Dysfunctional purinergic signaling correlates with disease severity in COVID-19 patients
- PMID: 36248842
- PMCID: PMC9562777
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1012027
Dysfunctional purinergic signaling correlates with disease severity in COVID-19 patients
Abstract
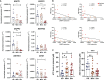
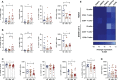
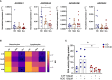
Ectonucleotidases modulate inflammatory responses by balancing extracellular ATP and adenosine (ADO) and might be involved in COVID-19 immunopathogenesis. Here, we explored the contribution of extracellular nucleotide metabolism to COVID-19 severity in mild and severe cases of the disease. We verified that the gene expression of ectonucleotidases is reduced in the whole blood of patients with COVID-19 and is negatively correlated to levels of CRP, an inflammatory marker of disease severity. In line with these findings, COVID-19 patients present higher ATP levels in plasma and reduced levels of ADO when compared to healthy controls. Cell type-specific analysis revealed higher frequencies of CD39+ T cells in severely ill patients, while CD4+ and CD8+ expressing CD73 are reduced in this same group. The frequency of B cells CD39+CD73+ is also decreased during acute COVID-19. Interestingly, B cells from COVID-19 patients showed a reduced capacity to hydrolyze ATP into ADP and ADO. Furthermore, impaired expression of ADO receptors and a compromised activation of its signaling pathway is observed in COVID-19 patients. The presence of ADO in vitro, however, suppressed inflammatory responses triggered in patients' cells. In summary, our findings support the idea that alterations in the metabolism of extracellular purines contribute to immune dysregulation during COVID-19, possibly favoring disease severity, and suggest that ADO may be a therapeutic approach for the disease.
Keywords: ATP; CD39; CD73; COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; adenosine; purinergic signaling.
Copyright © 2022 Pietrobon, Andrejew, Custódio, Oliveira, Scholl, Teixeira, de Brito, Glaser, Kazmierski, Goffinet, Turdo, Yendo, Aoki, Figueiró, Battastini, Ulrich, Benard, Duarte and Sato.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
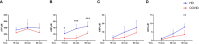
Similar articles
-
Elevated CD39+T-Regulatory Cells and Reduced Levels of Adenosine Indicate a Role for Tolerogenic Signals in the Progression from Moderate to Severe COVID-19.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 18;24(24):17614. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417614. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139439 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations in CD39/CD73 axis of T cells associated with COVID-19 severity.J Cell Physiol. 2022 Aug;237(8):3394-3407. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30805. Epub 2022 Jun 27. J Cell Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35754396 Free PMC article.
-
High levels of extracellular ATP lead to different inflammatory responses in COVID-19 patients according to the severity.J Mol Med (Berl). 2022 Apr;100(4):645-663. doi: 10.1007/s00109-022-02185-4. Epub 2022 Mar 6. J Mol Med (Berl). 2022. PMID: 35249135 Free PMC article.
-
ATP and Its Metabolite Adenosine as Regulators of Dendritic Cell Activity.Front Immunol. 2018 Nov 9;9:2581. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02581. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30473700 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Purinergic signaling in B cells.Acta Biochim Pol. 2018;65(1):1-7. doi: 10.18388/abp.2017_1588. Epub 2018 Jan 23. Acta Biochim Pol. 2018. PMID: 29360885 Review.
Cited by
-
Adenosine A2A receptor as a potential regulator of Mycobacterium leprae survival mechanisms: new insights into leprosy neural damage.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jun 28;15:1399363. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1399363. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39005937 Free PMC article.
-
Self-DNA driven inflammation in COVID-19 and after mRNA-based vaccination: lessons for non-COVID-19 pathologies.Front Immunol. 2024 Feb 19;14:1259879. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1259879. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38439942 Free PMC article.
-
A Prospective Study Investigating Immune Checkpoint Molecule and CD39 Expression on Peripheral Blood Cells for the Prognostication of COVID-19 Severity and Mortality.Viruses. 2024 May 20;16(5):810. doi: 10.3390/v16050810. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38793691 Free PMC article.
-
Adenosine A2AR in viral immune evasion and therapy: unveiling new avenues for treating COVID-19 and AIDS.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Aug 8;51(1):894. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-09839-1. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39115571 Review.
-
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis in Long-COVID Scenario and the Therapeutic Potential of the Purinergic System in Neuromodulation.Brain Sci. 2024 Feb 16;14(2):180. doi: 10.3390/brainsci14020180. Brain Sci. 2024. PMID: 38391754 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

