The effect of hotel employee resilience during COVID-19: The moderation role of perceived risk and challenge stressors
- PMID: 36741920
- PMCID: PMC9886732
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tmp.2023.101087
The effect of hotel employee resilience during COVID-19: The moderation role of perceived risk and challenge stressors
Abstract
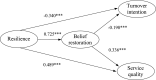
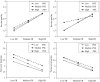
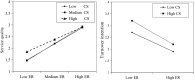
The effect of hotel employee resilience during major crises lacks sufficient empirical investigation. This research aimed to develop a conceptual model of hotel employee resilience effects on turnover intentions and service quality with belief restoration as mediation and challenge stressors and perceived risk as moderation variables. A questionnaire survey was conducted with 28 star-rated hotels (including two 3-star, fifteen 4-star, and eleven 5-star hotels) in southeastern, northeastern, central, and western China against the background of the COVID-19 pandemic, and with operational (e.g., front office, food and beverage, housekeeping) and administrative (e.g., human resource, sales, finance) departments. A total of 1318 valid questionnaires were collected. The results showed that: (1) employee resilience predicted employee service quality positively and turnover intentions negatively; (2) belief restoration partially mediated the impact of employee resilience on service quality and turnover intentions; and (3) perceived risk and challenge stressors had diverse moderation effects (e.g., U-shaped, linear) in the impacts of resilience, and they were important external and internal situational factors that influenced the impact of employee resilience. This research revealed the effects and situational conditions of hotel employee resilience during a major crisis, which provides a theoretical basis for establishing hotel crisis response strategies.
Keywords: Belief restoration; Resilience; Self-determination theory; Service quality; Turnover intentions.
© 2023 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Key Factors Influencing Low-Carbon Behaviors of Staff in Star-Rated Hotels-An Empirical Study of Eastern China.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Nov 6;17(21):8222. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17218222. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 33172168 Free PMC article.
-
How the COVID-19 pandemic affected hotel Employee stress: Employee perceptions of occupational stressors and their consequences.Int J Hosp Manag. 2021 Feb;93:102798. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhm.2020.102798. Epub 2020 Dec 5. Int J Hosp Manag. 2021. PMID: 36919180 Free PMC article.
-
The COVID-19 pandemic: The mitigating role of government and hotel support of hotel employees in Egypt.Tour Manag. 2021 Aug;85:104305. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2021.104305. Epub 2021 Feb 20. Tour Manag. 2021. PMID: 36567706 Free PMC article.
-
Hotels in contexts of uncertainty: Measuring organisational resilience.Tour Manag Perspect. 2020 Oct;36:100747. doi: 10.1016/j.tmp.2020.100747. Epub 2020 Oct 1. Tour Manag Perspect. 2020. PMID: 33024657 Free PMC article.
-
Influences of Distributive Injustice and Job Insecurity Amid COVID-19 on Unethical Pro-Organisational Behaviour: Mediating Role of Employee Turnover Intention.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Jun 8;19(12):7040. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19127040. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35742287 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The influencing factors of nurses' job engagement in tertiary, A grade hospitals in East China: A cross-sectional study.Nurs Open. 2024 Sep;11(9):e70037. doi: 10.1002/nop2.70037. Nurs Open. 2024. PMID: 39312278 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of family boundary flexibility on employees' work engagement: a study based on person-environment fit theory perspective.Front Psychol. 2023 Sep 28;14:1185239. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1185239. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 37842711 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aguiar-Quintana T., Nguyen T.H.H., Araujo-Cabrera Y., Sanabria-Díaz J.M. Do job insecurity, anxiety and depression caused by the COVID-19 pandemic influence hotel employees’ self-rated task performance? The moderating role of employee resilience. International Journal of Hospitality Management. 2021;94:1–10. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aiken L.S., West S.G., Reno R.R. Sage; New York: 1991. Multiple regression: Testing and interpreting interactions.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources