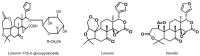
Nomilin and Its Analogues in Citrus Fruits: A Review of Its Health Promotion Effects and Potential Application in Medicine
- PMID: 36615463
- PMCID: PMC9822165
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28010269
Nomilin and Its Analogues in Citrus Fruits: A Review of Its Health Promotion Effects and Potential Application in Medicine
Abstract
Nomilin is one of the major limonoids, which are plant secondary metabolites also known as tetranortriterpenoids. Nomilin is found mostly in common edible citrus fruits including lemons, limes, oranges, grapefruits, mandarins, along with traditional Chinese medicines derived from citrus fruits, such as tangerine seed, tangerine peel, fructus aurantii immaturus, etc. A number of studies have demonstrated that nomilin and its analogues exhibit a variety of biological and pharmacological activities. These include anti-cancer, immune-modulatory, anti-inflammatory, anti-obesity, anti-viral, anti-osteoclastogenic, anti-oxidant, and neuro-protective effects. Thus, nomilin and its analogues have emerged as a potential therapy for human diseases. The purpose of this review is to chronicle the evolution of nomilin research from examining its history, structure, occurrence, to its pharmacological and disease-preventing properties as well as its potential utilization in medicine and food science.
Keywords: biological activities; citrus fruits; health promotion; nomilin; tetranortriterpenoid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Chemistry and Pharmacology of Citrus Limonoids.Molecules. 2016 Nov 13;21(11):1530. doi: 10.3390/molecules21111530. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 27845763 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vivo induction of phase II detoxifying enzymes, glutathione transferase and quinone reductase by citrus triterpenoids.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2010 Sep 17;10:51. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-10-51. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2010. PMID: 20846448 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal and spatial variations on accumulation of nomilin and limonin in the pummelos.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2016 Sep;106:23-9. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.04.039. Epub 2016 Apr 23. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27135815
-
Citrus nomilin down-regulates TNF-α-induced proliferation of aortic smooth muscle cells via apoptosis and inhibition of IκB.Eur J Pharmacol. 2017 Sep 15;811:93-100. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2017.05.043. Epub 2017 May 25. Eur J Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28551013
-
Citrus Genus and Its Waste Utilization: A Review on Health-Promoting Activities and Industrial Application.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Oct 20;2021:2488804. doi: 10.1155/2021/2488804. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. Retraction in: Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Dec 13;2023:9849716. doi: 10.1155/2023/9849716 PMID: 34795782 Free PMC article. Retracted. Review.
Cited by
-
Nomilin Reversed Cardiotoxicity Caused by Co-exposure to Zearalenone and Deoxynivalenol via the Keap1/Nrf2 Signaling Pathway in Zebrafish.Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 2024 Dec;79(4):901-908. doi: 10.1007/s11130-024-01228-0. Epub 2024 Sep 13. Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39269625
-
Chemometric discrimination of eight citrus plants utilizing chromatographic and spectroscopic techniques and insights into their biological potentials.Curr Res Food Sci. 2024 Jul 4;9:100803. doi: 10.1016/j.crfs.2024.100803. eCollection 2024. Curr Res Food Sci. 2024. PMID: 39076680 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the Mechanism of Action of the Degraded Limonoid Prieurianin.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 22;25(7):3597. doi: 10.3390/ijms25073597. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612409 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pregnane X receptor agonist nomilin extends lifespan and healthspan in preclinical models through detoxification functions.Nat Commun. 2023 Jun 8;14(1):3368. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-39118-9. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37291126 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial Distribution and Antioxidant Activity of Extracts from Citrus Fruits.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Mar 23;12(4):781. doi: 10.3390/antiox12040781. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37107156 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hasegawa S., Miyake M. Biochemistry and biological functions of citrus limonoids. Food Rev. Int. 1996;12:413–415. doi: 10.1080/87559129609541089. - DOI
-
- Hasegawa S., Bennett R.D., Verdon C.P. Limonoids in Citrus Seeds: Origin and Relative Concentration. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1980;28:922–925. doi: 10.1021/jf60231a016. - DOI
-
- Guadagni D.G., Maier V.P., Turnbaugh J.G. Effect of some Citrus Juice Constituents on Taste Thresholds for Limonin and Naringin Bitterness. J. Sci. Fd. Agric. 1973;24:1277–1288. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.2740241018. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources