Advances on the anti-tumor mechanisms of the carotenoid Crocin
- PMID: 37404473
- PMCID: PMC10315134
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.15535
Advances on the anti-tumor mechanisms of the carotenoid Crocin
Abstract
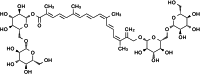
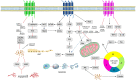
Saffron is located in the upper part of the crocus stigma of iridaceae, which has a long history of medicinal use. Crocin (molecular formula C44H64O24) is a natural floral glycoside ester compound extracted from saffron, which is a type carotenoid. Modern pharmacological studies have shown that crocin has multiple therapeutic effects including anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant, anti-hyperlipidemic and anti-stone effects. In recent years, crocin has been widely noticed due to its considerable anti-tumor effects manifested by the induction of tumor cell apoptosis, inhibition of tumor cell proliferation, inhibition of tumor cell invasion and metastasis, enhancement of chemotherapy sensitivity and improvement of immune status. The anti-tumor effects have been shown in various malignant tumors such as gastric cancer, liver cancer, cervical cancer, breast cancer and colorectal cancer. In this review, we compiled recent studies on the anti-tumor effects of crocin and summarized its anti-tumor mechanism for developing ideas of treating malignancies and exploring anti-tumor drugs.
Keywords: Cancer; Crocin; Mechanism; Nanoliposome; Tumor.
©2023 Bao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Crocetin and Crocin from Saffron in Cancer Chemotherapy and Chemoprevention.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2019;19(1):38-47. doi: 10.2174/1871520619666181231112453. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30599111 Review.
-
A comprehensive review on anticancer mechanisms of the main carotenoid of saffron, crocin.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2017 Nov;69(11):1419-1427. doi: 10.1111/jphp.12776. Epub 2017 Jul 3. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28675431 Review.
-
Improvement of cytotoxic and apoptogenic properties of crocin in cancer cell lines by its nanoliposomal form.Pharm Biol. 2011 Oct;49(10):1039-45. doi: 10.3109/13880209.2011.563315. Pharm Biol. 2011. PMID: 21936628
-
Saffron-Based Crocin Prevents Early Lesions of Liver Cancer: In vivo, In vitro and Network Analyses.Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2016;11(1):121-33. doi: 10.2174/1574892810666151102110248. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2016. PMID: 26522014
-
A Comparative Study on Anti-Invasion, Antimigration, and Antiadhesion Effects of the Bioactive Carotenoids of Saffron on 4T1 Breast Cancer Cells Through Their Effects on Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway Genes.DNA Cell Biol. 2018 Aug;37(8):697-707. doi: 10.1089/dna.2018.4248. Epub 2018 Jul 3. DNA Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29969282
Cited by
-
Advancements in Utilizing Natural Compounds for Modulating Autophagy in Liver Cancer: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic _targets.Cells. 2024 Jul 12;13(14):1186. doi: 10.3390/cells13141186. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39056768 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Combined Effect of Green Tea, Saffron, Resveratrol, and Citicoline against Neurodegeneration Induced by Oxidative Stress in an In Vitro Model of Cognitive Decline.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2024 Oct 1;2024:7465045. doi: 10.1155/2024/7465045. eCollection 2024. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2024. PMID: 39380915 Free PMC article.
-
NMR Study of Water-Soluble Carotenoid Crocin: Formation of Mixed Micelles, Interaction with Lipid Membrane and Antioxidant Activity.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 11;25(6):3194. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063194. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38542168 Free PMC article.
-
Saffron, a Potential Bridge between Nutrition and Disease Therapeutics: Global Health Challenges and Therapeutic Opportunities.Plants (Basel). 2024 May 25;13(11):1467. doi: 10.3390/plants13111467. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38891276 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

