Decreased resistin plasmatic concentrations in patients with Alzheimer's disease: A case-control study
- PMID: 36439765
- PMCID: PMC9694389
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e11738
Decreased resistin plasmatic concentrations in patients with Alzheimer's disease: A case-control study
Abstract
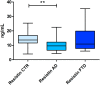
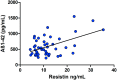
Previous studies suggested a role for adipokines in ageing and in several age-related diseases. The purpose of our study was to further elucidate adipokines involvement in neurodegeneration, investigating adiponectin, leptin and resistin in Alzheimer's disease (AD) and Frontotemporal Dementia (FTD). We enrolled for the study 70 subjects: 26 AD, 21 FTD, and 23 with other neurological (but not neurodegenerative) conditions (CTR, control group). According to a standardized protocol, we measured adipokines plasmatic levels, blood parameters of glucidic and lipidic metabolism, ESR, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) markers of neurodegeneration (beta-amyloid, total-Tau, phosphorylated-Tau) and anthropometric parameters. In comparison with control group, we found lower resistin concentrations in patients with dementia, and in particular in AD (p < 0.001). In multivariate analysis, AD relative risk was reduced by resistin, when controlling for sex, age and anthropometric/metabolic parameters (RR = 0.71, P < 0.0001). Considering CSF biomarkers, we found a direct correlation between resistin and Aβ1-42 CSF concentration in patients (p < 0.001, r = 0.50). Lower resistin characterized AD patients in our study and AD, but not FTD, diagnosis risk was found to be inversely associated with resistin when controlling for confounders. We hypothesize that resistin-linked metabolic profile has to be reconsidered and further investigated in AD.
Keywords: Adipokines; Adiponectin; Alzheimer's disease; Frontotemporal dementia; Leptin; Resistin.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Assessing adipokines as potential biomarkers of dementia, Alzheimer's disease, and mild cognitive impairment: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Obes Rev. 2023 Aug;24(8):e13573. doi: 10.1111/obr.13573. Epub 2023 May 10. Obes Rev. 2023. PMID: 37165483 Review.
-
Relationship between β-Secretase, inflammation and core cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers for Alzheimer's disease.J Alzheimers Dis. 2014;42(1):157-67. doi: 10.3233/JAD-140240. J Alzheimers Dis. 2014. PMID: 24820015
-
Association of Adipokines with Alzheimer's Disease in a Chinese Cohort.J Alzheimers Dis. 2023;96(2):523-533. doi: 10.3233/JAD-220860. J Alzheimers Dis. 2023. PMID: 37807776
-
Cerebrospinal Fluid YKL-40 and Chitotriosidase Levels in Frontotemporal Dementia Vary by Clinical, Genetic and Pathological Subtype.Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2020;49(1):56-76. doi: 10.1159/000506282. Epub 2020 Apr 28. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2020. PMID: 32344399 Free PMC article.
-
Novel fluid biomarkers to differentiate frontotemporal dementia and dementia with Lewy bodies from Alzheimer's disease: A systematic review.J Neurol Sci. 2020 Aug 15;415:116886. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2020.116886. Epub 2020 May 11. J Neurol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32428759 Review.
Cited by
-
Adiponectin and resistin modulate the progression of Alzheimer´s disease in a metabolic syndrome model.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Sep 4;14:1237796. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1237796. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37732123 Free PMC article.
-
The Causal Associations between Adipokines and Alzheimer's Disease: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study.J Alzheimers Dis Rep. 2024 Jan 18;8(1):75-83. doi: 10.3233/ADR-230110. eCollection 2024. J Alzheimers Dis Rep. 2024. PMID: 38312531 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Prince M., Bryce R., Albanese E., Wimo A., Ribeiro W., Ferri C.P. The global prevalence of dementia: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Alzheimers Dement. 2013;9(1):63–75. - PubMed
-
- Fantuzzi G. Adipose tissue, adipokines, and inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005;115(5):911–919. - PubMed
-
- Blüher M., Mantzoros C.S. From leptin to other adipokines in health and disease: facts and expectations at the beginning of the 21st century. Metabolism. 2015;64(1):131–145. - PubMed
-
- Fasshauer M., Blüher M. Adipokines in health and disease. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2015;36(7):461–470. - PubMed
-
- Lee K.S., Chung J.H., Choi T.K., Suh S.Y., Oh B.H., Hong C.H. Peripheral cytokines and chemokines in Alzheimer’s disease. Dement. Geriatr. Cognit. Disord. 2009;28(4):281–287. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

