (>24 kg/m2).
Keywords: BMI; diabetic peripheral neuropathy; serum albumin; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
© 2022 Hu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare they do not have conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Serum albumin was negatively associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy in Chinese population: a cross-sectional study.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2021 Sep 15;13(1):100. doi: 10.1186/s13098-021-00718-4. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2021. PMID: 34526116 Free PMC article.
-
Association between serum cystatin C and diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a cross-sectional study of a Chinese type 2 diabetic population.Eur J Endocrinol. 2014 Nov;171(5):641-8. doi: 10.1530/EJE-14-0381. Epub 2014 Sep 2. Eur J Endocrinol. 2014. PMID: 25184282
-
Decreased Physiological Serum Total Bile Acid Concentrations in Patients with Type 2 Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2021 Jun 28;14:2883-2892. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S313488. eCollection 2021. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2021. PMID: 34234486 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between Tumor Necrosis Factor-α and Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: a Meta-Analysis.Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Mar;54(2):983-996. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-9702-z. Epub 2016 Jan 21. Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 26797519 Review.
-
Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and peripheral neuropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Endocrinol Invest. 2015 May;38(5):513-8. doi: 10.1007/s40618-014-0210-6. Epub 2014 Dec 21. J Endocrinol Invest. 2015. PMID: 25527161 Review.
Cited by
-
Electrochemical Skin Conductance by Sudoscan in Non-Dialysis Chronic Kidney Disease Patients.J Clin Med. 2023 Dec 28;13(1):187. doi: 10.3390/jcm13010187. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 38202194 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation of Albumin, Red Cell Distribution Width and Other Biochemical and Hematological Parameters with Glycated Hemoglobin in Diabetic, Prediabetic and Non-Diabetic Patients.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 23;25(15):8037. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158037. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125606 Free PMC article.
-
Interpretable machine learning models for detecting peripheral neuropathy and lower extremity arterial disease in diabetics: an analysis of critical shared and unique risk factors.BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2024 Jul 22;24(1):200. doi: 10.1186/s12911-024-02595-z. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2024. PMID: 39039521 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between advanced lung cancer inflammation index and long-term all-cause, cardiovascular, and cancer mortality among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: NHANES, 1999-2018.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Nov 28;14:1298345. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1298345. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 38111710 Free PMC article.
-
Differentiation of HSA and BSA and Instantaneous Detection of HSO3 - Using Confined Space of Serum Albumins and Live Cell Imaging of Exogenous/Endogenous HSO3.ACS Omega. 2023 Jan 5;8(2):2639-2647. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c07163. eCollection 2023 Jan 17. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 36687064 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Polydefkis M, Griffin JW, McArthur J. New insights into diabetic polyneuropathy. JAMA. 2003;290(10):1371–1376. - PubMed
-
- Barle H, Nyberg B, Essén P, et al. The synthesis rates of total liver protein and plasma albumin determined simultaneously in vivo in humans. Hepatology. 1997;25(1):154–158. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources