[Changes of YAP activity at the early stage of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and its spatiotemporal relationship with ductular reaction in mice]
- PMID: 36210705
- PMCID: PMC9550545
- DOI: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2022.09.08
[Changes of YAP activity at the early stage of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and its spatiotemporal relationship with ductular reaction in mice]
Abstract
Objective: To explore the changes in Yes-associated protein (YAP) activity at the early stage of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and the spatiotemporal relationship between YAP and ductular reaction (DR).
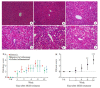
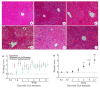
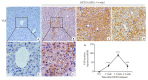
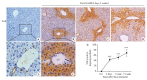
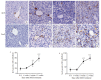
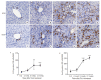
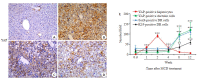
Methods: Male C57BL/6J mouse models of NASH were established by feeding with a methionine- and choline-deficient (MCD) diet or a thioacetamide (TAA) diet for 12 weeks. At different time points during the feeding, liver histology of the mice was observed with HE and Masson trichrome staining. The mRNA expressions of YAP and its _target genes (Ctgf, Cyr61, Acta2) were determined by qPCR, and the total protein expression level of YAP was measured with immunoblotting. The expression and distribution of YAP and the markers of DR (K19 and Sox9) were observed with immunohistochemical staining.
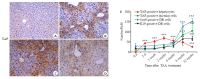
Results: At the early stage of NASH induced by MCD diet (1 to 4 weeks), the mRNA expression of YAP and its _target genes and the total protein expression of YAP increased significantly (P < 0.01). The number of YAP-positive hepatocytes reached the peak level of 90.8 (cells per ×400 field of view) at week 2 and then decreased to 30.8 at week 4 (P < 0.001); YAP-positive ductular cells appeared near the portal area, where DR began to occur. From 8 to 12 weeks, numerous K19/Sox9-positive DR cells were observed in the hepatic lobules around the central vein (P < 0.01), while only a few YAP-positive hepatocytes were present in the liver tissue (P > 0.05), and the number of YAP-positive ductular cells gradually increased with time (P < 0.001). At the early stage of NASH induced by TAA diet (3 days to 2 weeks), the mRNA expression of YAP and its _target genes and the total protein expression of YAP increased significantly (P < 0.05), and the number of YAP-positive hepatocytes reached the peak of 69.2 at week 2 and then decreased to 55.2 at week 4 (P < 0.001); YAP-positive ductular cells first appeared at the initial location of DR near the central vein. From 6 to 12 weeks, numerous K19/Sox9-positive DR cells occurred in the hepatic lobules around the central vein (P < 0.01). While the number of YAP-positive hepatocytes decreased (P < 0.001), the number of YAP-positive ductular cells continued to increase (P < 0.001).
Conclusion: During the development of NASH, YAP activation occurs earlier than DR but they are spatiotemporally correlated. YAP activation in hepatocytes may participate in DR by promoting hepatocyte dedifferentiation.
目的: 探究非酒精性脂肪性肝炎(NASH)早期Yes-相关蛋白(YAP)活性变化特点及其与胆管反应(DR)发生的时空关系。
方法: 通过蛋氨酸胆碱缺乏(MCD)饮食、硫代乙酰胺(TAA)饮食喂养雄性C57BL/6J小鼠12周,构建NASH小鼠模型。通过HE、Masson染色评估肝脏病理学改变,qPCR技术检测YAP及其靶基因(Ctgf、Cyr61、Acta2)的mRNA表达情况;免疫印记检测YAP的总蛋白表达水平;免疫组化检测YAP、DR标志(K19和Sox9)表达与分布情况。
结果: 在MCD饮食诱导的NASH疾病早期(1~4周),肝组织YAP及其靶基因Ctgf、Cyr6、Acta2的mRNA表达量和YAP总蛋白表达量均增加(P < 0.01)。YAP阳性肝细胞数量在第2周达到峰值90.8/×400视野后,第4周减少至30.8/×400视野(P < 0.001),并在汇管区附近(即DR发生初始位置)观察到YAP阳性胆管样细胞。8~12周时可在中央静脉周围肝小叶中观察到大量的K19/Sox9阳性DR细胞(P < 0.01),同时肝组织中仅有少量YAP阳性肝细胞(P > 0.05),且YAP阳性胆管样细胞数量逐渐增加(P < 0.001)。在TAA饮食诱导的NASH疾病早期(3 d~2周),肝组织YAP及其靶基因Ctgf、Cyr6、Acta2的mRNA表达量和YAP总蛋白表达量均增加(P < 0.05)。YAP阳性肝细胞数量在2周达到峰值69.2/×400视野;4周减少至55.2/×400视野(P < 0.001),并且在中央静脉附近(即DR发生初始位置)观察到YAP阳性胆管样细胞。6~12周时可在中央静脉周围肝小叶中观察到大量的K19/Sox9阳性DR细胞(P < 0.01),同时YAP阳性肝细胞数量持续减少(P < 0.001),YAP阳性胆管样细胞数量持续增加(P < 0.001)。
结论: NASH损伤肝脏组织中,YAP激活早于DR发生,YAP活性变化特点及其分布与DR发生分布具有时空相关关系,同时肝细胞内的YAP激活似乎可以诱导肝细胞转分化为胆管样细胞,参与DR发生。
Keywords: YAP; ductular reaction; nonalcoholic steatohepatitis; spatiotemporal relationship.
Figures
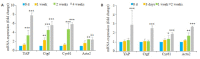

Similar articles
-
[Functional characteristics of YAP-positive hepatocytes expression in an early stage of NASH with transcriptome sequence analysis].Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2022 Jun 20;30(6):649-655. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20200702-00364. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 36038328 Chinese.
-
Comparison of murine steatohepatitis models identifies a dietary intervention with robust fibrosis, ductular reaction, and rapid progression to cirrhosis and cancer.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2020 Jan 1;318(1):G174-G188. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00041.2019. Epub 2019 Oct 21. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31630534 Free PMC article.
-
Notch signaling and progenitor/ductular reaction in steatohepatitis.PLoS One. 2017 Nov 15;12(11):e0187384. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0187384. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29140985 Free PMC article.
-
A Comparison of the Gene Expression Profiles of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease between Animal Models of a High-Fat Diet and Methionine-Choline-Deficient Diet.Molecules. 2022 Jan 27;27(3):858. doi: 10.3390/molecules27030858. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35164140 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ductular Reaction in Liver Diseases: Pathological Mechanisms and Translational Significances.Hepatology. 2019 Jan;69(1):420-430. doi: 10.1002/hep.30150. Epub 2018 Dec 27. Hepatology. 2019. PMID: 30070383 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
AICAR Ameliorates Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease via Modulation of the HGF/NF-κB/SNARK Signaling Pathway and Restores Mitochondrial and Endoplasmic Reticular Impairments in High-Fat Diet-Fed Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 8;24(4):3367. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043367. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36834782 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
