Immunostimulatory Activity of Lactic Acid Bacteria Cell-Free Supernatants through the Activation of NF-κB and MAPK Signaling Pathways in RAW 264.7 Cells
- PMID: 36422317
- PMCID: PMC9698684
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms10112247
Immunostimulatory Activity of Lactic Acid Bacteria Cell-Free Supernatants through the Activation of NF-κB and MAPK Signaling Pathways in RAW 264.7 Cells
Abstract
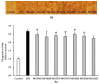
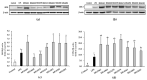
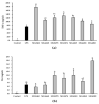
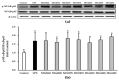
Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) can improve host health and has strong potential for use as a health functional food. Specific strains of LAB have been reported to exert immunostimulatory effects. The primary goal of this study was to evaluate the immunostimulatory activities of novel LAB strains isolated from humans and foods and to investigate the probiotic properties of these strains. Cell-free supernatants (CFS) obtained from selected LAB strains significantly increased phagocytosis and level of nitric oxide (NO) and pro-inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and interleukin (IL)-6 in RAW264.7 macrophage cells. The protein expression of inducible NO synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase (COX)-2, which are immunomodulators, was also upregulated by CFS treatment. CFS markedly induced the phosphorylation of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and MAPKs (ERK, JNK, and p38). In addition, the safety of the LAB strains used in this study was demonstrated by hemolysis and antibiotic resistance tests. Their stability was confirmed under simulated gastrointestinal conditions. Taken together, these results indicate that the LAB strains selected in this study could be useful as probiotic candidates with immune-stimulating activity.
Keywords: RAW264.7 macrophage cells; immune-stimulating activity; lactic acid bacteria; probiotics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Anti-inflammatory effect of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum T1 cell-free supernatants through suppression of oxidative stress and NF-κB- and MAPK-signaling pathways.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023 Oct 31;89(10):e0060823. doi: 10.1128/aem.00608-23. Epub 2023 Sep 13. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37702501 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic Glabridin Derivatives Inhibit LPS-Induced Inflammation via MAPKs and NF-κB Pathways in RAW264.7 Macrophages.Molecules. 2023 Feb 24;28(5):2135. doi: 10.3390/molecules28052135. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36903379 Free PMC article.
-
Design, synthesis fusidic acid derivatives alleviate acute lung injury via inhibiting MAPK/NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway.Eur J Med Chem. 2023 Nov 5;259:115697. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.115697. Epub 2023 Aug 1. Eur J Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 37544187
-
Ethyl acetate fraction from Nymphaea hybrida Peck modulates inflammatory responses in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells and acute inflammation murine models.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Apr 6;269:113698. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113698. Epub 2020 Dec 15. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33338590
-
Gallic Acid-g-Chitosan Modulates Inflammatory Responses in LPS-Stimulated RAW264.7 Cells Via NF-κB, AP-1, and MAPK Pathways.Inflammation. 2016 Feb;39(1):366-374. doi: 10.1007/s10753-015-0258-2. Inflammation. 2016. PMID: 26412258
Cited by
-
Gamma Amino Butyric Acid (GABA) and Ferulic Acid Esterase (FAE) Producing Psychobiotic Bacteria Isolated from Cereal-Based Fermented Food.Curr Microbiol. 2024 Jan 10;81(2):59. doi: 10.1007/s00284-023-03580-x. Curr Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38195794
-
Immunostimulatory Effect of Ovomucin Hydrolysates by Pancreatin in RAW 264.7 Macrophages via Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) Signaling Pathway.Food Sci Anim Resour. 2024 Jul;44(4):885-898. doi: 10.5851/kosfa.2024.e25. Epub 2024 Jul 1. Food Sci Anim Resour. 2024. PMID: 38974730 Free PMC article.
-
Immune-Stimulating Potential of Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus LM1019 in RAW 264.7 Cells and Immunosuppressed Mice Induced by Cyclophosphamide.Microorganisms. 2023 Sep 13;11(9):2312. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11092312. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37764156 Free PMC article.
-
Applications of Probiotics and Their Potential Health Benefits.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 2;24(21):15915. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115915. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958897 Free PMC article.
-
Lactobacillus johnsonii LJO02 (DSM 33828) Cell-Free Supernatant and Vitamin D Improve Wound Healing and Reduce Interleukin-6 Production in Staphylococcus aureus-Infected Human Keratinocytes.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Dec 21;16(1):18. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16010018. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 38276496 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Geum N.G., Eo H.J., Kim H.J., Park G.H., Son H.J., Jeong J.B. Immune-enhancing activity of Hydrangea macrophylla subsp. serrata leaves through TLR4/ROS-dependent activation of JNK and NF-κB in RAW264.7 cells and immunosuppressed mice. J. Funct. Foods. 2020;73:104139. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2020.104139. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

