Transcriptional regulation of cyclophilin D by BMP/Smad signaling and its role in osteogenic differentiation
- PMID: 35635445
- PMCID: PMC9191891
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.75023
Transcriptional regulation of cyclophilin D by BMP/Smad signaling and its role in osteogenic differentiation
Abstract
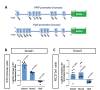
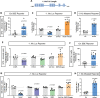
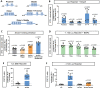
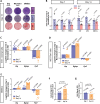
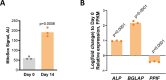
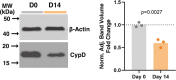
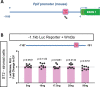
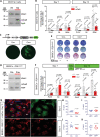
Cyclophilin D (CypD) promotes opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (MPTP) which plays a key role in both cell physiology and pathology. It is, therefore, beneficial for cells to tightly regulate CypD and MPTP but little is known about such regulation. We have reported before that CypD is downregulated and MPTP deactivated during differentiation in various tissues. Herein, we identify BMP/Smad signaling, a major driver of differentiation, as a transcriptional regulator of the CypD gene, Ppif. Using osteogenic induction of mesenchymal lineage cells as a BMP/Smad activation-dependent differentiation model, we show that CypD is in fact transcriptionally repressed during this process. The importance of such CypD downregulation is evidenced by the negative effect of CypD 'rescue' via gain-of-function on osteogenesis both in vitro and in a mouse model. In sum, we characterized BMP/Smad signaling as a regulator of CypD expression and elucidated the role of CypD downregulation during cell differentiation.
Keywords: BMP/Smad; bone; cyclophilin D; human; mitochondria; mouse; osteoprogenitor; permeability transition; regenerative medicine; stem cells.
© 2022, Sautchuk et al.
Conflict of interest statement
RS, BK, KE, JJ, GP, HA, RE No competing interests declared
Figures


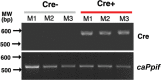
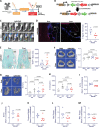
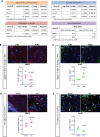
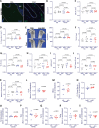

Similar articles
-
Cyclophilin D, regulator of the mitochondrial permeability transition, impacts bone development and fracture repair.Bone. 2024 Dec;189:117258. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2024.117258. Epub 2024 Sep 18. Bone. 2024. PMID: 39299628
-
Phosphorylation of cyclophilin D at serine 191 regulates mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening and cell death after ischemia-reperfusion.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Aug 19;11(8):661. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-02864-5. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 32814770 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial permeability transition regulator, cyclophilin D, is transcriptionally activated by C/EBP during adipogenesis.J Biol Chem. 2023 Dec;299(12):105458. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105458. Epub 2023 Nov 8. J Biol Chem. 2023. PMID: 37949231 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclophilin D-mediated Mitochondrial Permeability Transition Regulates Mitochondrial Function.Curr Pharm Des. 2023;29(8):620-629. doi: 10.2174/1381612829666230313111314. Curr Pharm Des. 2023. PMID: 36915987 Review.
-
Small-molecule inhibitors of cyclophilin D as potential therapeutics in mitochondria-related diseases.Med Res Rev. 2022 Sep;42(5):1822-1855. doi: 10.1002/med.21892. Epub 2022 May 16. Med Res Rev. 2022. PMID: 35575048 Review.
Cited by
-
Activated CYPD in COPD: Filling in the Puzzle of how Perturbed Epithelial Respiration Leads to Disturbed Respiratory Function.Lung. 2023 Jun;201(3):251-252. doi: 10.1007/s00408-023-00623-9. Epub 2023 Jun 1. Lung. 2023. PMID: 37261530 No abstract available.
-
Role of the Mitochondrial Permeability Transition in Bone Metabolism and Aging.J Bone Miner Res. 2023 Apr;38(4):522-540. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.4787. Epub 2023 Mar 9. J Bone Miner Res. 2023. PMID: 36779737 Free PMC article.
-
Furanoditerpenes from Spongia (Spongia) tubulifera Display Mitochondrial-Mediated Neuroprotective Effects by _targeting Cyclophilin D.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2022 Aug 17;13(16):2449-2463. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.2c00208. Epub 2022 Jul 28. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35901231 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Mitochondrial Permeability Transition in Bone Metabolism, Bone Healing, and Bone Diseases.Biomolecules. 2024 Oct 17;14(10):1318. doi: 10.3390/biom14101318. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39456250 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Blocking Mitochondrial Pyruvate Transport Alters Corneal Myofibroblast Phenotype: A New _target for Treating Fibrosis.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2023 Oct 3;64(13):36. doi: 10.1167/iovs.64.13.36. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2023. PMID: 37870848 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alavian KN, Beutner G, Lazrove E, Sacchetti S, Park HA, Licznerski P, Li H, Nabili P, Hockensmith K, Graham M, Porter GA, Jonas EA. An uncoupling channel within the c-subunit ring of the F1FO ATP synthase is the mitochondrial permeability transition pore. PNAS. 2014;111:10580–10585. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1401591111. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ambrosi TH, Marecic O, McArdle A, Sinha R, Gulati GS, Tong X, Wang Y, Steininger HM, Hoover MY, Koepke LS, Murphy MP, Sokol J, Seo EY, Tevlin R, Lopez M, Brewer RE, Mascharak S, Lu L, Ajanaku O, Conley SD, Seita J, Morri M, Neff NF, Sahoo D, Yang F, Weissman IL, Longaker MT, Chan CKF. Aged skeletal stem cells generate an inflammatory degenerative niche. Nature. 2021;597:256–262. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03795-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

