Effects of electroacupuncture on bladder dysfunction and the expression of PACAP38 in a diabetic rat model
- PMID: 36699677
- PMCID: PMC9868671
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2022.1008269
Effects of electroacupuncture on bladder dysfunction and the expression of PACAP38 in a diabetic rat model
Abstract
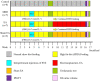
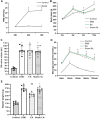
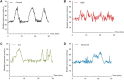
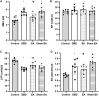
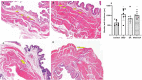
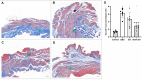
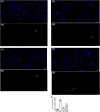
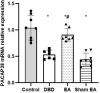
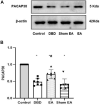
Objective: To explore the effects and the possible mechanism of electroacupuncture (EA) on diabetic bladder dysfunction (DBD) in streptozotocin-high fat diet (STZ-HFD) induced type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) rats. Methods: The experiment was divided into Control, diabetic bladder dysfunction, electroacupuncture, and Sham electroacupuncture group. After 8 weeks of electroacupuncture intervention, the body mass, 24 h urine volume, intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test (IPGTT), and urodynamics were detected. After the wet weight of the bladder was detected, the hematoxylin-eosin (HE), Masson's trichrome, and TUNEL were used to analyze histological changes. The PACAP38 expressions in the bladder were detected by Real-time PCR and Western blot. Results: Compared to the Control group, the bladder wet weight, 24 h urine volume, blood glucose, maximum bladder capacity, bladder compliance, bladder wall thickness, the smooth muscle/collagen ratio, and apoptosis rate of the diabetic bladder dysfunction group were significantly increased. Moreover, the body mass and leak point pressure were significantly reduced. Compared with the Sham electroacupuncture group, the bladder wet weight, maximum bladder capacity, bladder compliance, bladder wall thickness, and apoptosis rate of the electroacupuncture group were significantly reduced. In contrast, the leak point pressure was increased. The PACAP38 mRNA and PACAP38 protein expression of the diabetic bladder dysfunction group were significantly lower than the Control group, while electroacupuncture treatment could upregulate PACAP38 mRNA levels and PACAP38 protein expression of diabetic bladder dysfunction model rats. Conclusion: electroacupuncture could ameliorate bladder dysfunction in the diabetic bladder dysfunction model rats by reversing bladder remodeling, which might be mainly mediated by regulating the PACAP38 level.
Keywords: cystometry; diabetic bladder dysfunction; electroacupuncture; pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide; type 2 diabetes mellitus rats.
Copyright © 2023 Han, Chen, Ha, Yang, Wang, Chen, Zhou, Long, Qiu and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Effect of electroacupuncture on urodynamics of neurogenic bladder and PACAP/cAMP/PKA signaling pathway in detrusor tissue of rats after suprasacral spinal cord injury].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2021 Sep 25;46(9):728-34. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.200880. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2021. PMID: 34558237 Chinese.
-
Effect of Electroacupuncture on Bladder Dysfunction via Regulation of MLC and MLCK Phosphorylation in a Rat Model of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Jun 10;2021:5558890. doi: 10.1155/2021/5558890. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34221075 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of electroacupuncture on urodynamics and Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathway in spinal cord tissue of rats with detrusor hyperreflexia after suprasacral spinal cord injury.Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2023 Oct 25;48(10):977-985. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.20230233. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2023. PMID: 37879947 Chinese, English.
-
[Effect of electroacupuncture on urodynamics and expression of Wnt-1, β-catenin, and Ngn1 in the spinal cord in rats with bladder detrusor hyperreflexia due to supersacral spinal cord transection].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2019 Oct 25;44(10):722-8. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.190129. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2019. PMID: 31657161 Chinese.
-
[Protective effect and mechanism of electroacupuncture of "Biao-Ben" acupoints combination for mitochondrial dysfunction in diabetic nephropathy rats].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2022 Sep 25;47(9):759-68. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.20210883. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2022. PMID: 36153450 Chinese.
References
-
- Braas K. M., May V., Zvara P., Nausch B., Kliment J., Dunleavy J. D., et al. (2006). Role for pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide in cystitis-induced plasticity of micturition reflexes. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 290 (4), R951–R962. PubMed PMID: 16322346. 10.1152/ajpregu.00734.2005 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

