Diabetes-related research priorities of people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes: a cross-sectional study in Germany
- PMID: 36460748
- PMCID: PMC9718826
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-24180-y
Diabetes-related research priorities of people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes: a cross-sectional study in Germany
Abstract
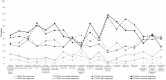
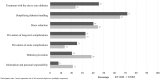
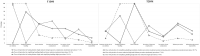
To investigate (i) the importance and priorities of research objectives for people with type 1 (T1DM) and type 2 diabetes (T2DM); (ii) subgroups with specific research priorities; (iii) associated factors (e.g., sociodemographic characteristics) of the subgroups. The cross-sectional survey was conducted in 2018 using data from 869 respondents (29.0% response, 31.2% female, mean age 61.3 years, 62.7% T2DM) from a German statutory health insurance population. Diabetes-related research priorities were assessed with a questionnaire. Subgroups and associated factors were identified using latent class analysis. Three subgroups were found in T1DM: (1) high priority for the research topic 'healing diabetes' and moderate priority for the research topic 'prevention of long-term complications', (2) priorities for simplifying handling (high) and stress reduction (moderate), (3) priorities for healing diabetes (high) and simplifying handling (high). Three subgroups were found in T2DM: (1) priorities for simplifying handling (moderate), diabetes prevention (moderate) and prevention of long-term complications (moderate), (2) priorities for stress reduction (high) and diabetes prevention (moderate), (3) priorities for simplifying handling (high) and stress reduction (high). Classes differed in age and HbA1c. Knowledge about research priorities enables researchers to align their work with the needs of people with diabetes.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Different information needs in subgroups of people with diabetes mellitus: a latent class analysis.BMC Public Health. 2020 Dec 10;20(1):1901. doi: 10.1186/s12889-020-09968-9. BMC Public Health. 2020. PMID: 33302924 Free PMC article.
-
What information needs do people with recently diagnosed diabetes mellitus have and what are the associated factors? A cross-sectional study in Germany.BMJ Open. 2018 Oct 31;8(10):e017895. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-017895. BMJ Open. 2018. PMID: 30385437 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics of Patients with Type-1 or Type-2 Diabetes Receiving Insulin Glargine U300: An Analysis of 7268 Patients Based on the DPV and DIVE Registries.Adv Ther. 2019 Jul;36(7):1628-1641. doi: 10.1007/s12325-019-00983-w. Epub 2019 May 22. Adv Ther. 2019. PMID: 31119688
-
Diabetes Research Matters: A Three-Round Priority-Setting Survey Consultation with Adults Living with Diabetes and Family Members in Australia.Patient. 2024 Jul;17(4):441-455. doi: 10.1007/s40271-024-00688-5. Epub 2024 Apr 6. Patient. 2024. PMID: 38582797 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of periodontal disease for glycaemic control in people with diabetes mellitus.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Nov 6;2015(11):CD004714. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004714.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Apr 14;4:CD004714. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004714.pub4 PMID: 26545069 Free PMC article. Updated. Review.
Cited by
-
Top 100 most-cited papers on diabetes mellitus in Dentistry: a bibliometric study.Braz Oral Res. 2024 Aug 5;38:e075. doi: 10.1590/1807-3107bor-2024.vol38.0075. eCollection 2024. Braz Oral Res. 2024. PMID: 39109771 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Saeedi, P. et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract.157, 107843. 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843 (2019). - PubMed
-
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 2. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: Standards of medical care in diabetes–2022. Diabetes Care45, S17–S38 (2022). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

