This is a preprint.
Cell state-dependent chromatin _targeting in NUT carcinoma
- PMID: 37131839
- PMCID: PMC10153199
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.04.18.537367
Cell state-dependent chromatin _targeting in NUT carcinoma
Update in
-
Cell state-dependent chromatin _targeting in NUT carcinoma.Genetics. 2023 Jul 6;224(3):iyad083. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyad083. Genetics. 2023. PMID: 37119804 Free PMC article.
Abstract
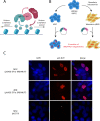
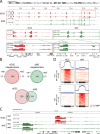
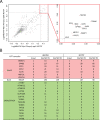
Aberrant transcriptional programming and chromatin dysregulation are common to most cancers. Whether by deranged cell signaling or environmental insult, the resulting oncogenic phenotype is typically manifested in transcriptional changes characteristic of undifferentiated cell growth. Here we analyze _targeting of an oncogenic fusion protein, BRD4-NUT, composed of two normally independent chromatin regulators. The fusion causes the formation of large hyperacetylated genomic regions or megadomains, mis-regulation of c-MYC , and an aggressive carcinoma of squamous cell origin. Our previous work revealed largely distinct megadomain locations in different NUT carcinoma patient cell lines. To assess whether this was due to variations in individual genome sequences or epigenetic cell state, we expressed BRD4-NUT in a human stem cell model and found that megadomains formed in dissimilar patterns when comparing cells in the pluripotent state with the same cell line following induction along a mesodermal lineage. Thus, our work implicates initial cell state as the critical factor in the locations of BRD4-NUT megadomains. These results, together with our analysis of c-MYC protein-protein interactions in a patient cell line, are consistent with a cascade of chromatin misregulation underlying NUT carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cell state-dependent chromatin _targeting in NUT carcinoma.Genetics. 2023 Jul 6;224(3):iyad083. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyad083. Genetics. 2023. PMID: 37119804 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical Screen Identifies Diverse and Novel Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors as Repressors of NUT Function: Implications for NUT Carcinoma Pathogenesis and Treatment.Mol Cancer Res. 2021 Nov;19(11):1818-1830. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-21-0259. Epub 2021 Jul 20. Mol Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34285087 Free PMC article.
-
Ectopic protein interactions within BRD4-chromatin complexes drive oncogenic megadomain formation in NUT midline carcinoma.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 May 23;114(21):E4184-E4192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1702086114. Epub 2017 May 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28484033 Free PMC article.
-
Supercharging BRD4 with NUT in carcinoma.Oncogene. 2021 Feb;40(8):1396-1408. doi: 10.1038/s41388-020-01625-0. Epub 2021 Jan 15. Oncogene. 2021. PMID: 33452461 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NUT Is a Driver of p300-Mediated Histone Hyperacetylation: From Spermatogenesis to Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Apr 29;14(9):2234. doi: 10.3390/cancers14092234. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35565363 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alekseyenko AA, Walsh EM, Zee BM, Pakozdi T, His P, Lemieux ME, Dal Cin P, Ince TA, Kharchenko PV, Kuroda MI, French CA. 2017. Ectopic protein interactions within BRD4-chromatin complexes drive oncogenic megadomain formation in NUT midline carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114(21): E4184–E4192. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen AE, Egli D, Niakan K, Deng J, Akutsu H, Yamaki M, Cowan C, Fitz-Gerald C, Zhang K, Melton DA, Eggan K. 2009. Optimal timing of inner cell mass isolation increases the efficiency of human embryonic stem cell derivation and allows generation of sibling cell lines. Cell Stem Cell 4(2): 103–106. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
