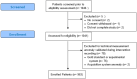
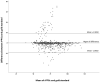
Accurate and Reliable Assessment of Heart Rate in Real-Life Clinical Settings Using an Imaging Photoplethysmography
- PMID: 36294422
- PMCID: PMC9604655
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11206101
Accurate and Reliable Assessment of Heart Rate in Real-Life Clinical Settings Using an Imaging Photoplethysmography
Abstract
Remote photoplethysmography imaging (rPPGc) is a new method measuring essential parameters, such as heart rate (HR), which uses a video camera during teleconsultation. Our work aimed to evaluate the accuracy of such remote measurements compared with existing contact point measurement methods in real-life clinical settings. The prospective hospital-based study recruited 1045 patients who required a pulmonary function test. For each patient, measurements of HR using a standard electrocardiogram acquisition system (gold standard) were carried out concomitantly with the measurements made by the rPPGc system (Caducy v1.0.0) taken within a 60 s timeframe. Age, gender, and skin phototype were collected. We performed an intraclass coefficient correlation (ICC) and Bland-Altman plotting to determine the accuracy and precision of the rPPGc algorithm readings. We achieved measurement of HR using the two methods in 963 patients. The ICC measured at a 60 s timeframe, and when we compared the rPPGc with the gold standard, it had a 95% confidence interval (CI95) value of 0.886 [0.871:0.899]. In all, 94.6% (n = 911) patients showed promising results with a CI95 in Bland-Altman plotting. Fifty-two measurements were discordant, and further analysis established the method's accuracy at 96.2%. Our results described a good accuracy and correlation between the rPPGc system and the gold standard, thus paving the way for more precise care via telemedicine.
Keywords: heart rate; remote photoplethysmography; vital signs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest regarding the content of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Remote Photoplethysmography Is an Accurate Method to Remotely Measure Respiratory Rate: A Hospital-Based Trial.J Clin Med. 2022 Jun 24;11(13):3647. doi: 10.3390/jcm11133647. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35806932 Free PMC article.
-
Innovative measurement of routine physiological variables (heart rate, respiratory rate and oxygen saturation) using a remote photoplethysmography imaging system: a prospective comparative trial protocol.BMJ Open. 2021 Aug 13;11(8):e047896. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-047896. BMJ Open. 2021. PMID: 34389569 Free PMC article.
-
A two-phased study on the use of remote photoplethysmography (rPPG) in paediatric care.Ann Transl Med. 2024 Jun 10;12(3):46. doi: 10.21037/atm-23-1896. Epub 2024 May 27. Ann Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38911566 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of consumer-grade contactless vital signs monitors: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Clin Monit Comput. 2022 Feb;36(1):41-54. doi: 10.1007/s10877-021-00734-9. Epub 2021 Jul 9. J Clin Monit Comput. 2022. PMID: 34240262 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Technology Assessment: Early Sense for Monitoring Vital Signs in Hospitalized Patients [Internet].Washington (DC): Department of Veterans Affairs (US); 2016 May. Washington (DC): Department of Veterans Affairs (US); 2016 May. PMID: 27606394 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Challenges and prospects of visual contactless physiological monitoring in clinical study.NPJ Digit Med. 2023 Dec 15;6(1):231. doi: 10.1038/s41746-023-00973-x. NPJ Digit Med. 2023. PMID: 38097771 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Remote Photoplethysmography and Motion Tracking Convolutional Neural Network with Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory: Non-Invasive Fatigue Detection Method Based on Multi-Modal Fusion.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Jan 11;24(2):0. doi: 10.3390/s24020455. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38257546 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Proceedings of the american physiological society. Am. J. Physiol.-Leg. Content. 1937;119:257–427. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1937.119.2.257. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources