Metabolomic Analysis of Lactobacillus acidophilus, L. gasseri, L. crispatus, and Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus Strains in the Presence of Pomegranate Extract
- PMID: 35663851
- PMCID: PMC9160967
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.863228
Metabolomic Analysis of Lactobacillus acidophilus, L. gasseri, L. crispatus, and Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus Strains in the Presence of Pomegranate Extract
Abstract
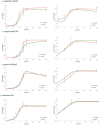
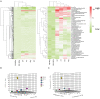
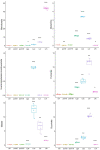
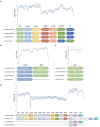
Lactobacillus species are prominent inhabitants of the human gastrointestinal tract that contribute to maintaining a balanced microbial environment that positively influences host health. These bacterial populations can be altered through use of probiotic supplements or via dietary changes which in turn affect the host health. Utilizing polyphenolic compounds to selectively stimulate the growth of commensal bacteria can have a positive effect on the host through the production of numerous metabolites that are biologically active. Four Lactobacillus strains were grown in the presence of pomegranate (POM) extract. Two strains, namely, L. acidophilus NCFM and L. rhamnosus GG, are commonly used probiotics, while the other two strains, namely, L. crispatus NCK1351 and L. gasseri NCK1342, exhibit probiotic potential. To compare and contrast the impact of POM on the strains' metabolic capacity, we investigated the growth of the strains with and without the presence of POM and identified their carbohydrate utilization and enzyme activity profiles. To further investigate the differences between strains, an un_targeted metabolomic approach was utilized to quantitatively and qualitatively define the metabolite profiles of these strains. Several metabolites were produced significantly and/or exclusively in some of the strains, including mevalonate, glutamine, 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide, phenyllactate, and fumarate. The production of numerous discrete compounds illustrates the unique characteristics of and diversity between strains. Unraveling these differences is essential to understand the probiotic function and help inform strain selection for commercial product formulation.
Keywords: Lactobacillus; metabolomics; pomegranate extract; prebiotic; probiotic.
Copyright © 2022 Chamberlain, O'Flaherty, Cobián and Barrangou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Impact of Pomegranate on Probiotic Growth, Viability, Transcriptome and Metabolism.Microorganisms. 2023 Feb 5;11(2):404. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11020404. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 36838369 Free PMC article.
-
An Un_targeted Metabolomic Analysis of Lacticaseibacillus (L.) rhamnosus, Lactobacillus (L.) acidophilus, Lactiplantibacillus (L.) plantarum and Limosilactobacillus (L.) reuteri Reveals an Upregulated Production of Inosine from L. rhamnosus.Microorganisms. 2024 Mar 26;12(4):662. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12040662. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38674606 Free PMC article.
-
In Vivo Transcriptome of Lactobacillus acidophilus and Colonization Impact on Murine Host Intestinal Gene Expression.mBio. 2021 Jan 26;12(1):e03399-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.03399-20. mBio. 2021. PMID: 33500337 Free PMC article.
-
Invited review: the scientific basis of Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM functionality as a probiotic.J Dairy Sci. 2001 Feb;84(2):319-31. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(01)74481-5. J Dairy Sci. 2001. PMID: 11233016 Review.
-
Anti-infective activities of lactobacillus strains in the human intestinal microbiota: from probiotics to gastrointestinal anti-infectious biotherapeutic agents.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2014 Apr;27(2):167-99. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00080-13. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2014. PMID: 24696432 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Antimicrobial Properties of Bacillus Probiotics as Animal Growth Promoters.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Feb 17;12(2):407. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12020407. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36830317 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolites Potentially Determine the High Antioxidant Properties of Limosilactobacillus fermentum U-21.BioTech (Basel). 2023 May 17;12(2):39. doi: 10.3390/biotech12020039. BioTech (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37218756 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Pomegranate on Probiotic Growth, Viability, Transcriptome and Metabolism.Microorganisms. 2023 Feb 5;11(2):404. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11020404. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 36838369 Free PMC article.
-
The use of omics technologies in creating LBP and postbiotics based on the Limosilactobacillus fermentum U-21.Front Microbiol. 2024 Jun 11;15:1416688. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1416688. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38919499 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative Analysis of Probiotic-Mediated Remodeling in Canine Gut Microbiota and Metabolites Using a Fermenter for an Intestinal Microbiota Model.Food Sci Anim Resour. 2024 Sep;44(5):1080-1095. doi: 10.5851/kosfa.2024.e41. Epub 2024 Sep 1. Food Sci Anim Resour. 2024. PMID: 39246539 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

