SARS-CoV-2 infection and lytic reactivation of herpesviruses: A potential threat in the postpandemic era?
- PMID: 35819034
- PMCID: PMC9350099
- DOI: 10.1002/jmv.27994
SARS-CoV-2 infection and lytic reactivation of herpesviruses: A potential threat in the postpandemic era?
Abstract
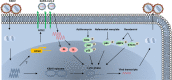
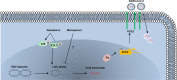
The outbreak of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), which is the causative pathogen for the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, has greatly stressed our healthcare system. In addition to severe respiratory and systematic symptoms, several comorbidities increase the risk of fatal disease outcomes, including chronic viral infections. Increasing cases of lytic reactivation of human herpesviruses in COVID-19 patients and vaccinated people have been reported recently. SARS-CoV2 coinfection, COVID-19 treatments, and vaccination may aggravate those herpesvirus-associated diseases by reactivating the viruses in latently infected host cells. In this review, we summarize recent clinical findings and limited mechanistic studies regarding the relationship between SARS-CoV-2 and different human herpesviruses that suggest an ongoing potential threat to human health in the postpandemic era.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; herpesvirus; lytic; pandemic.
© 2022 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Shedding Light on the Effect of Natural Anti-Herpesvirus Alkaloids on SARS-CoV-2: A Treatment Option for COVID-19.Viruses. 2020 Apr 23;12(4):476. doi: 10.3390/v12040476. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32340120 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 infection and vaccines: potential triggers of Herpesviridae reactivation.An Bras Dermatol. 2023 May-Jun;98(3):347-354. doi: 10.1016/j.abd.2022.09.004. Epub 2023 Feb 10. An Bras Dermatol. 2023. PMID: 36803914 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2 proteins and anti-COVID-19 drugs induce lytic reactivation of an oncogenic virus.Commun Biol. 2021 Jun 3;4(1):682. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-02220-z. Commun Biol. 2021. PMID: 34083759 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19: a conundrum to decipher.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020 May;24(10):5830-5841. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202005_21378. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32495923
-
Nervous system involvement in SARS-coronavirus infection: a review on lessons learned from the previous outbreaks, ongoing pandemic and what to expect in the future.Int J Neurosci. 2022 Sep;132(9):930-938. doi: 10.1080/00207454.2020.1853724. Epub 2021 Feb 3. Int J Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 33208006 Review.
Cited by
-
Human herpesvirus reactivation and its potential role in the pathogenesis of post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection.Geroscience. 2024 Aug 29. doi: 10.1007/s11357-024-01323-9. Online ahead of print. Geroscience. 2024. PMID: 39207648
-
Viral DNAemia and DNA Virus Seropositivity and Mortality in Pediatric Sepsis.JAMA Netw Open. 2024 Feb 5;7(2):e240383. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.0383. JAMA Netw Open. 2024. PMID: 38407904 Free PMC article.
-
A Machine Learning Approach to Identify Potential miRNA-Gene Regulatory Network Contributing to the Pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 Infection.Biochem Genet. 2024 Apr;62(2):987-1006. doi: 10.1007/s10528-023-10458-x. Epub 2023 Jul 29. Biochem Genet. 2024. PMID: 37515735
-
The reactivation of herpesviruses in severe COVID-19; a retrospective analysis of a critical care cohort.Clin Infect Pract. 2023 Jul;19:100232. doi: 10.1016/j.clinpr.2023.100232. Epub 2023 May 23. Clin Infect Pract. 2023. PMID: 37251495 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Immunohematologic Biomarkers in COVID-19: Insights into Pathogenesis, Prognosis, and Prevention.Pathog Immun. 2023 Jun 26;8(1):17-50. doi: 10.20411/pai.v8i1.572. eCollection 2023. Pathog Immun. 2023. PMID: 37427016 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Whitley RJ. Herpesviruses. In: Baron S, ed. Medical Microbiology. 4th ed. University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston; 1996. - PubMed
-
- Payne S. Chapter 34—family Herpesviridae. In: Payne S, ed. Viruses. Academic Press; 2017:269‐278.
-
- Virgin HW, Wherry EJ, Ahmed R. Redefining chronic viral infection. Cell. 2009;138(1):30‐50. - PubMed
-
- Lukac DM, Renne R, Kirshner JR, Ganem D. Reactivation of Kaposi's sarcoma‐associated herpesvirus infection from latency by expression of the ORF 50 transactivator, a homolog of the EBV R protein. Virology. 1998;252(2):304‐312. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

