A novel deep learning segmentation model for organoid-based drug screening
- PMID: 36588731
- PMCID: PMC9794595
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1080273
A novel deep learning segmentation model for organoid-based drug screening
Abstract
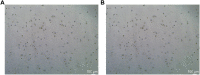
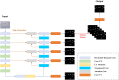
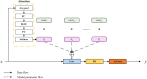
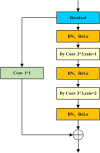
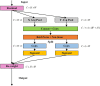
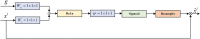
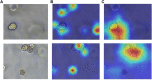
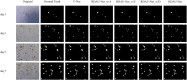
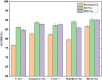
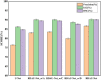
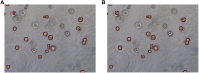
Organoids are self-organized three-dimensional in vitro cell cultures derived from stem cells. They can recapitulate organ development, tissue regeneration, and disease progression and, hence, have broad applications in drug discovery. However, the lack of effective graphic algorithms for organoid growth analysis has slowed the development of organoid-based drug screening. In this study, we take advantage of a bladder cancer organoid system and develop a deep learning model, the res-double dynamic conv attention U-Net (RDAU-Net) model, to improve the efficiency and accuracy of organoid-based drug screenings. In this RDAU-Net model, the dynamic convolution and attention modules are integrated. The feature-extracting capability of the encoder and the utilization of multi-scale information are substantially enhanced, and the semantic gap caused by skip connections has been filled, which substantially improved its anti-interference ability. A total of 200 images of bladder cancer organoids on culture days 1, 3, 5, and 7, with or without drug treatment, were employed for training and testing. Compared with the other variations of the U-Net model, the segmentation indicators, such as Intersection over Union and dice similarity coefficient, in the RDAU-Net model have been improved. In addition, this algorithm effectively prevented false identification and missing identification, while maintaining a smooth edge contour of segmentation results. In summary, we proposed a novel method based on a deep learning model which could significantly improve the efficiency and accuracy of high-throughput drug screening and evaluation using organoids.
Keywords: RDAU-Net model; bladder cancer organoid; deep learning; drug screening; organoid segmentation.
Copyright © 2022 Wang, Wu, Zhang, Yu, Li, Guo and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[A review on depth perception techniques in organoid images].Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2024 Oct 25;41(5):1053-1061. doi: 10.7507/1001-5515.202404036. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39462675 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
A deep learning model for drug screening and evaluation in bladder cancer organoids.Front Oncol. 2023 Apr 24;13:1064548. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1064548. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37168370 Free PMC article.
-
An RDAU-NET model for lesion segmentation in breast ultrasound images.PLoS One. 2019 Aug 23;14(8):e0221535. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0221535. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31442268 Free PMC article.
-
Feature-guided attention network for medical image segmentation.Med Phys. 2023 Aug;50(8):4871-4886. doi: 10.1002/mp.16253. Epub 2023 Feb 16. Med Phys. 2023. PMID: 36746870
-
mResU-Net: multi-scale residual U-Net-based brain tumor segmentation from multimodal MRI.Med Biol Eng Comput. 2024 Mar;62(3):641-651. doi: 10.1007/s11517-023-02965-1. Epub 2023 Nov 19. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2024. PMID: 37981627 Review.
Cited by
-
A Convexity-Preserving Level-Set Method for the Segmentation of Tumor Organoids.Bioengineering (Basel). 2024 Jun 12;11(6):601. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering11060601. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38927837 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing the power of artificial intelligence for human living organoid research.Bioact Mater. 2024 Aug 30;42:140-164. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.08.027. eCollection 2024 Dec. Bioact Mater. 2024. PMID: 39280585 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[A review on depth perception techniques in organoid images].Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2024 Oct 25;41(5):1053-1061. doi: 10.7507/1001-5515.202404036. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39462675 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
References
-
- Buades Antoni, Coll Bartomeu, Morel J-M. IEEE.A non-local algorithm for image denoising. Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR'05). San Diego, CA, USA June 2005
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

