Early Life Pain Experience Changes Adult Functional Pain Connectivity in the Rat Somatosensory and the Medial Prefrontal Cortex
- PMID: 36192150
- PMCID: PMC9653276
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0416-22.2022
Early Life Pain Experience Changes Adult Functional Pain Connectivity in the Rat Somatosensory and the Medial Prefrontal Cortex
Abstract
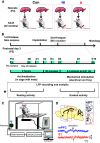
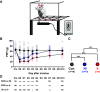
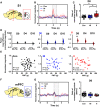
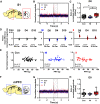
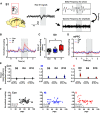
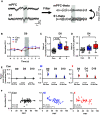
Early life pain (ELP) experience alters adult pain behavior and increases injury-induced pain hypersensitivity, but the effect of ELP on adult functional brain connectivity is not known. We have performed continuous local field potential (LFP) recording in the awake adult male rats to test the effect of ELP on functional cortical connectivity related to pain behavior. Primary somatosensory cortex (S1) and medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) LFPs evoked by mechanical hindpaw stimulation were recorded simultaneously with pain reflex behavior for 10 d after adult incision injury. We show that, after adult injury, sensory evoked S1 LFP δ and γ energy and S1 LFP δ/γ frequency coupling are significantly increased in ELP rats compared with controls. Adult injury also induces increases in S1-mPFC functional connectivity, but this is significantly prolonged in ELP rats, lasting 4 d compared with 1 d in controls. Importantly, the increases in LFP energy and connectivity in ELP rats were directly correlated with increased behavioral pain hypersensitivity. Thus, ELP alters adult brain functional connectivity, both within and between cortical areas involved in sensory and affective dimensions of pain. The results reveal altered brain connectivity as a mechanism underlying the effects of ELP on adult pain perception.SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT Pain and stress in early life has a lasting impact on pain behavior and may increase vulnerability to chronic pain in adults. Here, we record pain-related cortical activity and simultaneous pain behavior in awake adult male rats previously exposed to pain in early life. We show that functional connectivity within and between the somatosensory cortex and the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) is increased in these rats and that these increases are correlated with their behavioral pain hypersensitivity. The results reveal that early life pain (ELP) alters adult brain connectivity, which may explain the impact of childhood pain on adult chronic pain vulnerability.
Keywords: brain; cortex; early life; neonatal; pain; γ oscillation.
Copyright © 2022 the authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Granger causality analysis of rat cortical functional connectivity in pain.J Neural Eng. 2020 Feb 7;17(1):016050. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/ab6cba. J Neural Eng. 2020. PMID: 31945754 Free PMC article.
-
The somatosensory link in fibromyalgia: functional connectivity of the primary somatosensory cortex is altered by sustained pain and is associated with clinical/autonomic dysfunction.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015 May;67(5):1395-1405. doi: 10.1002/art.39043. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015. PMID: 25622796 Free PMC article.
-
Cortical Pain Processing in the Rat Anterior Cingulate Cortex and Primary Somatosensory Cortex.Front Cell Neurosci. 2019 Apr 24;13:165. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00165. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31105532 Free PMC article.
-
Multielectrode Recordings in the Somatosensory System.In: Nicolelis MAL, editor. Methods for Neural Ensemble Recordings. 2nd edition. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2008. Chapter 6. In: Nicolelis MAL, editor. Methods for Neural Ensemble Recordings. 2nd edition. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2008. Chapter 6. PMID: 21204443 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
The medial prefrontal cortex in the rat: evidence for a dorso-ventral distinction based upon functional and anatomical characteristics.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2003 Oct;27(6):555-79. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2003.09.003. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2003. PMID: 14599436 Review.
Cited by
-
Uncovering brain functional connectivity disruption patterns of lung cancer-related pain.Brain Imaging Behav. 2024 Jun;18(3):576-587. doi: 10.1007/s11682-023-00836-9. Epub 2024 Feb 6. Brain Imaging Behav. 2024. PMID: 38316730
-
Experience of early-life pain in premature infants is associated with atypical cerebellar development and later neurodevelopmental deficits.BMC Med. 2023 Nov 14;21(1):435. doi: 10.1186/s12916-023-03141-w. BMC Med. 2023. PMID: 37957651 Free PMC article.
-
Neonatal paw pricking alters adolescent behavior in a sex-dependent manner and sucrose partially remediates the effects.Physiol Behav. 2024 Dec 1;287:114695. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2024.114695. Epub 2024 Sep 15. Physiol Behav. 2024. PMID: 39288866
-
Complications of Preterm Birth-The Importance of Care for the Outcome: A Narrative Review.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Jun 20;60(6):1014. doi: 10.3390/medicina60061014. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 38929631 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic Alcohol Drinking Drives Sex-Specific Differences in Affective Behavior and Medial Prefrontal Cortex Activity in CRF1:Cre:tdTomato Transgenic Rats.eNeuro. 2023 Jul 13;10(7):ENEURO.0055-23.2023. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0055-23.2023. Print 2023 Jul. eNeuro. 2023. PMID: 37414553 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
