The role of enkephalinergic systems in substance use disorders
- PMID: 35993087
- PMCID: PMC9391026
- DOI: 10.3389/fnsys.2022.932546
The role of enkephalinergic systems in substance use disorders
Abstract
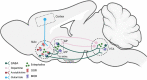
Enkephalin, an endogenous opioid peptide, is highly expressed in the reward pathway and may modulate neurotransmission to regulate reward-related behaviors, such as drug-taking and drug-seeking behaviors. Drugs of abuse also directly increase enkephalin in this pathway, yet it is unknown whether or not changes in the enkephalinergic system after drug administration mediate any specific behaviors. The use of animal models of substance use disorders (SUDs) concurrently with pharmacological, genetic, and molecular tools has allowed researchers to directly investigate the role of enkephalin in promoting these behaviors. In this review, we explore neurochemical mechanisms by which enkephalin levels and enkephalin-mediated signaling are altered by drug administration and interrogate the contribution of enkephalin systems to SUDs. Studies manipulating the receptors that enkephalin _targets (e.g., mu and delta opioid receptors mainly) implicate the endogenous opioid peptide in drug-induced neuroadaptations and reward-related behaviors; however, further studies will need to confirm the role of enkephalin directly. Overall, these findings suggest that the enkephalinergic system is involved in multiple aspects of SUDs, such as the primary reinforcing properties of drugs, conditioned reinforcing effects, and sensitization. The idea of dopaminergic-opioidergic interactions in these behaviors remains relatively novel and warrants further research. Continuing work to elucidate the role of enkephalin in mediating neurotransmission in reward circuitry driving behaviors related to SUDs remains crucial.
Keywords: circuitry; enkephalin; opioid; reward; substance use disorder.
Copyright © 2022 Rysztak and Jutkiewicz.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Delta Opioid Receptors and Enkephalinergic Signaling within Locus Coeruleus Promote Stress Resilience.Brain Sci. 2022 Jun 29;12(7):860. doi: 10.3390/brainsci12070860. Brain Sci. 2022. PMID: 35884666 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal ethanol exposure and enkephalinergic neurotransmission.Vitam Horm. 2019;111:313-337. doi: 10.1016/bs.vh.2019.05.005. Epub 2019 Jun 10. Vitam Horm. 2019. PMID: 31421706
-
Localization of brain reinforcement mechanisms: intracranial self-administration and intracranial place-conditioning studies.Behav Brain Res. 1999 Jun;101(2):129-52. doi: 10.1016/s0166-4328(99)00022-4. Behav Brain Res. 1999. PMID: 10372570 Review.
-
A microdialysis profile of Met-enkephalin release in the rat nucleus accumbens following alcohol administration.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2005 Oct;29(10):1821-8. doi: 10.1097/01.alc.0000183008.62955.2e. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2005. PMID: 16269911
-
15 years of genetic approaches in vivo for addiction research: Opioid receptor and peptide gene knockout in mouse models of drug abuse.Neuropharmacology. 2014 Jan;76 Pt B(0 0):204-17. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.08.028. Epub 2013 Sep 10. Neuropharmacology. 2014. PMID: 24035914 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
NPAS4 supports cocaine-conditioned cues in rodents by controlling the cell type-specific activation balance in the nucleus accumbens.Nat Commun. 2024 Aug 8;15(1):5971. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-50099-1. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39117647 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Kynu, Defb2, Camp, and Penk Expression Levels as Psoriasis Marker in the Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis Model.Mediators Inflamm. 2024 Jul 16;2024:5821996. doi: 10.1155/2024/5821996. eCollection 2024. Mediators Inflamm. 2024. PMID: 39045230 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of endogenous opioid signaling by inhibitors of puromycin-sensitive aminopeptidase.Eur J Med Chem. 2024 Sep 5;275:116604. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2024.116604. Epub 2024 Jun 17. Eur J Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38917665
-
Lateral hypothalamic proenkephalin neurons drive threat-induced overeating associated with a negative emotional state.Nat Commun. 2023 Oct 28;14(1):6875. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-42623-6. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37898655 Free PMC article.
-
A Complex Relationship Among the Circadian Rhythm, Reward Circuit and Substance Use Disorder (SUD).Psychol Res Behav Manag. 2024 Oct 9;17:3485-3501. doi: 10.2147/PRBM.S473310. eCollection 2024. Psychol Res Behav Manag. 2024. PMID: 39411118 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

