Effects of 4-hexylresorcinol administration on the submandibular glands in a growing rat model
- PMID: 35668488
- PMCID: PMC9172157
- DOI: 10.1186/s13005-022-00320-7
Effects of 4-hexylresorcinol administration on the submandibular glands in a growing rat model
Abstract
Background: 4-Hexylresorcinol (4HR) is a food additive and class I histone deacetylase inhibitor. In this study, we examined the effects of 4HR administration on the submandibular gland in a growing rat model.
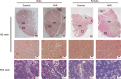
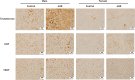
Methods: Four-week-old rats were used in this study. The experimental group (nine males and eight females) received 12.8 mg/kg of 4HR weekly for 12 weeks. Ten rats (five males and five females) were used as controls. The submandibular glands of rats were collected 12 weeks after the first administration of 4HR. The weight of the glands was measured. Histological analysis, immunoprecipitation-high-performance liquid chromatography (IP-HPLC), and western blotting were performed.
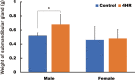
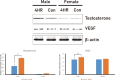
Results: The weights of the rat submandibular glands were higher in the experimental groups than in the control group, especially in male rats (P < 0.05). The vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and testosterone in the submandibular glands were more highly expressed in 4HR-treated male rats than in untreated rats, as detected by both western blotting and immunohistochemistry. The IP-HPLC results demonstrated that the expression levels of Ki67, epidermal growth factor, and testosterone in the submandibular glands were higher in 4HR-treated male rats than in untreated rats.
Conclusions: This study demonstrated that the systemic administration of 4HR increased the weight of submandibular glands in male rats. In addition, the testosterone and VEGF expression levels in the submandibular glands increased owing to 4HR administration.
Keywords: 4-hexylresorcinol; Angiogenesis; Salivary gland; Testosterone.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of 4-Hexylresorcinol on Craniofacial Growth in Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 19;22(16):8935. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168935. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445640 Free PMC article.
-
Topical delivery of 4-hexylresorcinol promotes wound healing via tumor necrosis factor-α suppression.Burns. 2016 Nov;42(7):1534-1541. doi: 10.1016/j.burns.2016.04.016. Epub 2016 May 16. Burns. 2016. PMID: 27198070
-
4-Hexylresorcinol and silk sericin increase the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor via different pathways.Sci Rep. 2019 Mar 5;9(1):3448. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-40027-5. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30837602 Free PMC article.
-
4-Hexylresorcinol: pharmacologic chaperone and its application for wound healing.Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg. 2022 Feb 1;44(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s40902-022-00334-w. Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg. 2022. PMID: 35103875 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toxicology and carcinogenesis studies of androstenedione (CAS No. 63-05-8) in F344/N rats and B6C3F1 mice (gavage studies).Natl Toxicol Program Tech Rep Ser. 2010 Sep;(560):1, 7-31,33-171 passim. Natl Toxicol Program Tech Rep Ser. 2010. PMID: 21037592 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Histone Deacetylases in the Pathogenesis of Salivary Gland Tumors and Therapeutic _targeting Options.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 12;24(12):10038. doi: 10.3390/ijms241210038. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37373187 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kim J-Y, Kweon H-Y, Kim D-W, Choi J-Y, Kim S-G. 4-Hexylresorcinol Inhibits Class I Histone Deacetylases in Human Umbilical Cord Endothelial Cells. Appl. Sci. 2021;11(8):3486. doi: 10.3390/app11083486. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

