Association of liver fibrosis biomarkers with overall and CVD mortality in the Korean population: The Dong-gu study
- PMID: 36512564
- PMCID: PMC9747044
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0277729
Association of liver fibrosis biomarkers with overall and CVD mortality in the Korean population: The Dong-gu study
Abstract
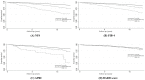
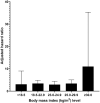
This study evaluated the associations of liver fibrosis biomarkers [non-alcoholic fatty liver disease fibrosis score (NFS), fibrosis-4 (FIB-4), aspartate aminotransferase/platelet ratio index (APRI), and BARD score] with mortality in Korean adults aged ≥50 years. We analyzed 7,702 subjects who participated in Dong-gu Study. The associations of liber fibrosis biomarkers with mortality were investigated using Cox proportional hazards models. Overall mortality increased with increasing NFS level [adjusted hazard ratio (aHR) 4.3, 95% confidence interval (CI) 3.3-5.5 for high risk vs. low risk], increasing FIB-4 level (aHR 3.5, 95% CI 2.9-4.4 for high risk vs. low risk), and increasing APRI level (aHR 3.5, 95% CI 2.1-5.8 for high risk vs. low risk) but not with BARD score. The Harrell's concordance index for overall mortality for the NFS and FIB-4 was greater than that for the APRI and BARD score. In conclusion, NFS, FIB-4, and APRI showed a significant relationship with the overall mortality, and NFS and FIB-4 showed a significant relationship with the CVD mortality after adjustment for covariates. In addition, the NFS and FIB-4 were more predictive of overall mortality than the APRI and BARD score in Korean adults aged ≥50 years.
Copyright: © 2022 Choi et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Noninvasive fibrosis tools in NAFLD: validation of APRI, BARD, FIB-4, NAFLD fibrosis score, and Hepamet fibrosis score in a Portuguese population.Postgrad Med. 2022 May;134(4):435-440. doi: 10.1080/00325481.2022.2058285. Epub 2022 Mar 30. Postgrad Med. 2022. PMID: 35332833
-
Modified AST to platelet ratio index improves APRI and better predicts advanced fibrosis and liver cirrhosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2021 Jul;45(4):101528. doi: 10.1016/j.clinre.2020.08.006. Epub 2020 Nov 29. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 33268036
-
Diagnostic Accuracy of Noninvasive Fibrosis Models to Detect Change in Fibrosis Stage.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Aug;17(9):1877-1885.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2018.12.031. Epub 2019 Jan 4. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 30616027 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of laboratory tests, ultrasound, or magnetic resonance elastography to detect fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A meta-analysis.Hepatology. 2017 Nov;66(5):1486-1501. doi: 10.1002/hep.29302. Epub 2017 Sep 26. Hepatology. 2017. PMID: 28586172 Review.
-
Liver Fibrosis Scores and Hospitalization, Mechanical Ventilation, Severity, and Death in Patients with COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis.Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Mar 29;2022:7235860. doi: 10.1155/2022/7235860. eCollection 2022. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 35369116 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Association between FIB-4, all-cause mortality, cardiovascular mortality, and cardiovascular disease risk among diabetic individuals: NHANES 1999-2008.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Sep 25;10:1172178. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1172178. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 37817864 Free PMC article.
-
Drivers of cardiovascular disease in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: the threats of oxidative stress.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Oct 1;11:1469492. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1469492. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 39411175 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomarkers of Hepatic Dysfunction and Cardiovascular Risk.Curr Cardiol Rep. 2023 Dec;25(12):1783-1795. doi: 10.1007/s11886-023-01993-5. Epub 2023 Nov 16. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37971635 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Screening strategies for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a holistic approach is needed.Clin Mol Hepatol. 2023 Apr;29(2):390-393. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2023.0059. Epub 2023 Mar 20. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 36935647 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Evaluation of MASLD Fibrosis, FIB-4 and APRI Score in MASLD Combined with T2DM and MACCEs Receiving SGLT2 Inhibitors Treatment.Int J Gen Med. 2024 Jun 5;17:2613-2625. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S460200. eCollection 2024. Int J Gen Med. 2024. PMID: 38855422 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sun W, Cui H, Li N, Wei Y, Lai S, Yang Y, et al.. Comparison of FIB-4 index, NAFLD fibrosis score and BARD score for prediction of advanced fibrosis in adult patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A meta-analysis study. Hepatol Res 2016;46(9):862–870. doi: 10.1111/hepr.12647 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aykut UE, Akyuz U, Yesil A, Eren F, Gerin F, Ergelen R, et al.. A comparison of FibroMeter™ NAFLD Score, NAFLD fibrosis score, and transient elastography as noninvasive diagnostic tools for hepatic fibrosis in patients with biopsy-proven non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Scand J Gastroenterol 2014;49(11):1343–1348. doi: 10.3109/00365521.2014.958099 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical