C/EBPα promotes triacylglycerol synthesis via regulating PPARG promoter activity in goat mammary epithelial cells
- PMID: 36547378
- PMCID: PMC9863032
- DOI: 10.1093/jas/skac412
C/EBPα promotes triacylglycerol synthesis via regulating PPARG promoter activity in goat mammary epithelial cells
Abstract
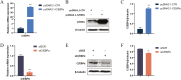
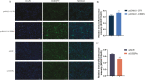
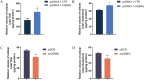
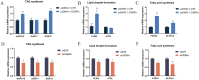
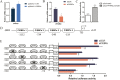
CCAAT/enhancer binding protein α (C/EBPα) is the key transcription factor involved in lipid metabolism, however, the role of C/EBPα in milk fat synthesis of dairy goats remains unknown. The objective of the present research was to clarify the function of C/EBPα in goat mammary epithelial cells (GMECs) and its impact on peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARG) promoter activity. In this study, C/EBPα overexpression increased its mRNA and protein levels by 42-fold and 6-fold, respectively. In contrast, transfecting siRNA _targeting C/EBPα decreased its mRNA level to 20% and protein abundance to 80% of the basal level. The contents of lipid droplets, triacylglycerol (TAG), and cholesterol were increased (P < 0.05) in C/EBPα-overexpressing GMECs, and knockdown of C/EBPα led to the opposite results. Overexpression of C/EBPα significantly increased the expression levels of genes involved in TAG synthesis (AGPAT6, DGAT2, P < 0.01), lipid droplet formation (PLIN2, P < 0.01), and fatty acid synthesis (FADS2, P < 0.05; ELOVL6, P < 0.01). Knockdown of C/EBPα decreased (P < 0.05) the expression levels of AGPAT6, DGAT1, DGAT2, PLIN2, FADS2, and ELOVL6. C/EBPα upregulated the expression level of PPARG (P < 0.05), and four C/EBPα binding regions were identified in the PPARG promoter at -1,112 to -1,102 bp, -734 to -724 bp, -248 to -238 bp, and -119 to -109 bp. Knockdown of C/EBPα reduced (P < 0.05) the PPARG promoter activity when the C/EBPα binding regions were mutated at -1,112 to -1,102 bp, -734 to -724 bp, and -248 to -238 bp locations of the promoter. However, the promoter activity did not change when the mutation was located at -119 bp. In conclusion, our results suggest that C/EBPα can promote TAG synthesis in GMECs through its effects on mRNA abundance of genes related to lipid metabolism and regulation of the PPARG promoter activity via C/EBPα binding regions.
Keywords: CCAAT/enhancer binding protein α; goat mammary epithelial cells; lactation; transcriptional regulation; triacylglycerol synthesis.
Plain language summary
Goat milk is beneficial for human health because of its nutritional value, especially milk fat, which is plentiful in goat milk. The molecular mechanism of milk fat synthesis is of great importance for developing processing technology and using genetic approaches to improve goat milk quality. The purpose of this study was to identify the role of CCAAT/enhancer binding protein α (C/EBPα) in goat mammary gland epithelial cells (GMECs) to provide support for understanding the mechanism of milk fat synthesis. Overexpression of C/EBPα increased the contents of lipid droplets, triacylglycerol, and cholesterol in GMECs. The expression levels of genes related to lipid metabolism were influenced after C/EBPα overexpression or inhibition. The promoter transcriptional activity of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma, which is the key transcription factor in milk fat synthesis, was regulated by C/EBPα through its binding regions. Our results indicate that C/EBPα affects lipid metabolism in GMECs by regulating PPARG transcription. This study provides support for milk fat synthesis regulation and improvement of milk quality in goats.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the American Society of Animal Science. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no real or perceived conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Goat FADS2 controlling fatty acid metabolism is directly regulated by SREBP1 in mammary epithelial cells.J Anim Sci. 2023 Jan 3;101:skad030. doi: 10.1093/jas/skad030. J Anim Sci. 2023. PMID: 36694375 Free PMC article.
-
The FoxO1-ATGL axis alters milk lipolysis homeostasis through PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in dairy goat mammary epithelial cells.J Anim Sci. 2023 Jan 3;101:skad286. doi: 10.1093/jas/skad286. J Anim Sci. 2023. PMID: 37638641 Free PMC article.
-
Sirtuin 1 Inhibits Fatty Acid Synthesis through Forkhead Box Protein O1-Mediated Adipose Triglyceride Lipase Expression in Goat Mammary Epithelial Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 14;25(18):9923. doi: 10.3390/ijms25189923. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337411 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of short-chain fatty acids on triacylglycerol accumulation, lipid droplet formation and lipogenic gene expression in goat mammary epithelial cells.Anim Sci J. 2016 Feb;87(2):242-9. doi: 10.1111/asj.12420. Epub 2015 Aug 24. Anim Sci J. 2016. PMID: 26304676 Review.
-
Regulation of Key Genes for Milk Fat Synthesis in Ruminants.Front Nutr. 2021 Nov 25;8:765147. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.765147. eCollection 2021. Front Nutr. 2021. PMID: 34901115 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Unveiling Novel Mechanism of CIDEB in Fatty Acid Synthesis Through ChIP-Seq and Functional Analysis in Dairy Goat.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 21;25(20):11318. doi: 10.3390/ijms252011318. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39457100 Free PMC article.
-
Research Progress on the Mechanism of Milk Fat Synthesis in Cows and the Effect of Conjugated Linoleic Acid on Milk Fat Metabolism and Its Underlying Mechanism: A Review.Animals (Basel). 2024 Jan 8;14(2):204. doi: 10.3390/ani14020204. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38254373 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Beigneux, A. P., Vergnes L., Qiao X., Quatela S., Davis R., Watkins S. M., Coleman R. A., Walzem R. L., Philips M., Reue K., . et al.. 2006. AGPAT6–a novel lipid biosynthetic gene required for triacylglycerol production in mammary epithelium. J. Lipid Res. 47:734–744. doi:10.1194/jlr.M500556-JLR200 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

