Sphingolipids and Lymphomas: A Double-Edged Sword
- PMID: 35565181
- PMCID: PMC9104519
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14092051
Sphingolipids and Lymphomas: A Double-Edged Sword
Abstract
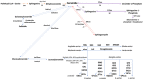
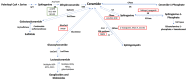
Lymphomas are a highly heterogeneous group of hematological neoplasms. Given their ethiopathogenic complexity, their classification and management can become difficult tasks; therefore, new approaches are continuously being sought. Metabolic reprogramming at the lipid level is a hot topic in cancer research, and sphingolipidomics has gained particular focus in this area due to the bioactive nature of molecules such as sphingoid bases, sphingosine-1-phosphate, ceramides, sphingomyelin, cerebrosides, globosides, and gangliosides. Sphingolipid metabolism has become especially exciting because they are involved in virtually every cellular process through an extremely intricate metabolic web; in fact, no two sphingolipids share the same fate. Unsurprisingly, a disruption at this level is a recurrent mechanism in lymphomagenesis, dissemination, and chemoresistance, which means potential biomarkers and therapeutical _targets might be hiding within these pathways. Many comprehensive reviews describing their role in cancer exist, but because most research has been conducted in solid malignancies, evidence in lymphomagenesis is somewhat limited. In this review, we summarize key aspects of sphingolipid biochemistry and discuss their known impact in cancer biology, with a particular focus on lymphomas and possible therapeutical strategies against them.
Keywords: cancer; lipid metabolism; lipidomics; lymphoma; sphingolipids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
An overview of sphingolipid metabolism: from synthesis to breakdown.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010;688:1-23. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-6741-1_1. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010. PMID: 20919643 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic applications of bioactive sphingolipids in hematological malignancies.Int J Cancer. 2010 Oct 1;127(7):1497-506. doi: 10.1002/ijc.25478. Int J Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20503271 Review.
-
Sphingolipid Metabolism in Tumor Cells.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2023 Jul;88(7):847-866. doi: 10.1134/S0006297923070015. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2023. PMID: 37751859 Review.
-
A Comprehensive Review: Sphingolipid Metabolism and Implications of Disruption in Sphingolipid Homeostasis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 28;22(11):5793. doi: 10.3390/ijms22115793. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34071409 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of sphingomyelin, glucosylceramide, ceramide, sphingosine, and sphingosine 1-phosphate by tandem mass spectrometry.Methods Enzymol. 2000;312:32-45. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(00)12898-8. Methods Enzymol. 2000. PMID: 11070861
Cited by
-
The role of ceranib-2 and its nanoform on the decrease of telomerase levels in human non-small cell cancer.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Aug 6;51(1):889. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-09838-2. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39105852
-
Metabolic Biomarkers Affecting Cell Proliferation and Prognosis in Polycythemia Vera.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Oct 7;14(19):4913. doi: 10.3390/cancers14194913. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36230834 Free PMC article.
-
Leveraging altered lipid metabolism in treating B cell malignancies.Prog Lipid Res. 2024 Jul;95:101288. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2024.101288. Epub 2024 Jul 2. Prog Lipid Res. 2024. PMID: 38964473 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

