A selectivity filter in the ER membrane protein complex limits protein misinsertion at the ER
- PMID: 37199759
- PMCID: PMC10200711
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.202212007
A selectivity filter in the ER membrane protein complex limits protein misinsertion at the ER
Abstract
Tail-anchored (TA) proteins play essential roles in mammalian cells, and their accurate localization is critical for proteostasis. Biophysical similarities lead to mis_targeting of mitochondrial TA proteins to the ER, where they are delivered to the insertase, the ER membrane protein complex (EMC). Leveraging an improved structural model of the human EMC, we used mutagenesis and site-specific crosslinking to map the path of a TA protein from its cytosolic capture by methionine-rich loops to its membrane insertion through a hydrophilic vestibule. Positively charged residues at the entrance to the vestibule function as a selectivity filter that uses charge-repulsion to reject mitochondrial TA proteins. Similarly, this selectivity filter retains the positively charged soluble domains of multipass substrates in the cytosol, thereby ensuring they adopt the correct topology and enforcing the "positive-inside" rule. Substrate discrimination by the EMC provides a biochemical explanation for one role of charge in TA protein sorting and protects compartment integrity by limiting protein misinsertion.
© 2023 Pleiner et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: R.M. Voorhees reported personal fees from Gate Biosciences and grants from Gate Biosciences outside the submitted work. R.M. Voorhees and G. Pinton Tomaleri are consultants for Gates Biosciences, and R.M. Voorhees is an equity holder. No other disclosures were reported.
Figures




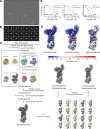
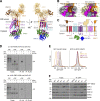
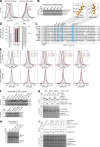

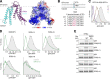
Comment in
-
Chasing the right tail: How the ER membrane complex recognizes its substrates.J Cell Biol. 2023 Aug 7;222(8):e202306035. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202306035. Epub 2023 Jul 12. J Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 37436711 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Structural and mechanistic basis of the EMC-dependent biogenesis of distinct transmembrane clients.Elife. 2020 Nov 25;9:e62611. doi: 10.7554/eLife.62611. Elife. 2020. PMID: 33236988 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for membrane insertion by the human ER membrane protein complex.Science. 2020 Jul 24;369(6502):433-436. doi: 10.1126/science.abb5008. Epub 2020 May 21. Science. 2020. PMID: 32439656 Free PMC article.
-
The ER membrane protein complex is a transmembrane domain insertase.Science. 2018 Jan 26;359(6374):470-473. doi: 10.1126/science.aao3099. Epub 2017 Dec 14. Science. 2018. PMID: 29242231 Free PMC article.
-
Cryo-EM insights into tail-anchored membrane protein biogenesis in eukaryotes.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2022 Aug;75:102428. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2022.102428. Epub 2022 Jul 16. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2022. PMID: 35850079 Review.
-
Capture and delivery of tail-anchored proteins to the endoplasmic reticulum.J Cell Biol. 2021 Aug 2;220(8):e202105004. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202105004. Epub 2021 Jul 15. J Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 34264263 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
EMC rectifies the topology of multipass membrane proteins.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2024 Jan;31(1):32-41. doi: 10.1038/s41594-023-01120-6. Epub 2023 Nov 13. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 37957425 Free PMC article.
-
The structural and biophysical basis of substrate binding to the hydrophobic groove in Ubiquilin Sti1 domains.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jul 10:2024.07.10.602902. doi: 10.1101/2024.07.10.602902. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39026758 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Protein insertion into the inner membrane of mitochondria: routes and mechanisms.FEBS Open Bio. 2024 Oct;14(10):1627-1639. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.13806. Epub 2024 Apr 25. FEBS Open Bio. 2024. PMID: 38664330 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural insights into human EMC and its interaction with VDAC.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 Mar 15;16(6):5501-5525. doi: 10.18632/aging.205660. Epub 2024 Mar 15. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 38517390 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

