Voltammetric Sensor Based on the Poly(p-aminobenzoic Acid) for the Simultaneous Quantification of Aromatic Aldehydes as Markers of Cognac and Brandy Quality
- PMID: 36850946
- PMCID: PMC9960838
- DOI: 10.3390/s23042348
Voltammetric Sensor Based on the Poly(p-aminobenzoic Acid) for the Simultaneous Quantification of Aromatic Aldehydes as Markers of Cognac and Brandy Quality
Abstract
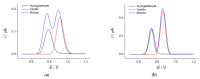
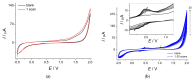
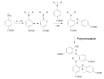
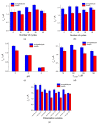
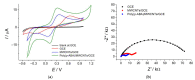
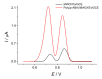
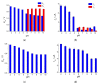
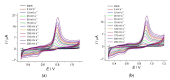
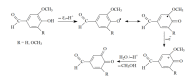
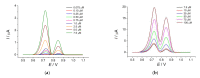
Cognac and brandy quality control is an actual topic in food analysis. Aromatic aldehydes, particularly syringaldehyde and vanillin, are one of the markers used for these purposes. Therefore, simple and express methods for their simultaneous determination are required. The voltammetric sensor based on the layer-by-layer combination of multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) and electropolymerized p-aminobenzoic acid (p-ABA) provides full resolution of the syringaldehyde and vanillin oxidation peaks. Optimized conditions of p-ABA electropolymerization (100 µM monomer in Britton-Robinson buffer pH 2.0, twenty cycles in the polarization window of -0.5 to 2.0 V with a potential scan rate of 100 mV·s-1) were found. The poly(p-ABA)-based electrode was characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), cyclic voltammetry, and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). Electrooxidation of syringaldehyde and vanillin is an irreversible two-electron diffusion-controlled process. In the differential pulse mode, the sensor allows quantification of aromatic aldehydes in the ranges of 0.075-7.5 and 7.5-100 µM for syringaldehyde and 0.50-7.5 and 7.5-100 µM for vanillin with the detection limits of 0.018 and 0.19 µM, respectively. The sensor was applied to cognac and brandy samples and compared to chromatography.
Keywords: aminobenzoic acid; carbon nanotubes; chemically modified electrodes; cognac and brandy; electropolymerization; food quality; syringaldehyde; vanillin; voltammetric sensors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Electropolymerized 4-Aminobenzoic Acid Based Voltammetric Sensor for the Simultaneous Determination of Food Azo Dyes.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Dec 11;14(24):5429. doi: 10.3390/polym14245429. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36559795 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous Determination of Ferulic Acid and Vanillin in Vanilla Extracts Using Voltammetric Sensor Based on Electropolymerized Bromocresol Purple.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Dec 31;22(1):288. doi: 10.3390/s22010288. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 35009830 Free PMC article.
-
Chronoamperometric estimation of cognac and brandy antioxidant capacity using MWNT modified glassy carbon electrode.Talanta. 2014 Jul;125:378-84. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2014.03.039. Epub 2014 Mar 25. Talanta. 2014. PMID: 24840460
-
Electrode Based on the MWCNTs and Electropolymerized Thymolphthalein for the Voltammetric Determination of Total Isopropylmethylphenols in Spices.Micromachines (Basel). 2023 Mar 11;14(3):636. doi: 10.3390/mi14030636. Micromachines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36985043 Free PMC article.
-
Voltammetric sensor based on cobalt-poly(methionine)-modified glassy carbon electrode for determination of estriol hormone in pharmaceuticals and urine.J Pharm Anal. 2019 Oct;9(5):347-357. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2019.04.001. Epub 2019 Apr 5. J Pharm Anal. 2019. PMID: 31929944 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ziyatdinova G., Salikhova I., Skorobogatova N., Chibisova M., Budnikov H. New electrochemistry based approaches to brandy quality evaluation using antioxidant parameters. Food Anal. Methods. 2015;8:1794–1803. doi: 10.1007/s12161-014-0059-5. - DOI
-
- Savchuk S.A., Kolesov G.M. Chromatographic techniques in the quality control of cognacs and cognac spirits. J. Anal. Chem. 2005;60:752–771. doi: 10.1007/s10809-005-0176-9. - DOI
-
- Sarvarova N.N., Cherkashina Y.A., Evgen’ev M.I. Application of chromatographic methods to the determination of cognac quality indicators. J. Anal. Chem. 2011;66:1190–1195. doi: 10.1134/S1061934811120094. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

