microRNA-203 functions as a natural Ras inhibitor in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 37168327
- PMCID: PMC10164818
microRNA-203 functions as a natural Ras inhibitor in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
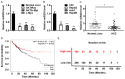
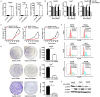
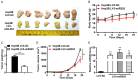
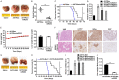
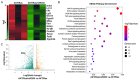
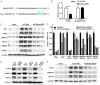
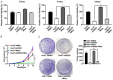
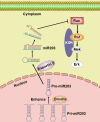
microRNA-203 (miR203) plays an important role in the formation and development of multiple types of cancers. However, its role in hepatic carcinogenesis has not been well studied. Mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling is known to be activated in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), but there is a lack of effective drugs _targeting this pathway for HCC treatment. In this study, we investigated the role of miR203 in HCC and the underlying mechanism. We found that miR203 was significantly downregulated in HCC cell lines and patient tissues compared with a hepatocyte cell line (L02) or normal liver tissues. Restoration of miR203 inhibited HCC cell growth and induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. In primary and xenograft HCC mouse models, miR203 also significantly blocked HCC growth. Bioinformatic analysis indicated that miR203 directly binds to the 3'UTR of NRas mRNA, resulting in decreased expression of NRas and inactivation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling. Activation of MAPK signaling by ectopic NRas expression rescued the cell proliferation blocked by miR203. Together, our findings illustrate the fundamental role of miR203 as a natural inhibitor of RAS/MAPK signaling in hepatic carcinogenesis in vitro and in vivo. In light of the critical and universal activation of the MAPK pathway in HCC, miR203 has the potential to serve as a nucleotide drug for the treatment of HCC with activated MAPK signaling.
Keywords: Ras; hepatocellular carcinoma; microRNA-203; mitogen activated protein kinase.
AJCR Copyright © 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
LINC00978 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma carcinogenesis partly via activating the MAPK/ERK pathway.Biosci Rep. 2020 Mar 27;40(3):BSR20192790. doi: 10.1042/BSR20192790. Biosci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32077915 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of MEK suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma growth through independent MYC and BIM regulation.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2019 Jun;42(3):369-380. doi: 10.1007/s13402-019-00432-4. Epub 2019 Feb 20. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2019. PMID: 30788663
-
Ras Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase Signaling and Kinase Suppressor of Ras as Therapeutic _targets for Hepatocellular Carcinoma.J Liver Cancer. 2021 Mar;21(1):1-11. doi: 10.17998/jlc.21.1.1. Epub 2021 Mar 31. J Liver Cancer. 2021. PMID: 37384270 Free PMC article. Review.
-
23-hydroxybetulinic acid reduces tumorigenesis, metastasis and immunosuppression in a mouse model of hepatocellular carcinoma via disruption of the MAPK signaling pathway.Anticancer Drugs. 2022 Oct 1;33(9):815-825. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000001325. Epub 2022 Sep 14. Anticancer Drugs. 2022. PMID: 36136986
-
Pleiotropic effects of methionine adenosyltransferases deregulation as determinants of liver cancer progression and prognosis.J Hepatol. 2013 Oct;59(4):830-41. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.04.031. Epub 2013 May 7. J Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 23665184 Review.
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–249. - PubMed
-
- El-Serag HB, Rudolph KL. Hepatocellular carcinoma: epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:2557–2576. - PubMed
-
- Farazi PA, DePinho RA. Hepatocellular carcinoma pathogenesis: from genes to environment. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:674–687. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
