Structural basis for heparan sulfate co-polymerase action by the EXT1-2 complex
- PMID: 36593275
- PMCID: PMC10160006
- DOI: 10.1038/s41589-022-01220-2
Structural basis for heparan sulfate co-polymerase action by the EXT1-2 complex
Abstract
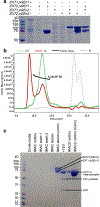
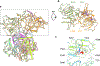
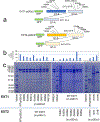
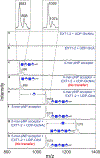
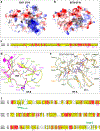
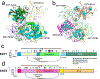
Heparan sulfate (HS) proteoglycans are extended (-GlcAβ1,4GlcNAcα1,4-)n co-polymers containing decorations of sulfation and epimerization that are linked to cell surface and extracellular matrix proteins. In mammals, HS repeat units are extended by an obligate heterocomplex of two exostosin family members, EXT1 and EXT2, where each protein monomer contains distinct GT47 (GT-B fold) and GT64 (GT-A fold) glycosyltransferase domains. In this study, we generated human EXT1-EXT2 (EXT1-2) as a functional heterocomplex and determined its structure in the presence of bound donor and acceptor substrates. Structural data and enzyme activity of catalytic site mutants demonstrate that only two of the four glycosyltransferase domains are major contributors to co-polymer syntheses: the EXT1 GT-B fold β1,4GlcA transferase domain and the EXT2 GT-A fold α1,4GlcNAc transferase domain. The two catalytic sites are over 90 Å apart, indicating that HS is synthesized by a dissociative process that involves a single catalytic site on each monomer.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
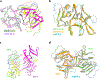
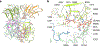




Similar articles
-
Structure of the human heparan sulfate polymerase complex EXT1-EXT2.Nat Commun. 2022 Nov 19;13(1):7110. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-34882-6. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36402845 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of EXT1, EXT2, and EXTL3 to heparan sulfate chain elongation.J Biol Chem. 2007 Nov 9;282(45):32802-10. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M703560200. Epub 2007 Aug 29. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17761672
-
In vitro polymerization of heparan sulfate backbone by the EXT proteins.J Biol Chem. 2003 Oct 17;278(42):41333-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M308314200. Epub 2003 Aug 7. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12907669
-
The exostosin family: proteins with many functions.Matrix Biol. 2014 Apr;35:25-33. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2013.10.001. Epub 2013 Oct 12. Matrix Biol. 2014. PMID: 24128412 Review.
-
The pathogenic roles of heparan sulfate deficiency in hereditary multiple exostoses.Matrix Biol. 2018 Oct;71-72:28-39. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2017.12.011. Epub 2017 Dec 24. Matrix Biol. 2018. PMID: 29277722 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The biosynthesis, degradation, and function of cell wall β-xylosylated xyloglucan mirrors that of arabinoxyloglucan.New Phytol. 2023 Dec;240(6):2353-2371. doi: 10.1111/nph.19305. Epub 2023 Oct 12. New Phytol. 2023. PMID: 37823344 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and mechanistic characterization of bifunctional heparan sulfate N-deacetylase-N-sulfotransferase 1.Nat Commun. 2024 Feb 13;15(1):1326. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-45419-4. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38351061 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanism of decision-making in glycosaminoglycan biosynthesis.Nat Commun. 2023 Oct 13;14(1):6425. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-42236-z. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37828045 Free PMC article.
-
_targeting heparan sulfate-protein interactions with oligosaccharides and monoclonal antibodies.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 May 19;10:1194293. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1194293. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 37275960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of a xyloglucan beta-xylopyranosyltransferase from Vaccinium corymbosum.Plant Direct. 2023 Jul 25;7(7):e514. doi: 10.1002/pld3.514. eCollection 2023 Jul. Plant Direct. 2023. PMID: 37502316 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carlsson P & Kjellen L in: Heparin—A Century of Progress (eds Lever R, Mulloy B & Page CP) 23–40 (Springer, 2012).
-
- Esko JD & Selleck SB Order out of chaos: assembly of ligand binding sites in heparan sulfate. Annu. Rev. Biochem 71, 435–471 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Bishop JR, Schuksz M & Esko JD Heparan sulphate proteoglycans fine-tune mammalian physiology. Nature 446, 1030–1037 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Kim SH, Turnbull J & Guimond S Extracellular matrix and cell signalling: the dynamic cooperation of integrin, proteoglycan and growth factor receptor. J. Endocrinol 209, 139–151 (2011). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

