Optimized Isolation and Characterization of C57BL/6 Mouse Hepatic Stellate Cells
- PMID: 35563686
- PMCID: PMC9102395
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11091379
Optimized Isolation and Characterization of C57BL/6 Mouse Hepatic Stellate Cells
Abstract
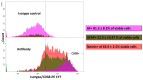
To obtain meaningful results of hepatic stellate cell (HSC) function, it is crucial to use highly pure HSC populations. Our aim was to optimize HSC isolation from mice livers without exploiting the characteristically transient vitamin A autofluorescence of HSC. HSCs were isolated from C57BL/6 mice using a two-step collagenase digestion and Nycodenz gradient separation followed by CD11b-negative sorting step in order to remove contaminating macrophages and dendritic cells. Isolated cells were analyzed for yield, viability, purity, and potential new markers using immunofluorescence and flow cytometry. We obtained a yield of 350,595 ± 100,773 HSC per mouse liver and a viability of isolated cells of 92.4 ± 3.1%. We observed a low macrophage/dendritic cell contamination of 1.22 ± 0.54%. Using flow cytometry, we demonstrated that CD38 was expressed at the surface of HSC subpopulations and that all expressed intracellular markers specific for HSC in the liver. This isolation method, avoiding fluorescent activated cell sorting (FACS), allowed isolation of HSCs with high purity. Further, flow cytometry analysis suggests that CD38 may be a reliable marker of HSCs and may include subpopulations of HSCs without retinoid droplets.
Keywords: CD11b; CD38; MACS; autofluorescence; hepatic stellate cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Isolation and time lapse microscopy of highly pure hepatic stellate cells.Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2015;2015:417023. doi: 10.1155/2015/417023. Epub 2015 Jul 16. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2015. PMID: 26258009 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct populations of hepatic stellate cells in the mouse liver have different capacities for retinoid and lipid storage.PLoS One. 2011;6(9):e24993. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024993. Epub 2011 Sep 16. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21949825 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and Culture of Primary Murine Hepatic Stellate Cells.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1627:165-191. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7113-8_11. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28836201
-
Human hepatic stellate cell isolation and characterization.J Gastroenterol. 2018 Jan;53(1):6-17. doi: 10.1007/s00535-017-1404-4. Epub 2017 Nov 1. J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 29094206 Review.
-
Hepatic stellate cell lipid droplets: a specialized lipid droplet for retinoid storage.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009 Jun;1791(6):467-73. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2008.11.001. Epub 2008 Nov 24. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009. PMID: 19071229 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Retinoids stored locally in the lung are required to attenuate the severity of acute lung injury in male mice.Nat Commun. 2023 Feb 15;14(1):851. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-36475-3. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 36792627 Free PMC article.
-
IRF3 activates RB to authorize cGAS-STING-induced senescence and mitigate liver fibrosis.Sci Adv. 2024 Mar;10(9):eadj2102. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adj2102. Epub 2024 Feb 28. Sci Adv. 2024. PMID: 38416816 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

