Steroid receptor coactivator-3 inhibition generates breast cancer antitumor immune microenvironment
- PMID: 36316775
- PMCID: PMC9620627
- DOI: 10.1186/s13058-022-01568-2
Steroid receptor coactivator-3 inhibition generates breast cancer antitumor immune microenvironment
Abstract
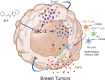
Background: The tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) generated by cancer-infiltrating immune cells has a crucial role in promoting or suppressing breast cancer progression. However, whether the steroid receptor coactivator-3 (SRC-3) modulates TIME to progress breast cancer is unclear. Therefore, the present study evaluates whether SRC-3 generates a tumor-promoting TIME in breast tumors using a syngeneic immune-intact mouse model of breast cancer.
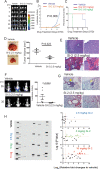
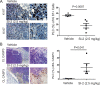
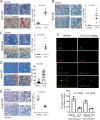
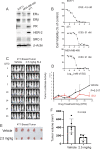
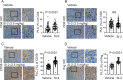
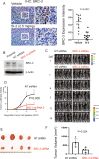
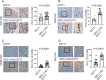
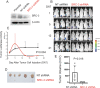
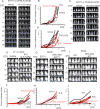
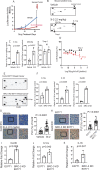
Methods: We employed E0771 and 4T1 breast cancer in immune-intact syngeneic female C57BL/6 and BALB/c mice, respectively. SI-2, a specific small-molecule inhibitor of SRC-3, was administered daily (2.5 mg/kg) to E0771 and 4T1 breast tumor-bearing immune-intact mice. In addition, SRC-3 knockdown (KD)-E0771 and SRC-3 KD-4T1 cells and their parental breast cancer cells were injected into their syngeneic immune-intact female mice versus immune-deficiency mice to validate that the host immune system is required for breast tumor suppression by SRC-3 KD in immune-intact mice. Furthermore, tumor-infiltrating immune cells (such as CD4+, CD8+, CD56+, and Foxp3+ cells) in E0771 and 4T1 breast cancers treated with SI-2 and in SRC-3 KD E0771 and 4T1 breast cancers were determined by immunohistochemistry. Additionally, cytokine levels in SI-2-treated and SRC-3 KD E0771 breast tumors and their control cancers were defined with a Mouse Cytokine Array.
Results: SRC-3 inhibition by SI-2 significantly suppressed the progression of breast cancer cells (E0771 and 4T1) into breast cancers in immune-intact syngeneic female mice. SRC-3 KD-E0771 and -4T1 breast cancer cells did not produce well-developed tumors in immune-intact syngeneic female mice compared to their parental cells, but SRC-3 KD breast cancers were well developed in immune-defective host mice. SRC-3 inhibition by SI-2 and SRC-3 KD effectively increased the numbers of cytotoxic immune cells, such as CD4+ and CD8+ T cells and CD56+ NK cells, and Interferon γ (Ifng) in breast cancers compared to vehicle. However, SI-2 treatment reduced the number of tumor-infiltrating CD4+/Foxp3+ regulatory T (Treg) cells compared to vehicle treatment. In addition, SRC-3 inhibition by SI-2 and SRC-3 KD increased C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 9 (Cxcl9) expression in breast cancer to recruit C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 3 (Cxcr3)-expressing cytotoxic immune cells into breast tumors.
Conclusions: SRC-3 is a critical immunomodulator in breast cancer, generating a protumor immune microenvironment. SRC-3 inhibition by SI-2 or SRC-3 KD activates the Cxcl9/Cxcr3 axis in breast tumors and enhances the antitumor immune microenvironment to suppress breast cancer progression.
Keywords: Antitumor immunity; Breast cancer; C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 9; E0771 cells; Interleukin 1 receptor antagonist; Steroid receptor coactivator inhibitor.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
BWO, DML, and JW are the co-founders of CoActigon Inc. JW is the co-founder of Chemical Biology Probes LLC.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Steroid receptor coactivator 3 is a key modulator of regulatory T cell-mediated tumor evasion.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Jun 6;120(23):e2221707120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2221707120. Epub 2023 May 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 37253006 Free PMC article.
-
Steroid Receptor Coactivator-3 is a Key Modulator of Regulatory T Cell-Mediated Tumor Evasion.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Mar 29:2023.03.28.534575. doi: 10.1101/2023.03.28.534575. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Jun 6;120(23):e2221707120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2221707120 PMID: 37034717 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Reduced infiltration of regulatory T cells in tumours from mice fed daily with gamma-tocotrienol supplementation.Clin Exp Immunol. 2021 Nov;206(2):161-172. doi: 10.1111/cei.13650. Epub 2021 Aug 18. Clin Exp Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34331768 Free PMC article.
-
SRC-3 has a role in cancer other than as a nuclear receptor coactivator.Int J Biol Sci. 2011;7(5):664-72. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.7.664. Epub 2011 May 24. Int J Biol Sci. 2011. PMID: 21647249 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of Immune Cell Heterogeneity on HER2+ Breast Cancer Prognosis and Response to Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Dec 17;13(24):6352. doi: 10.3390/cancers13246352. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34944971 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Critical Roles of SRC-3 in the Development and Progression of Breast Cancer, Rendering It a Prospective Clinical _target.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Oct 31;15(21):5242. doi: 10.3390/cancers15215242. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37958417 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Steroid receptor coactivators in Treg and Th17 cell biology and function.Front Immunol. 2024 Apr 18;15:1389041. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1389041. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38698860 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Steroid receptor coactivators - their role in immunity.Front Immunol. 2022 Dec 13;13:1079011. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1079011. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36582250 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Knockdown of SCN5A alters metabolic-associated genes and aggravates hypertrophy in the cardiomyoblast.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 May 17;51(1):661. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-09594-3. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38758505
-
Steroid receptor coactivator 3 is a key modulator of regulatory T cell-mediated tumor evasion.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Jun 6;120(23):e2221707120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2221707120. Epub 2023 May 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 37253006 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bautista S, Vallès H, Walker RL, Anzick S, Zeillinger R, Meltzer P, Theillet C. In breast cancer, amplification of the steroid receptor coactivator gene AIB1 is correlated with estrogen and progesterone receptor positivity. Clin Cancer Res. 1998;4(12):2925–2929. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

