Active Food Packaging Made of Biopolymer-Based Composites
- PMID: 36614617
- PMCID: PMC9821968
- DOI: 10.3390/ma16010279
Active Food Packaging Made of Biopolymer-Based Composites
Abstract
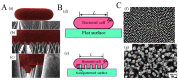
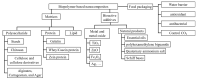
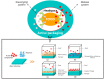
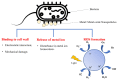
Food packaging plays a vital role in protecting food products from environmental damage and preventing contamination from microorganisms. Conventional food packaging made of plastics produced from unrenewable fossil resources is hard to degrade and poses a negative impact on environmental sustainability. Natural biopolymers are attracting interest for reducing environmental problems to achieve a sustainable society, because of their abundance, biocompatibility, biodegradability, chemical stability, and non-toxicity. Active packaging systems composed of these biopolymers and biopolymer-based composites go beyond simply acting as a barrier to maintain food quality. This review provides a comprehensive overview of natural biopolymer materials used as matrices for food packaging. The antioxidant, water barrier, and oxygen barrier properties of these composites are compared and discussed. Furthermore, biopolymer-based composites integrated with antimicrobial agents-such as inorganic nanostructures and natural products-are reviewed, and the related mechanisms are discussed in terms of antimicrobial function. In summary, composites used for active food packaging systems can inhibit microbial growth and maintain food quality.
Keywords: active packaging; antibacterial mechanism; antimicrobial packaging; biopolymers; composites; metal oxide nanoparticles; polyphenols.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Synergistic Integration of Carbon Quantum Dots in Biopolymer Matrices: An Overview of Current Advancements in Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Active Packaging.Molecules. 2024 Oct 30;29(21):5138. doi: 10.3390/molecules29215138. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39519777 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress in food packaging applications of biopolymer-nanometal composites - A comprehensive review.Biomater Adv. 2024 Sep;162:213921. doi: 10.1016/j.bioadv.2024.213921. Epub 2024 Jun 6. Biomater Adv. 2024. PMID: 38870740 Review.
-
Bio-based active food packaging materials: Sustainable alternative to conventional petrochemical-based packaging materials.Food Res Int. 2020 Nov;137:109625. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109625. Epub 2020 Aug 14. Food Res Int. 2020. PMID: 33233213 Review.
-
Valorization of Seafood Waste for Food Packaging Development.Foods. 2024 Jul 3;13(13):2122. doi: 10.3390/foods13132122. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38998628 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chitosan Based Biodegradable Composite for Antibacterial Food Packaging Application.Polymers (Basel). 2023 May 9;15(10):2235. doi: 10.3390/polym15102235. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37242810 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Review of Bio-Based Biodegradable Polymers: Smart Solutions for Sustainable Food Packaging.Foods. 2024 Sep 24;13(19):3027. doi: 10.3390/foods13193027. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39410063 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fabrication and Application of Tannin Double Quaternary Ammonium Salt/Polyvinyl Alcohol as Efficient Sterilization and Preservation Material for Food Packaging.Molecules. 2024 Sep 9;29(17):4264. doi: 10.3390/molecules29174264. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39275112 Free PMC article.
-
Vanillin Cross-Linked Chitosan Film with Controlled Release of Green Tea Polyphenols for Active Food Packaging.ACS Food Sci Technol. 2023 Oct 9;3(10):1680-1693. doi: 10.1021/acsfoodscitech.3c00222. eCollection 2023 Oct 20. ACS Food Sci Technol. 2023. PMID: 37881445 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sathyanarayana S.R., Warke V.G., Mahajan G.B., Annapure U.S. Comparative studies of microbial and heavy metal safety assessment of the herbs cultivated in hydroponically and regular soil system. J. Food Saf. 2021;41:e12936. doi: 10.1111/jfs.12936. - DOI
-
- Pogreba-Brown K., Austhof E., Armstrong A., Schaefer K., Villa Zapata L., McClelland D.J., Batz M.B., Kuecken M., Riddle M., Porter C.K. Chronic gastrointestinal and joint-related sequelae associated with common foodborne illnesses: A scoping review. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2020;17:67–86. doi: 10.1089/fpd.2019.2692. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- WHO Foodborne Disease. [(accessed on 2 April 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/foodborne-diseases#tab=tab_1.
-
- WHO Listeriosis. [(accessed on 2 April 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/listeriosis.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

