Blood-brain barrier and gut barrier dysfunction in chronic kidney disease with a focus on circulating biomarkers and tight junction proteins
- PMID: 35292710
- PMCID: PMC8924178
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-08387-7
Blood-brain barrier and gut barrier dysfunction in chronic kidney disease with a focus on circulating biomarkers and tight junction proteins
Abstract
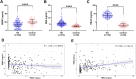
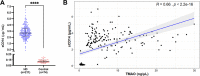
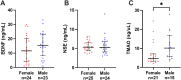
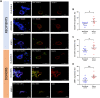
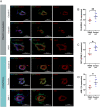
Kidney failure and associated uraemia have implications for the cardiovascular system, brain, and blood-brain barrier (BBB). We aim to examine BBB disruption, by assessing brain-derived neurotropic factor (BDNF), neuron-specific enolase (NSE) levels, and gut-blood barrier (GBB) disruption by trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO), in chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients. Additionally, endothelial tight-junction protein expressions and modulation via TMAO were assessed. Serum from chronic kidney disease (CKD) female and male haemodialysis (HD) patients, and controls, were used to measure BDNF and NSE by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays, and TMAO by mass spectrometry. Immunofluorescent staining of subcutaneous fat biopsies from kidney transplant recipients, and controls, were used to measure microvascular expression of tight-junction proteins (claudin-5, occludin, JAM-1), and control microvasculature for TMAO effects. HD patients versus controls, had significantly lower and higher serum levels of BDNF and NSE, respectively. In CKD biopsies versus controls, reduced expression of claudin-5, occludin, and JAM-1 were observed. Incubation with TMAO significantly decreased expression of all tight-junction proteins in the microvasculature. Uraemia affects BBB and GBB resulting in altered levels of circulating NSE, BDNF and TMAO, respectively, and it also reduces expression of tight-junction proteins that confer BBB maintenance. TMAO serves as a potential candidate to alter BBB integrity in CKD.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
PS serves on Scientific Advisory Boards of Baxter, AstraZeneca and REATA. All other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Disintegration of colonic epithelial tight junction in uremia: a likely cause of CKD-associated inflammation.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012 Jul;27(7):2686-93. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfr624. Epub 2011 Nov 29. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012. PMID: 22131233 Free PMC article.
-
miR-27a-3p regulates expression of intercellular junctions at the brain endothelium and controls the endothelial barrier permeability.PLoS One. 2022 Jan 13;17(1):e0262152. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0262152. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35025943 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of VEGF- and tight junction-related proteins in the neocortical microvasculature of patients with drug-resistant temporal lobe epilepsy.Microvasc Res. 2020 Nov;132:104059. doi: 10.1016/j.mvr.2020.104059. Epub 2020 Aug 13. Microvasc Res. 2020. PMID: 32798551
-
Blood-brain barrier dysfunction in ischemic stroke: _targeting tight junctions and transporters for vascular protection.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2018 Sep 1;315(3):C343-C356. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00095.2018. Epub 2018 Jun 27. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29949404 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Basic Requirement of Tight Junction Proteins in Blood-Brain Barrier Function and Their Role in Pathologies.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 21;25(11):5601. doi: 10.3390/ijms25115601. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38891789 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Levels of Cell-Free DNA in Kidney Failure Patients before and after Renal Transplantation.Cells. 2023 Dec 6;12(24):2774. doi: 10.3390/cells12242774. Cells. 2023. PMID: 38132094 Free PMC article.
-
Increased IgA-mediated responses to the gut paracellular pathway and blood-brain barrier proteins predict delirium due to hip fracture in older adults.Front Neurol. 2024 Feb 6;15:1294689. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1294689. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38379706 Free PMC article.
-
Sweet, bloody consumption - what we eat and how it affects vascular ageing, the BBB and kidney health in CKD.Gut Microbes. 2024 Jan-Dec;16(1):2341449. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2024.2341449. Epub 2024 Apr 30. Gut Microbes. 2024. PMID: 38686499 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drugs with a negative impact on cognitive function (Part 1): chronic kidney disease as a risk factor.Clin Kidney J. 2023 Sep 18;16(12):2365-2377. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfad241. eCollection 2023 Dec. Clin Kidney J. 2023. PMID: 38045996 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasma Aβ42:Aβ40 ratio as a biomarker for cognitive impairment in haemodialysis patients: a multicentre study.Clin Kidney J. 2023 Jul 19;16(11):2129-2140. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfad173. eCollection 2023 Nov. Clin Kidney J. 2023. PMID: 37915896 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

