Recent Advances in Novel Recombinant RNAs for Studying Post-transcriptional Gene Regulation in Drug Metabolism and Disposition
- PMID: 37170982
- PMCID: PMC10825985
- DOI: 10.2174/1389200224666230425232433
Recent Advances in Novel Recombinant RNAs for Studying Post-transcriptional Gene Regulation in Drug Metabolism and Disposition
Abstract
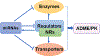
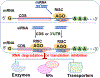
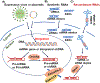
Drug-metabolizing enzymes and transporters are major determinants of the absorption, disposition, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) of drugs, and changes in ADME gene expression or function may alter the pharmacokinetics/ pharmacodynamics (PK/PD) and further influence drug safety and therapeutic outcomes. ADME gene functions are controlled by diverse factors, such as genetic polymorphism, transcriptional regulation, and coadministered medications. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a superfamily of regulatory small noncoding RNAs that are transcribed from the genome to regulate _target gene expression at the post-transcriptional level. The roles of miRNAs in controlling ADME gene expression have been demonstrated, and such miRNAs may consequently influence cellular drug metabolism and disposition capacity. Several types of miRNA mimics and small interfering RNA (siRNA) reagents have been developed and widely used for ADME research. In this review article, we first provide a brief introduction to the mechanistic actions of miRNAs in post-transcriptional gene regulation of drug-metabolizing enzymes, transporters, and transcription factors. After summarizing conventional small RNA production methods, we highlight the latest advances in novel recombinant RNA technologies and applications of the resultant bioengineered RNA (BioRNA) agents to ADME studies. BioRNAs produced in living cells are not only powerful tools for general biological and biomedical research but also potential therapeutic agents amenable to clinical investigations.
Keywords: Drug-metabolizing enzyme; microRNA; recombinant RNA; regulation; siRNA; transporter.
Copyright© Bentham Science Publishers; For any queries, please email at epub@benthamscience.net.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors are named inventors of issued and pending patents related to RNA bioengineering technology and use that are owned by the University of California, Davis; and Dr. Yu is a founder of AimRNA, Inc. that intends to license the intellectual property.
Figures
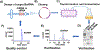
Similar articles
-
Recombinant Technologies Facilitate Drug Metabolism, Pharmacokinetics, and General Biomedical Research.Drug Metab Dispos. 2023 Jun;51(6):685-699. doi: 10.1124/dmd.122.001008. Epub 2023 Mar 22. Drug Metab Dispos. 2023. PMID: 36948592 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA Pharmacoepigenetics: Posttranscriptional Regulation Mechanisms behind Variable Drug Disposition and Strategy to Develop More Effective Therapy.Drug Metab Dispos. 2016 Mar;44(3):308-19. doi: 10.1124/dmd.115.067470. Epub 2015 Nov 13. Drug Metab Dispos. 2016. PMID: 26566807 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Noncoding microRNAs: small RNAs play a big role in regulation of ADME?Acta Pharm Sin B. 2012 Apr;2(2):93-101. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2012.02.011. Epub 2012 Mar 31. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2012. PMID: 32154096 Free PMC article.
-
Efflux ABC transporters in drug disposition and their posttranscriptional gene regulation by microRNAs.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 24;15:1423416. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1423416. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39114355 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioengineered miR-27b-3p and miR-328-3p modulate drug metabolism and disposition via the regulation of _target ADME gene expression.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2019 May;9(3):639-647. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2018.12.002. Epub 2018 Dec 11. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2019. PMID: 31193825 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li AP, Screening for human ADME/Tox drug properties in drug discovery, Drug discovery today, 6 (2001) 357–366. - PubMed
-
- Storelli F, Yin M, Kumar AR, Ladumor MK, Evers R, Chothe PP, Enogieru OJ, Liang X, Lai Y, Unadkat JD, The next frontier in ADME science: Predicting transporter-based drug disposition, tissue concentrations and drug-drug interactions in humans, Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 238 (2022) 108271. - PubMed
-
- DeGorter M, Xia C, Yang J, Kim R, Drug transporters in drug efficacy and toxicity, Annual review of pharmacology and toxicology, 52 (2012) 249–273. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

