The α-mating factor secretion signals and endogenous signal peptides for recombinant protein secretion in Komagataella phaffii
- PMID: 36527112
- PMCID: PMC9756452
- DOI: 10.1186/s13068-022-02243-6
The α-mating factor secretion signals and endogenous signal peptides for recombinant protein secretion in Komagataella phaffii
Abstract
Background: The budding yeast Komagataella phaffii (Pichia pastoris) is widely employed to secrete proteins of academic and industrial interest. For secretory proteins, signal peptides are the sorting signal to direct proteins from cytosol to extracellular matrix, and their secretion efficiency directly impacts the yields of the _targeted proteins in fermentation broth. Although the α-mating factor (MF) secretion signal from S. cerevisiae, the most common and widely used signal sequence for protein secretion, works in most cases, limitation exists as some proteins cannot be secreted efficiently. As the optimal choice of secretion signals is often protein specific, more secretion signals need to be developed to augment protein expression levels in K. phaffii.
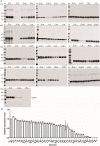
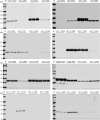
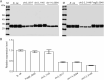
Results: In this study, the secretion efficiency of 40 α-MF secretion signals from various yeast species and 32 endogenous signal peptides from K. phaffii were investigated using enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) as the model protein. All of the evaluated α-MF secretion signals successfully directed EGFP secretion except for the secretion signals of the yeast D. hansenii CBS767 and H. opuntiae. The secretion efficiency of α-MF secretion signal from Wickerhamomyces ciferrii was higher than that from S. cerevisiae. 24 out of 32 endogenous signal peptides successfully mediated EGFP secretion. The signal peptides of chr3_1145 and FragB_0048 had similar efficiency to S. cerevisiae α-MF secretion signal for EGFP secretion and expression.
Conclusions: The screened α-MF secretion signals and endogenous signal peptides in this study confer an abundance of signal peptide selection for efficient secretion and expression of heterologous proteins in K. phaffii.
Keywords: Komagataella phaffii; Peptide signal; Protein secretion; α-Mating factor.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Komagataella phaffii as a Platform for Heterologous Expression of Enzymes Used for Industry.Microorganisms. 2024 Feb 7;12(2):346. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12020346. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38399750 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optimizing Pichia pastoris protein secretion: Role of N-linked glycosylation on the α-mating factor secretion signal leader.J Biotechnol. 2024 Aug 10;391:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2024.04.008. Epub 2024 Apr 16. J Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38636846
-
Komagataella phaffii (Pichia pastoris) as a Powerful Yeast Expression System for Biologics Production.Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2024 Jun 12;16(2):19. doi: 10.31083/j.fbe1602019. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2024. PMID: 38939917 Review.
-
Alternative secretory signal sequences for recombinant protein production in Pichia pastoris.Enzyme Microb Technol. 2023 Aug;168:110256. doi: 10.1016/j.enzmictec.2023.110256. Epub 2023 May 13. Enzyme Microb Technol. 2023. PMID: 37196384
-
An improved secretion signal enhances the secretion of model proteins from Pichia pastoris.Microb Cell Fact. 2018 Oct 12;17(1):161. doi: 10.1186/s12934-018-1009-5. Microb Cell Fact. 2018. PMID: 30314480 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Boosting Expression of a Specifically _targeted Antimicrobial Peptide K in Pichia pastoris by Employing a 2A Self-Cleaving Peptide-Based Expression System.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Oct 18;13(10):986. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13100986. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39452252 Free PMC article.
-
Study of Potential Blocking Peptides _targeting the SARS-CoV-2 RBD/hACE2 Interaction.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Sep 20;17(9):1240. doi: 10.3390/ph17091240. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39338402 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering Saccharomyces cerevisiae for _targeted hydrolysis and fermentation of glucuronoxylan through CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing.Microb Cell Fact. 2024 Mar 16;23(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s12934-024-02361-w. Microb Cell Fact. 2024. PMID: 38493086 Free PMC article.
-
Komagataella phaffii as a Platform for Heterologous Expression of Enzymes Used for Industry.Microorganisms. 2024 Feb 7;12(2):346. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12020346. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38399750 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Huang J, Xia J, Yang Z, Guan F, Cui D, Guan G, Jiang W, Li Y. Improved production of a recombinant Rhizomucor miehei lipase expressed in Pichia pastoris and its application for conversion of microalgae oil to biodiesel. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2014;7:111. doi: 10.1186/1754-6834-7-111. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lunsdorf H, Gurramkonda C, Adnan A, Khanna N, Rinas U. Virus-like particle production with yeast: ultrastructural and immunocytochemical insights into Pichia pastoris producing high levels of the hepatitis B surface antigen. Microb Cell Fact. 2011;10:48. doi: 10.1186/1475-2859-10-48. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
